Delta Depositional Environments & Stratigraphy | GEO GIRL
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth exploration of delta depositional environments, focusing on the key factors that influence delta formation and distribution. It covers the essential components of deltaic systems, such as river flow, tidal and wave influences, and sediment types. The video explains the distinct morphologies of river-dominated, wave-dominated, and tidal-dominated deltas. The presenter walks through the various phases of delta distribution, from sediment deposition to erosion during transgression. The video also discusses stratigraphy in fluvial and storm-wave influenced systems and offers insights into the unique features of delta environments, encouraging further exploration through related videos.
Takeaways
- 😀 Deltas form in coastal or shoreline environments, both in marine and lacustrine systems (lake deltas).
- 😀 Deltas require a river to provide sediment for their formation and progradation (the outward growth of the delta).
- 😀 Delta formation can be influenced by progradation, regression, and transgression, with transgression leading to erosion of deltaic deposits.
- 😀 Wave and tidal influences significantly affect delta deposition and distribution, contributing to different delta morphologies.
- 😀 River-dominated lacustrine deltas generally don't experience strong wave and tidal reworking, whereas marine deltas are more influenced by these factors.
- 😀 The geometry of a delta is influenced by the relative strength of river, wave, and tidal forces, creating distinct delta types (river-dominated, wave-dominated, and tide-dominated).
- 😀 Seven main factors control the distribution and morphology of deltas, including river outflow, body of water density, river plume interaction with marine processes, and sediment type.
- 😀 The density difference between river water and basin water influences sediment deposition. For example, hypopycnal flows (less dense river water) lead to different sedimentation patterns compared to hyperpycnal flows (denser river water).
- 😀 Marine processes like wave action, tides, and ocean currents can rework deltaic sediments, affecting the faces and morphology of a delta, including through longshore drift and storms.
- 😀 Delta morphology is also shaped by the physical position of the delta in the basin, with factors like proximity to the shelf edge affecting sediment distribution and fan morphology.
Q & A
What are the main influences that affect deltaic systems?
-Deltaic systems are primarily influenced by three factors: river flow (fluvial influence), tidal effects, and wave activity. These forces determine the distribution and morphology of delta deposits, impacting the formation of different delta types.
How does the density difference between river outflow and basin water affect delta formation?
-The density difference between the river outflow and the basin water affects sediment deposition. If the river water is less dense than the basin water (hypopycnal flow), sediment stays suspended longer. In contrast, when the river water is denser (hyperpycnal flow), turbidity currents form, which lead to distinct sedimentary structures like submarine fans.
What role does the position of a delta in the basin play in its morphology?
-The physical position of the delta in the basin, especially its proximity to the shelf edge or slope, influences how sediment is distributed. Deltas that reach the shelf edge create different morphological features compared to those that only extend onto the shelf.
Why do marine processes like waves and tides play a significant role in deltaic environments?
-Marine processes such as waves and tides can rework and redistribute sediment deposited by rivers, altering the shape and distribution of deltaic deposits. These processes can cause erosion, lobe migration, and elongation of deltaic systems, especially in environments with significant wave or tidal influence.
How does the type of sediment fed into a delta affect its development?
-The type of sediment, whether mud, sand, or gravel, impacts the delta’s morphology. For example, fine muds lead to more widespread and finer deposits, while coarser sands result in more elongated deltas. The grain size also affects the velocity at which sediment settles, influencing how the delta's faces are distributed.
What is the role of depositional slopes in delta formation?
-The slope of the basin where the delta forms influences sediment distribution. Shallow slopes lead to wide, fan-shaped deltas, while steeper slopes cause more elongated delta deposits. A steep slope can also cause submarine fan features when the sediment is rapidly deposited in deeper waters.
How does the interaction of river plumes with marine processes affect delta morphology?
-River plumes interact with marine processes like tides and waves, which can rework and elongate deltaic deposits. For example, longshore drift caused by waves moves sediments parallel to the shoreline, altering the distribution and morphology of the delta.
