Pengujian Antimikroba/Antibakteri/Kirby Bauer/Paper Disc/Uji Daya Hambat/Mc Farland/Turbidimetri
Summary
TLDRThis video demonstrates the process of antimicrobial testing using the Kirby-Bauer method, starting with sterilization and preparation of materials. The procedure involves creating bacterial suspensions, preparing fresh herbal extracts (ginger and garlic), and conducting tests with control antibiotics. The testing includes inoculating Petri dishes with Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, followed by placing sterilized discs soaked in herbal extracts and antibiotics. After incubation, the results are analyzed by measuring the inhibition zones, determining the effectiveness of the extracts. The test results are then compared to standard values to assess antimicrobial activity.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Kirby-Bauer antimicrobial testing method is used in the experiment to assess the effectiveness of different substances against bacteria.
- 😀 Before starting the test, the work surface is sanitized using 70% alcohol, and sterilized Muller-Hinton agar medium is prepared.
- 😀 The process begins by sterilizing the medium bottle's outer surface with alcohol, then pouring it aseptically into petri dishes, filling them to a depth of approximately 5 mm.
- 😀 Fresh ginger and garlic are prepared and crushed in a sterilized mortar and pestle to extract their juices for the test.
- 😀 The bacterial test subjects are Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus, which were incubated for one day before preparation.
- 😀 A bacterial suspension is created by diluting the bacteria with 0.85% NaCl and matching its turbidity with a McFarland 0.5 standard.
- 😀 The suspension's turbidity is measured with a spectrophotometer, ensuring it reaches the standard absorbance value of 0.1.
- 😀 The test is performed on Muller-Hinton agar by inoculating it with bacterial suspensions using a sterile swab in a zigzag motion.
- 😀 Paper disks soaked in various substances (like garlic and ginger extracts, antibiotics, and sterile water) are placed on the inoculated agar to observe antimicrobial effects.
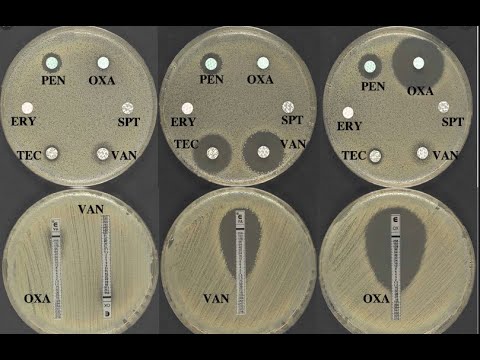
- 😀 After incubating the petri dishes at 37°C for 24 hours, clear zones (zones of inhibition) are observed around the disks, indicating the effectiveness of the substances against the bacteria.
- 😀 The size of the inhibition zones is measured and compared with a standard table to assess whether the substances are resistant, intermediate, or sensitive to the tested bacteria.
Q & A
What is the purpose of using the Kirby-Bauer method in this experiment?
-The Kirby-Bauer method is used to test the antimicrobial properties of substances, in this case, fresh ginger and garlic, by observing their ability to inhibit the growth of bacteria.
Why is it important to clean the work surface with 70% alcohol before starting the experiment?
-Cleaning the work surface with 70% alcohol helps to sterilize the environment, preventing contamination and ensuring the accuracy of the experiment.
What type of agar medium is used in this experiment, and why is it chosen?
-Muller Hinton agar (MH) is used because it is a standard medium for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, providing an ideal environment for bacterial growth.
How is the bacterial suspension prepared for the test?
-The bacterial suspension is prepared by diluting bacteria in a 0.85% NaCl solution and adjusting the turbidity to match the McFarland 0.5 standard, ensuring the correct bacterial concentration.
What is the purpose of using a spectrophotometer in this experiment?
-The spectrophotometer is used to measure the absorbance of the bacterial suspension, ensuring that the turbidity matches the McFarland 0.5 standard for proper bacterial concentration.
Why are the paper disks soaked in different substances (e.g., garlic extract, ginger extract, antibiotics, and sterile water)?
-The paper disks are soaked in different substances to test their antimicrobial activity against the bacteria. The antibiotics serve as a positive control, while the extracts and sterile water act as experimental and negative controls.
What does the presence of a zone of inhibition around a paper disk indicate?
-A zone of inhibition indicates that the substance on the paper disk has inhibited bacterial growth in that area, showing its antimicrobial activity.
How is the effectiveness of the antimicrobial substances measured?
-The effectiveness is measured by the size of the inhibition zone. A larger zone indicates stronger antimicrobial activity. The diameter of the zone is calculated using both vertical and horizontal measurements, then compared to standard values.
What is the significance of comparing the zone of inhibition of the extracts to the control groups?
-Comparing the zone of inhibition of the extracts to the control groups (antibiotic and sterile water) helps determine whether the extracts have significant antimicrobial activity, and how they perform relative to the known antibiotic.
What does the term 'McFarland 0.5 standard' refer to in this experiment?
-The McFarland 0.5 standard refers to a turbidity standard used to estimate the bacterial concentration in a suspension. A suspension that matches this standard contains approximately 1.5 × 10^8 CFU/mL of bacteria.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)