Module 05 Magnetic Field Inside of a Solenoid (Part 3)
Summary
TLDRIn this video for Module 5, viewers explore the magnetic field inside a solenoid. The module covers the relationship between electric current, the number of coils, and the resulting magnetic field. It guides through experiments designed to determine the vacuum permeability constant (μ₀), and how the magnetic field behaves inside and outside the solenoid. The video includes details on the equipment, basic theory, and step-by-step procedures for conducting the experiments, along with data analysis methods and how to format a report. This content is essential for understanding the principles of electromagnetism in a laboratory setting.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video explains the third segment of Module 5, focusing on the magnetic field inside a solenoid.
- 😀 It is recommended for all participants in the basic physics laboratory to watch the first and second videos of Module 5 for better understanding.
- 😀 The outline of the video includes goals, equipment, theory, experiment procedures, data analysis, discussion, and report format.
- 😀 The four main goals of Module 5 are: determine the relationship between current and magnetic field, the number of coils and magnetic field, calculate the vacuum permeability constant, and calculate the magnetic field inside and outside the solenoid.
- 😀 Seven tools and materials are used in the experiment, including a labquest interface, a power supply, a multimeter, a magnetic field sensor, and a slinky solenoid with a minimum length of 1.5 meters.
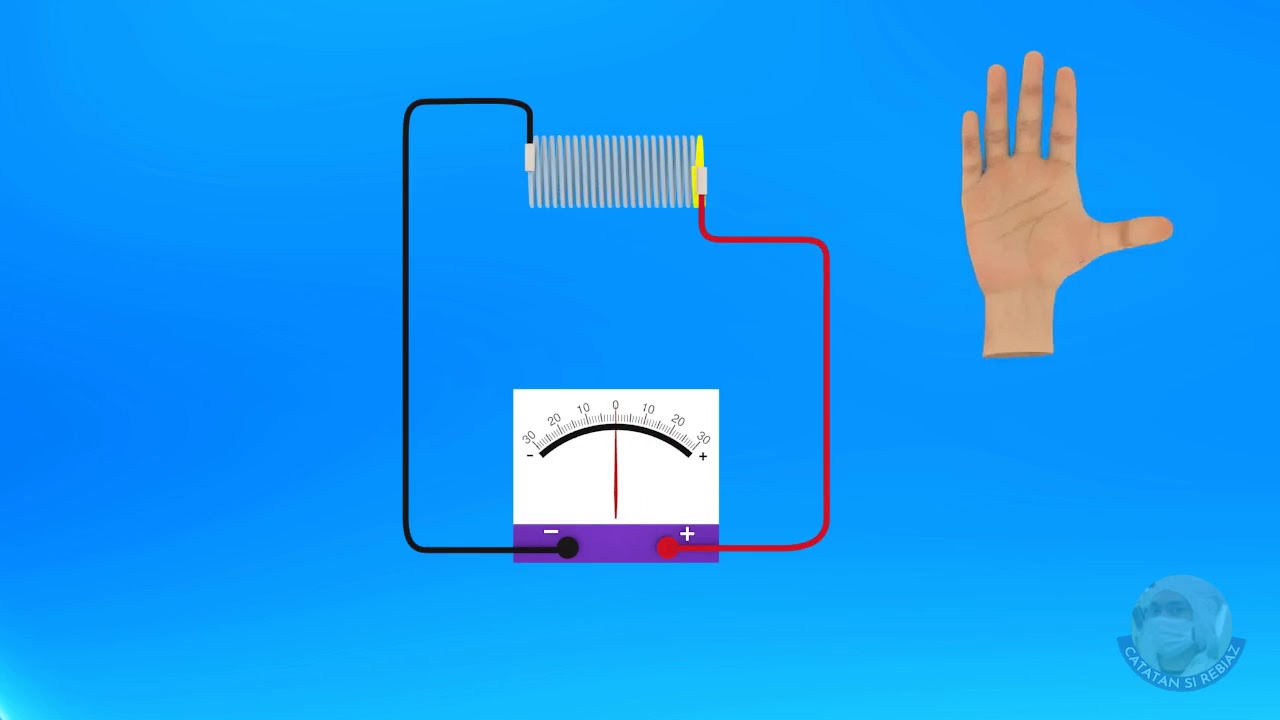
- 😀 A solenoid is a coil wound from wire that creates a magnetic field when electric current is passed through it, with the strength of the magnetic field depending on the current and the number of coils.
