How to do a Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
Summary
TLDRThe Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test is a standardized method used to determine the in vitro susceptibility of bacteria and fungi to various antimicrobial agents. Performed in laboratories, it helps clinicians and microbiologists select appropriate antimicrobial treatments for infections. The process involves placing antimicrobial-impregnated disks on an inoculated agar plate and observing the growth inhibition zones. Results are analyzed using established breakpoints to classify organisms as resistant, intermediate, or susceptible. This video serves as a guide for conducting the test, with emphasis on correct procedures, equipment, and the importance of using up-to-date interpretive criteria for accurate results.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test determines the in vitro susceptibility of bacteria and fungi to various antimicrobial agents.
- 😀 It is a standardized procedure widely used by clinicians and microbiologists for selecting the appropriate treatment for infections.
- 😀 The test involves placing antimicrobial-impregnated filter paper disks onto an agar plate inoculated with the microorganism.
- 😀 Antimicrobial agents diffuse from the disk into the surrounding agar, creating a zone of inhibition if the microorganism is susceptible.
- 😀 The size of the inhibition zone is used to assess the microorganism's resistance, susceptibility, or intermediate status toward a drug.
- 😀 CLSI M100 and FDA STIC guidelines provide the breakpoints for interpreting zone sizes and determining susceptibility.
- 😀 Laboratories must use the most current breakpoints to avoid mismanagement of patient therapy due to outdated data.
- 😀 Materials needed for the test include Mueller Hinton agar plates, cotton swabs, antimicrobial disks, and a 0.5 McFarland Turbidity Standard.
- 😀 The inoculum must be adjusted to a 0.5 McFarland standard and applied within 15 minutes of preparation to ensure accurate results.
- 😀 Antimicrobial disks should be spaced at least 24mm apart on the agar surface to prevent overlapping zones of inhibition.
- 😀 Zone diameters are measured with precision tools like calipers or a ruler and interpreted based on the relevant breakpoint criteria.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test?
-The purpose of the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test is to determine the in vitro susceptibility of bacteria and fungi to various antimicrobial compounds, helping guide the selection of antimicrobial agents for appropriate treatment of infections.
What are the benefits of the Kirby-Bauer test?
-The main benefits of the test are its flexibility in drug selection and the ability to obtain overnight results, making it a valuable tool for clinicians and microbiologists in the selection of antimicrobials.
How is the Kirby-Bauer test performed?
-The test is performed by placing antimicrobial-impregnated filter paper disks onto the surface of an agar plate that has been inoculated with the microorganism. The antimicrobial agents diffuse from the disk into the agar and inhibit the microorganism's growth, creating a clear zone of inhibition if the organism is susceptible.
What does the presence of a zone of inhibition indicate?
-The presence of a clear zone around the antimicrobial disk indicates that the microorganism is susceptible to the antimicrobial agent, while no zone or a smaller zone suggests resistance.
What are 'breakpoints' in the context of the Kirby-Bauer test?
-Breakpoints refer to zone diameters established for each antimicrobial agent that determine whether a microorganism is resistant, intermediate, or susceptible to a given antimicrobial. These criteria are provided by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) and the FDA's Susceptibility Test Interpretive Criteria (STIC).
What is the significance of using current breakpoints in the Kirby-Bauer test?
-Using current breakpoints is crucial as outdated breakpoints may lead to misinterpretation of results, potentially resulting in inappropriate patient therapy and ineffective treatment of infections.
What materials are needed to perform a Kirby-Bauer test?
-Materials required include Mueller Hinton agar plates, sterile cotton or dacron swabs, Tryptic Soy Broth, antimicrobial disks, a 0.5 McFarland turbidity standard, forceps, a ruler or sliding caliper, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
How is the inoculum prepared for the Kirby-Bauer test?
-The inoculum is prepared by making a direct broth suspension of 3-5 isolated colonies from a non-selective agar plate, adjusting the suspension to achieve a turbidity equivalent to a 0.5 McFarland standard. This suspension is then used to inoculate the Mueller Hinton agar.
What should be done if the inoculum concentration is too light?
-If the inoculum concentration is too light, resulting in visible colonies instead of a confluent lawn, the test must be repeated. The inoculum should be adjusted to the correct turbidity level before applying it to the agar plate.
Why is it important to place antimicrobial disks with appropriate spacing on the agar plate?
-It is important to space the antimicrobial disks at least 24mm apart to avoid overlapping inhibition zones, which could interfere with accurate interpretation of results. Additionally, disks that produce small zones should be placed next to those with larger zones.
How are the results of the Kirby-Bauer test interpreted?
-The zones of inhibition are measured in millimeters, and the results are compared to the breakpoint tables provided by CLSI M100 or FDA STIC. These measurements help categorize the microorganism as resistant, intermediate, or susceptible to the antimicrobial agent.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
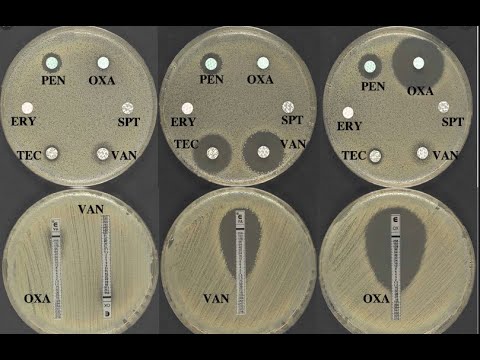
Disk diffusion assay: Kirby-Bauer Test

Antibiotic Sensitivity Test or Antibiotic Susceptibility Test | Blood Talks: Microbiology

Pengujian Antimikroba/Antibakteri/Kirby Bauer/Paper Disc/Uji Daya Hambat/Mc Farland/Turbidimetri

Etest for antibiotic susceptibility

METODE PENGUJIAN ANTIBAKTERI (METODE DIFUSI AGAR & METODE DILUSI)
Animation of Antimicrobial Resistance
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)