3 Proses Penyembuhan Luka
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the stages of wound healing in the human body. It covers three main phases: the inflammatory phase, where the body stops bleeding and clears the wound area of bacteria and debris; the proliferative phase, where new cells and tissues form to repair the wound; and the maturation phase, where the new tissue strengthens and the wound heals fully, potentially leaving a scar. Each stage involves specific processes, such as blood clotting, tissue regeneration, and collagen synthesis, all essential for efficient recovery and minimal scarring.
Takeaways
- 😀 The wound healing process is divided into three main phases: Inflammatory, Proliferation, and Maturation.
- 😀 Inflammatory phase begins immediately after injury and lasts up to 3 days, focusing on stopping bleeding and clearing the wound of debris and bacteria.
- 😀 Hemostasis is the first step in the inflammatory phase, where platelets form a clot to stop bleeding, followed by vasoconstriction.
- 😀 Phagocytosis occurs during inflammation, where white blood cells like neutrophils and macrophages clean up the wound area.
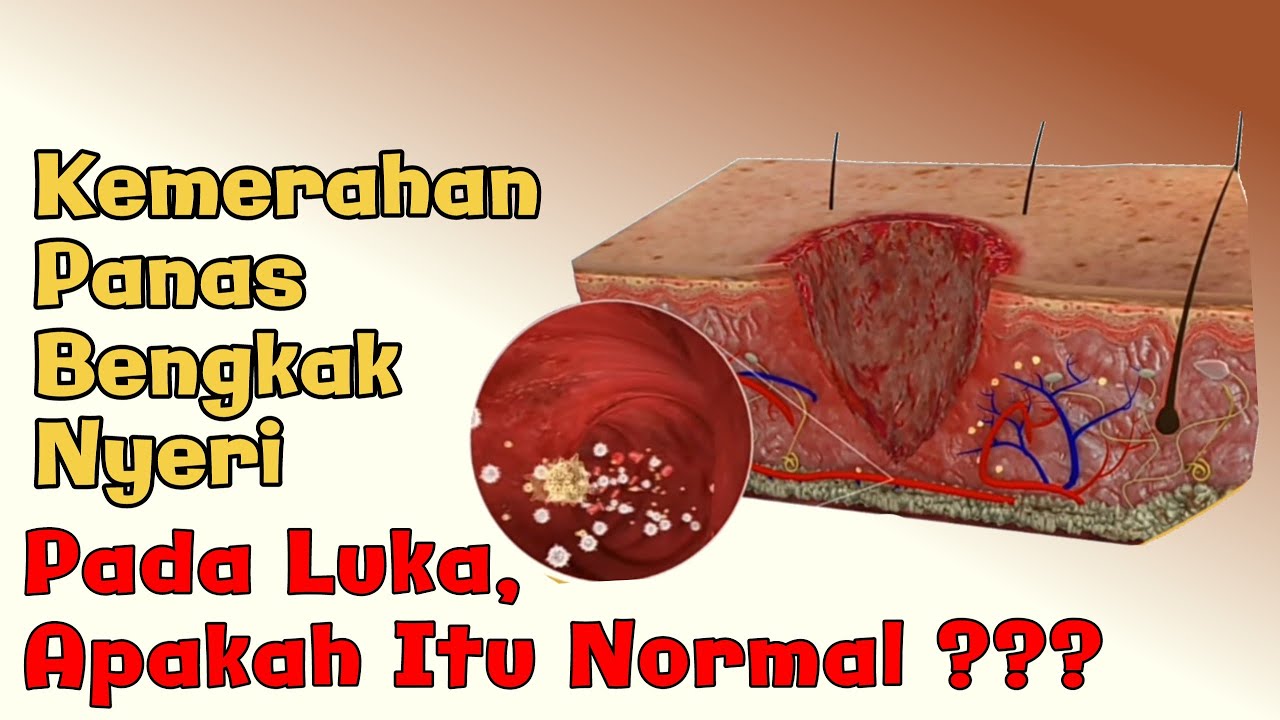
- 😀 Common signs of inflammation include redness (rubor), warmth (calor), swelling (tumor), pain (dolor), and loss of function (functio laesa).
- 😀 The Proliferation phase involves the creation of new tissue, including the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) and granulation tissue.
- 😀 Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels to supply oxygen and nutrients necessary for healing.
- 😀 Granulation tissue formation is driven by fibroblasts, which produce collagen to strengthen the wound area.
- 😀 Epithelialization is the process of forming new epithelial cells that cover the wound surface, ultimately leading to skin closure.
- 😀 The Maturation phase involves the maturation of the newly formed tissue, strengthening the wound through continued collagen production. This phase can take 1-2 years for full tissue recovery.
Q & A
What are the three main stages of wound healing described in the script?
-The three main stages of wound healing are inflammation, proliferation, and maturation.
What happens during the inflammatory phase of wound healing?
-During the inflammatory phase, the body stops bleeding and clears the wound area of foreign bodies, dead cells, and bacteria. This includes hemostasis and phagocytosis.
What is the role of platelets in the hemostasis process?
-Platelets form clots at the wound site to stop bleeding, and they help trigger vasoconstriction, which narrows blood vessels to prevent further blood loss.
What are the key signs of inflammation observed during wound healing?
-The signs of inflammation include redness (rubor), heat (calor), swelling (tumor), pain (dolor), and loss of function (functio laesa).
What is the process of phagocytosis in the inflammatory phase?
-Phagocytosis involves white blood cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, moving to the wound area to consume and destroy bacteria and dead cells, preventing infection.
How does angiogenesis contribute to wound healing?
-Angiogenesis is the process of forming new blood vessels to supply the wound with oxygen and nutrients, which is essential for tissue repair and regeneration.
What is granulation tissue and why is it important in the proliferation phase?
-Granulation tissue is formed by fibroblasts and contains collagen, which helps strengthen the wound site. It is crucial for the foundation of new tissue during wound healing.
How does epithelialization contribute to wound healing?
-Epithelialization is the formation of new epithelial cells that cover the wound's surface, helping to close the wound and protect it from further damage or infection.
What is the role of collagen during the maturation phase of wound healing?
-Collagen plays a crucial role in strengthening the new tissue by increasing its tensile strength, reducing the risk of the wound reopening.
How long does the maturation phase of wound healing last, and what happens during this phase?
-The maturation phase can last from day 21 to 1-2 years. During this phase, the tissue becomes stronger, and the wound may form a scar, transitioning from red to white as it matures.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)