What happens during delta lobe abandonment and transgression?
-During transgression, previously deposited delta lobes may undergo erosion due to rising sea levels and wave dominance. This causes the delta system to migrate, forming new lobes as the river finds new channels, altering the overall shape and evolution of the delta.
What are the key stratigraphic features of a river-dominated delta?
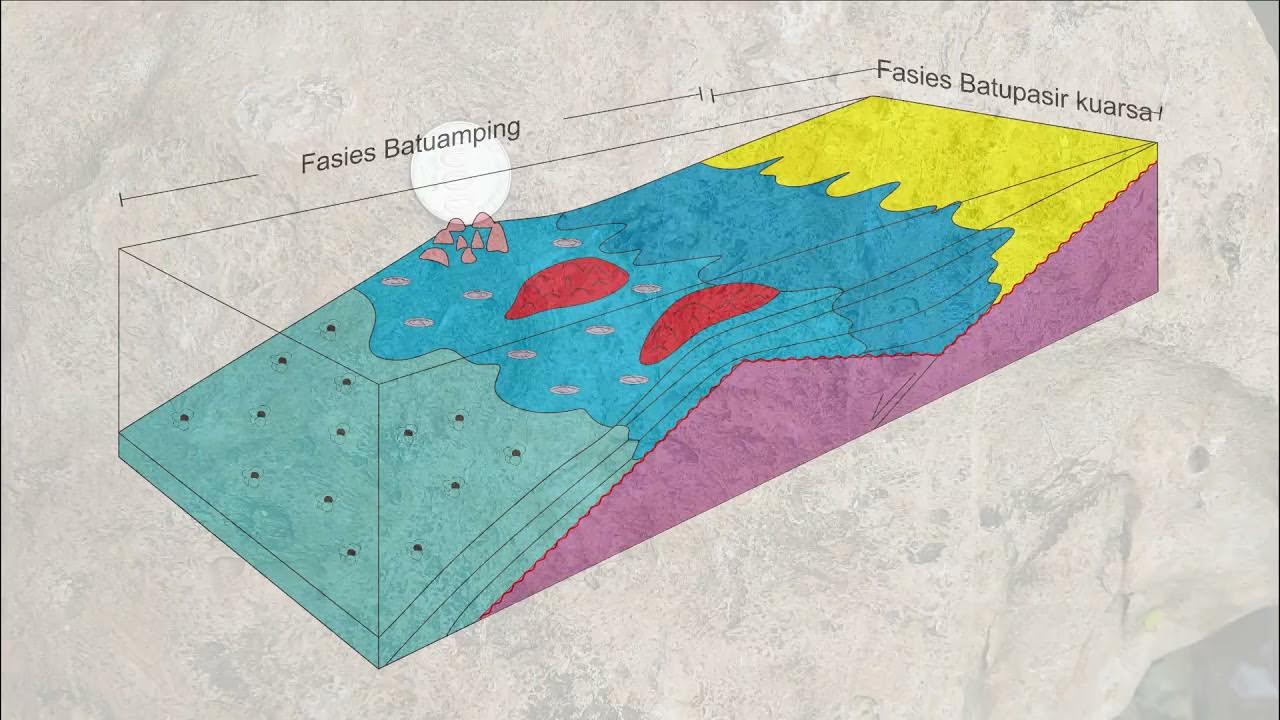
-In a river-dominated delta, the stratigraphy typically includes distributory mouth bars with medium to coarse sand, heterolithic deposits of fine sand and silt, and distal delta deposits dominated by mud. These features are a result of river dominance in sediment transport and deposition.
How does storm wave influence affect delta environments?
-Storm waves significantly alter delta environments by increasing wave power, which can rework previously deposited sediments, create new beach or shoreface features, and influence sedimentary structures like cross-bedding. In some cases, they may lead to complete reworking of delta deposits, resulting in a wave-dominated shoreface.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)