- 😀 The basic theory includes using Ampere's Law to calculate the magnetic field, with a formula that relates magnetic field (B) to current (I), number of coils (N), and solenoid length (L).
- 😀 In the first experiment, the relationship between current and magnetic field is examined, with varying current values and a resulting magnetic field measurement.
- 😀 In the second experiment, the relationship between the number of coils and the magnetic field is analyzed by varying the length of the solenoid, showing how the magnetic field changes with coil density.
- 😀 The final experiment measures the distribution of the magnetic field inside and outside the solenoid using a magnetic field sensor, assessing the effect of current on the field at various positions along the solenoid.
- 😀 The report format includes sections like module and title, day, date, time, objectives, materials, theory, data analysis, conclusion, and answers to specific lab questions.
Q & A
What is the main objective of Module 5 in the experiment?
-The main objective of Module 5 is to explore the magnetic field inside a solenoid, focusing on determining the relationship between current and magnetic field, the number of coils and magnetic field, calculating the vacuum permeability constant, and measuring the magnetic field inside and outside the solenoid.
What are the key tools and materials used in this experiment?
-The tools and materials used in the experiment include the LabQuest interface, DC power supply (3A), ammeter (perimeter), magnetic field sensor, connection cables, and a slinky solenoid with a stand. The solenoid needs to be at least 1.5 meters in length.
How is the magnetic field calculated in this experiment?
-The magnetic field inside the solenoid is calculated using Ampère's Law. The equation used is B = (μ₀ * I * N) / L for the center of the solenoid, and for the ends, a modified equation is used with 2L instead of L. Here, B is the magnetic field, μ₀ is the permeability constant, I is the current, N is the number of coils, and L is the length of the solenoid.
What is the relationship between current and magnetic field in this experiment?
-The relationship between current and magnetic field is linear. As the current increases, the magnetic field inside the solenoid also increases. This can be seen in the data, where a linear regression yields the equation B = 0.1693 * I - 0.0075.
How is the permeability constant (μ₀) determined in this experiment?
-The permeability constant (μ₀) is calculated from the gradient of the linear regression graph of current versus magnetic field. By dividing the gradient by the number of coils per unit length (N/L), the value of μ₀ is determined.
What error percentage was observed when calculating the permeability constant (μ₀) in this experiment?
-The error percentage when calculating μ₀ was 7.08%, which is the difference between the experimental value and the reference value.
What is the significance of the experiment on the relationship between the number of coils and magnetic field?
-This experiment investigates how the number of coils per unit length (N/L) affects the magnetic field. It shows that as N/L increases, the magnetic field strength also increases. This relationship is key to understanding the impact of coil density on the solenoid's magnetic field.
How does varying the length of the solenoid affect the experiment?
-Varying the length of the solenoid changes the N/L ratio, which in turn affects the magnetic field. The experiment measures this by adjusting the solenoid length from 0.6 to 1.5 meters, keeping the current constant.
What is the focus of the third experiment in this module?
-The third experiment focuses on measuring the magnetic field inside and outside the solenoid. This involves recording the magnetic field strength at different points along the solenoid, both with and without current, to understand how the field is distributed.
What is the format for the final report in this module?
-The final report should include the module title, date, time, student information, lab assistants' details, objectives, materials, basic theory, data and processing, analysis, and conclusion. The conclusion should directly address the experiment's objectives in bullet-point form.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)