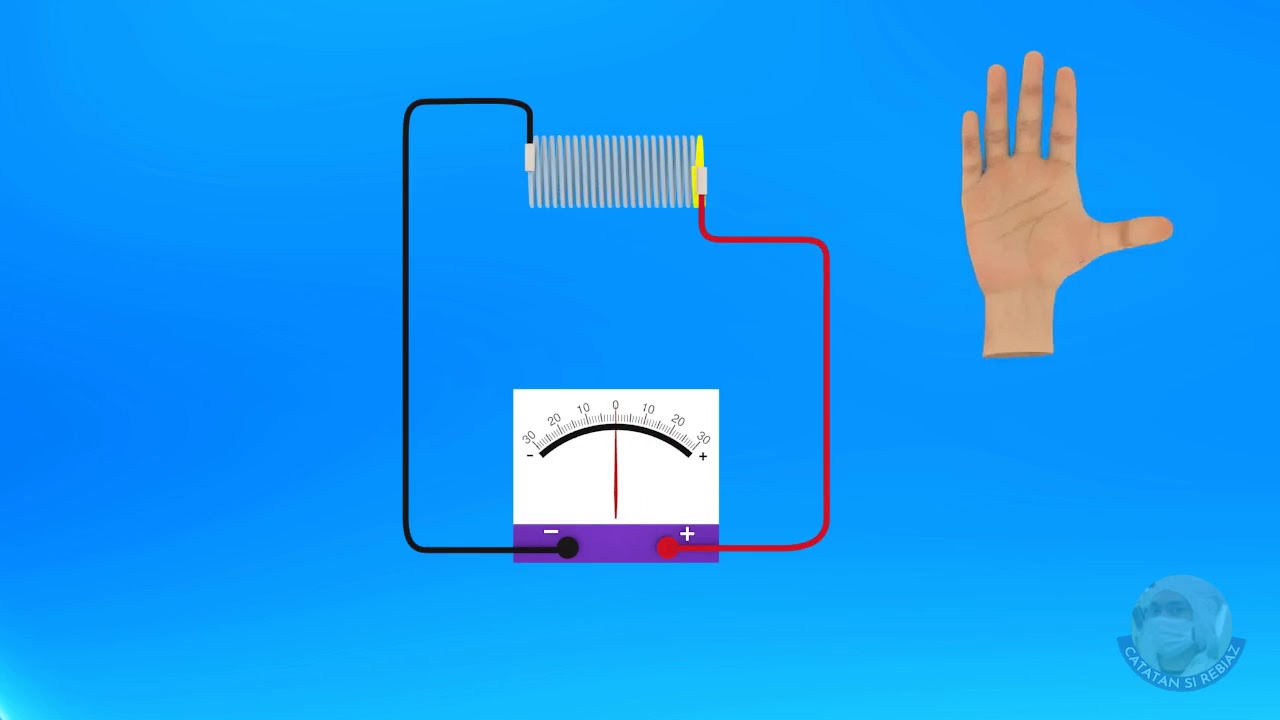
Medan Magnet dalam Solenoida
Summary
TLDRThis transcript details a basic physics lab experiment focusing on the magnetic field of a solenoid. The procedure involves setting up equipment like a power supply, solenoid, rheostat, and magnetometer sensor. Students adjust variables such as current and solenoid length while recording data for the magnetic field strength. The experiment concludes with calculations to determine the permeability constant and analyzing the relationship between the magnetic field, current, and solenoid turns. It also covers several analytical questions related to the experiment, such as the effect of solenoid turns and the comparison of experimental and theoretical results.
Takeaways
- 😀 The experiment involves a practical demonstration of magnetic fields using a solenoid setup.
- 😀 The equipment used in the experiment includes a power supply, solenoid, rheostat, connecting cables, magnetic field sensor, interface, and digital multimeter.
- 😀 The solenoid in this experiment is 50 cm long and is used to observe and measure magnetic fields.
- 😀 The procedure involves setting up the equipment in a specific order, adjusting current using the rheostat, and connecting the components correctly.
- 😀 The magnetic field sensor is placed inside the solenoid to detect and record the magnetic field strength.
- 😀 The experiment requires varying the current from 0.5 A to 2.9 A and recording the magnetic field at different intervals.
- 😀 The length of the solenoid is adjusted from 20 cm to 50 cm, and the magnetic field is measured for each configuration.
- 😀 The collected data is used to create a graph that shows the relationship between magnetic field strength and electric current.
- 😀 The experiment also involves calculating the permeability constant (μ₀) using the slope of the graph of magnetic field versus current.
- 😀 The results of the experiment will help analyze the relationship between magnetic field strength, current, solenoid length, and number of coils.
- 😀 Factors affecting the permeability constant and magnetic field measurements, such as temperature and pressure, are discussed, and the theoretical values are compared with experimental results.
Q & A
What is the main objective of this experiment?
-The main objective of this experiment is to understand and measure the magnetic field inside a solenoid and its relationship with the electric current flowing through it.
What equipment is required for this experiment?
-The experiment requires a power supply (6V), a solenoid (50 cm), a rheostat, connecting cables, a magnetic field sensor, a EuroLab interface, and a digital multimeter.
How do you connect the components in this experiment?
-First, connect the power supply to the rheostat, then connect the rheostat to the solenoid in a series circuit. The magnetic field sensor is connected to the EuroLab interface, which is then linked to a computer.
What is the role of the rheostat in this experiment?
-The rheostat is used to regulate the electric current flowing through the solenoid, allowing you to vary the current during the experiment.
What should be the position of the magnetic field sensor in the solenoid?
-The magnetic field sensor should be placed at the center of the solenoid to accurately measure the magnetic field strength.
How should the length of the solenoid be adjusted during the experiment?
-The solenoid should be adjusted to 50 cm and the spacing between the coils should be set to ensure a homogeneous magnetic field.
What is the formula used to calculate the slope of the magnetic field vs current graph?
-The slope of the graph is calculated using the formula: (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1), where y2 and y1 represent the magnetic field values (B2 and B1), and x2 and x1 represent the corresponding current values (I2 and I1).
How is the permeability constant (μ₀) determined from the graph?
-The permeability constant (μ₀) is calculated by dividing the slope of the magnetic field vs current graph by the number of turns per unit length of the solenoid.
What is the relationship between the magnetic field and the current in the solenoid?
-The magnetic field strength inside a solenoid is directly proportional to the current flowing through it. As the current increases, the magnetic field strength also increases.
How do you compare the permeability constants obtained from two experiments?
-The permeability constant from two experiments can be compared by calculating the relative deviation using the formula: K = μ₀ from the first experiment divided by the μ₀ from the second experiment, where μ₀ represents the permeability constant.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)