What shifts the IS or LM curves
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the factors that influence shifts in the IS-LM model. It covers how consumer behavior, investment expectations, government spending, and net exports shift the IS curve, while changes in money supply, transaction technologies, and price levels shift the LM curve. The video provides clear insights into the relationship between GDP, interest rates, investment, savings, and money markets. Understanding these shifts is crucial to grasping the dynamics of the IS-LM model and how economic policies and external factors affect equilibrium in the economy.
Takeaways
- 😀 The IS-LM model is used to analyze the relationship between the goods market and the money market, with GDP on the x-axis and the interest rate on the y-axis.
- 😀 The IS curve shows equilibrium between investment and savings in the economy, and shifts when factors affecting investment or consumption change.
- 😀 If consumers decide to save less, the IS curve shifts to the right, as higher GDP is needed to keep investment and savings in balance.
- 😀 If consumers save more, the IS curve shifts to the left, as a lower interest rate is required to reduce savings and stimulate spending.
- 😀 Changes in investment levels, influenced by expectations about the future, cause the IS curve to shift. Positive expectations shift it to the right, while negative expectations shift it to the left.
- 😀 Expansionary government policy (e.g., increased spending or tax cuts) shifts the IS curve to the right, while contractionary policy (e.g., higher taxes or reduced spending) shifts it to the left.
- 😀 An increase in exports, often due to currency depreciation or foreign growth, shifts the IS curve to the right, while a decrease in exports shifts it to the left.
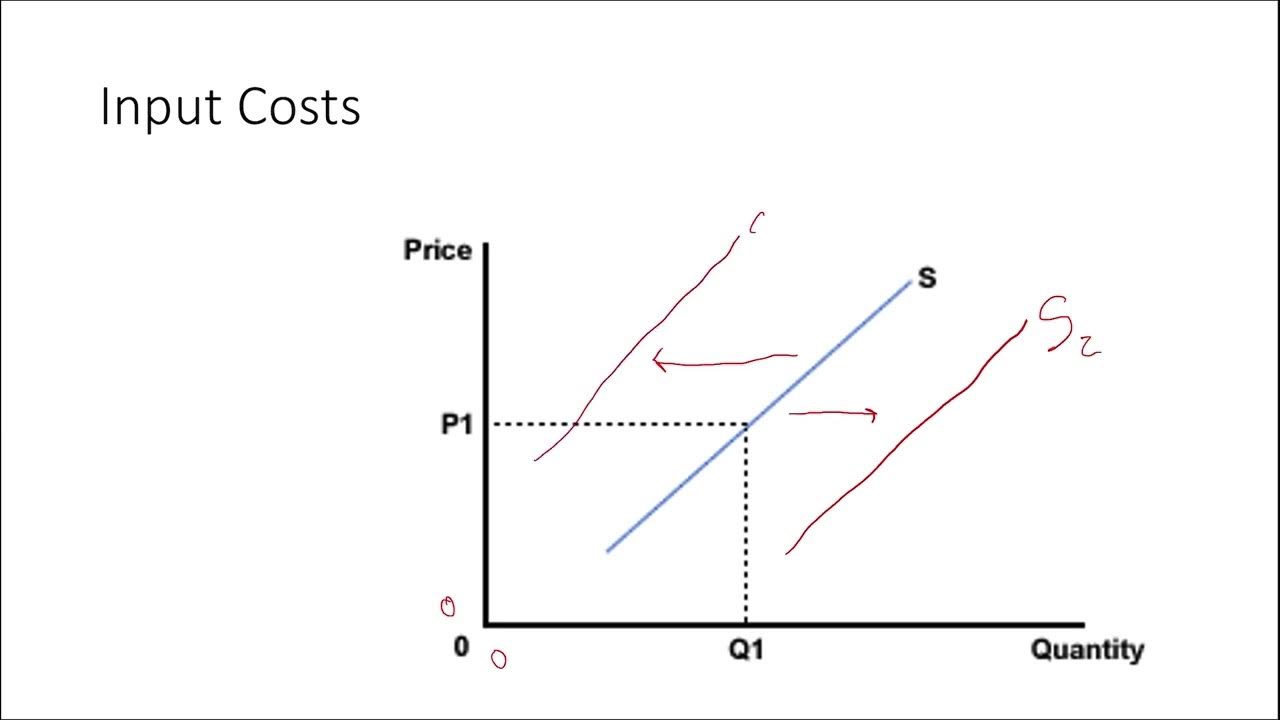
- 😀 The LM curve represents equilibrium in the money market, where money demand equals money supply, and shifts based on changes in money supply or the price level.
- 😀 An increase in the money supply, such as through central bank actions, shifts the LM curve to the right, indicating that a higher GDP is needed for equilibrium at any given interest rate.
- 😀 Technological advancements, such as the use of credit cards, increase the real money supply without changing the physical money supply, shifting the LM curve to the right.
- 😀 Changes in the price level impact the LM curve: a rise in prices reduces the real money supply and shifts the LM curve to the left, while a decrease in prices increases the real money supply and shifts the LM curve to the right.
Q & A
What is the IS-LM model used to represent?
-The IS-LM model is used to represent the equilibrium relationship between interest rates, GDP, and the money market in an economy. It shows how changes in these variables affect the economy's overall equilibrium.
What does the IS curve show in the IS-LM model?
-The IS curve shows every equilibrium point where investment and savings are in balance. It reflects the relationship between GDP and interest rates that maintains this balance.
Why does the IS curve slope downward?
-The IS curve slopes downward because as the interest rate decreases, GDP needs to increase to maintain equilibrium between investment and savings.
How does an increase in consumer consumption affect the IS curve?
-If consumers decide to save less and increase consumption, the IS curve shifts to the right. This is because a higher consumption at any given interest rate requires a higher GDP to maintain equilibrium.
What impact does an increase in government spending have on the IS curve?
-An increase in government spending shifts the IS curve to the right, reflecting an expansionary fiscal policy that stimulates the economy.
How do changes in exports affect the IS curve?
-An increase in exports, often due to currency depreciation or other factors that make a country's goods more competitive abroad, shifts the IS curve to the right. Conversely, a decrease in exports shifts the IS curve to the left.
What factors can shift the LM curve?
-The LM curve can shift due to changes in the money supply, transaction technologies (such as credit cards), and the price level. For instance, an increase in money supply or improvements in transaction technology shift the LM curve to the right.
What is the relationship between money supply and the LM curve?
-If the central bank increases the money supply (e.g., by buying Treasury bills), the LM curve shifts to the right, indicating that a higher level of GDP is required for money market equilibrium. A decrease in money supply shifts the LM curve to the left.
How does a change in the price level affect the LM curve?
-An increase in the price level reduces the real money supply, shifting the LM curve to the left. Conversely, a decrease in prices increases the real money supply, shifting the LM curve to the right.
What role do technological changes, like credit card usage, play in shifting the LM curve?
-Technological changes, such as the increased use of credit cards, effectively increase the real money supply. This shift in the money market conditions causes the LM curve to shift to the right, even if the physical money supply remains unchanged.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)