How Starter Motors Work
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the detailed process of how a car's starter motor system works. It describes how turning the ignition key sends a small electric current to the solenoid coil, activating both the pulling and holding coils to create a magnetic field. This field moves a piston, engaging the pinion gear with the flywheel, allowing the engine to start. Once the engine runs faster than the starter motor, the system disengages. The video also covers how the car battery recharges. Viewers are encouraged to check out related videos for more insights on automotive engineering.
Takeaways
- 🔑 Turning the ignition key sends a small electric current to the solenoid coil.
- 🔋 The solenoid is made up of two coils: the pulling coil and the holding coil.
- 🔌 The holding coil is connected to the starter motor casing, returning current to the battery via the car's frame.
- ⚡ Both coils are energized, creating a magnetic field that pulls the piston back, allowing the contactor plate to connect across the main terminals.
- 🚫 The pulling coil turns off once both ends become the same voltage, as no current flows through it.
- 📉 The holding coil continues running since it requires less energy to hold the piston in position.
- 🛠️ As the piston moves, it pulls a lever that rotates the pinion, locking it into the flywheel to start the engine.
- 🔄 The rotor spins rapidly due to the electromagnetic field produced by the coil, creating torque that turns the flywheel.
- 🌀 When the engine begins rotating faster than the starter motor, the overrunning clutch unlocks, allowing the pinion gear to spin freely.
- 🔋 Releasing the key cuts power to the solenoid, disengaging the pinion gear, while the alternator recharges the battery as the engine runs on its own.
Q & A
What happens when the ignition key is turned?
-When the ignition key is turned, a small current of electricity flows into the solenoid coil, which activates both the pulling and holding coils, creating a strong magnetic field.
What are the functions of the pulling coil and the holding coil?
-The pulling coil is responsible for pulling the piston back by creating a strong magnetic field, while the holding coil maintains the piston in position with far less energy after the pulling coil turns off.
How does the pulling coil turn off?
-The pulling coil turns off when both ends of the coil reach the same voltage, causing no voltage difference across it, so no current flows through the pulling coil.
What happens after the piston moves back?
-As the piston moves back, it pulls on a lever, which pivots and transfers motion to the drive sleeve. This pushes the pinion forward, slightly rotating it to lock the rollers in the clutch and slide the pinion into the flywheel.
What role does the contactor plate play?
-The contactor plate connects across the main terminals, allowing a large current to flow through it and into the starter motor, powering the motor to turn the flywheel.
How does the current flow through the starter motor?
-The current flows through the contactor plate, through the thick wire to the brushes, then to the commutator plates, through the coil, and back through another commutator plate and brush, which is grounded to the car's frame.
How does the rotor or armature rotate?
-The rotor rotates by the interaction between the electromagnetic field generated by the starter motor coil and the permanent magnet or field winding in the stator. This causes the rotor to rotate with high speed and torque.
What happens when the flywheel starts the combustion process?
-Once the flywheel starts the combustion process, the engine rotates the flywheel faster than the starter motor, unlocking the overrunning clutch so the pinion gear can spin freely.
What happens when the key is released after starting the engine?
-When the key is released, the power to the solenoid coil is cut off, releasing the piston. A spring pushes the lever back, removing the pinion gear from the flywheel, and the starter motor stops running.
How does the battery recharge after the engine starts?
-Once the engine is running, the alternator takes over and recharges the battery, allowing the combustion engine to continue running by itself.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Cara Kerja Motor Starter Mobil Paling Gampang Dipahami
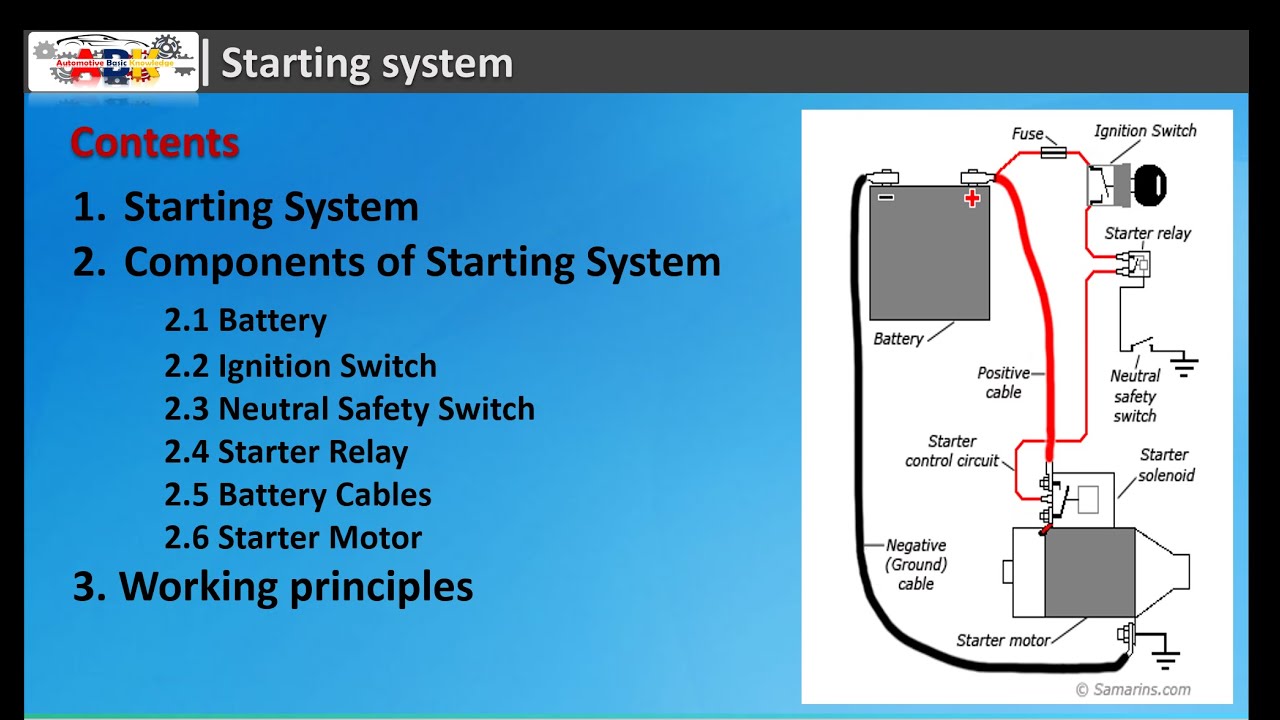
Basic Starting System

Starter Motor Explained - How a car's electric starter motor works
CARA KERJA SISTEM STATER SEPEDA MOTOR

SISTEM STARTER KONVENSIONAL: Komponen dan Fungsi Komponen Motor Starter Konvensional pada Mobil

Automotive Electrical System Basics - EricTheCarGuy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)