MACAM GAYA DALAM STRUKTUR BANGUNAN
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial focuses on the fundamentals of structural mechanics, particularly various forces in building structures. It explains key concepts such as internal and external forces, including tension, compression, bending, shear, torsion, and bearing stress. The video provides real-life examples of structural failures caused by excessive loads and natural forces like wind and earthquakes. It also emphasizes the importance of stability, strength, and stiffness in building design, offering practical advice on maintaining structural integrity through elements like diagonal bracing and shear walls. The lesson is aimed at students studying structural engineering.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses structural mechanics, focusing on the various types of forces acting on buildings.
- 😀 The primary learning objectives are understanding the different forces in building structures and presenting them in a technical manner.
- 😀 Forces in a building structure are classified into internal forces (e.g., tensile, compressive, bending, shear, torsion, and axial stress) and external forces (e.g., wind, earthquake).
- 😀 A force is defined as something that causes an object to move or change its state of motion, either by speeding up, slowing down, or causing it to stop.
- 😀 Forces are represented by vectors that indicate their magnitude, direction, and point of application.
- 😀 In engineering mechanics, forces are denoted as 'P' for structural mechanics, differing from the physics notation of 'F'.
- 😀 Structural forces like tension and compression act on elements such as beams and cables, leading to failure if the force exceeds the material's capacity.
- 😀 Shear forces cause parts of a structure to slide or move relative to each other, and torsional forces cause twisting or rotation around a fixed point.
- 😀 Stability in a structure refers to its ability to resist collapsing, tipping, or slipping under horizontal loads such as wind or earthquakes.
- 😀 Effective structural stability can be achieved by adding diagonal elements, using shear walls, and ensuring the connection between structural elements to prevent failure.
Q & A
What is the definition of force in the context of structural mechanics?
-In structural mechanics, force is defined as something that causes an object or material point to move, whether from rest to motion, or from slow motion to faster motion. It can be considered as a push or a pull on an object.
What are the different types of forces that act on a building structure?
-The forces acting on a building structure are classified into external forces (like wind and earthquakes) and internal forces (like the building's own weight, structural tension, compression, bending, shear, torsion, and bearing stresses).
What is the difference between external and internal forces?
-External forces are those that come from outside the structure, such as wind or earthquakes, while internal forces are those generated within the structure itself, such as tension, compression, or bending due to the weight and load of the building.
What is the concept of 'tension' force in structural engineering?
-Tension force refers to the force that tries to stretch or pull apart an element within a structure, like the force experienced by a cable or beam under tension. It tends to pull elements towards each other until they are at risk of breaking.
What does 'compression' force do in a structure?
-Compression force pushes or squeezes elements of a structure, causing them to shorten. This force is typically seen in columns or supports under heavy load, which may lead to buckling if the structure cannot handle the force.
How does 'bending' force affect structural elements?
-Bending force occurs when a load applied to a structural element causes it to curve or bend. This can be seen in beams or slabs under load, and excessive bending can lead to structural failure or deformation.
What is the role of shear force in a structure?
-Shear force causes adjacent parts of a structure to slide or shift against each other. This force can lead to the structural failure if the materials or connections are not strong enough to resist it.
What is torsion and how does it affect a structure?
-Torsion is the twisting force that causes a structural element to rotate around its axis. This type of force is commonly seen in elements like shafts or beams subjected to rotational loads.
What are bearing stresses in a building structure?
-Bearing stresses occur at the points where a structural element is supported or connected to another element. These stresses act perpendicular to the contact surface and are crucial for the stability and integrity of the connection.
What are some structural responses to prevent collapse due to external forces?
-To prevent structural collapse, responses such as using wide, rigid foundations, adding diagonal elements to improve stability, and reinforcing with shear walls or columns are essential. These measures help in distributing the load and resisting forces like wind and earthquakes.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Mekanika Statis Tentu: Struktur dan Elemen Bangunan

PENGERTIAN DAN JENIS-JENIS GAYA DALAM PADA STRUKTUR - MUDAH
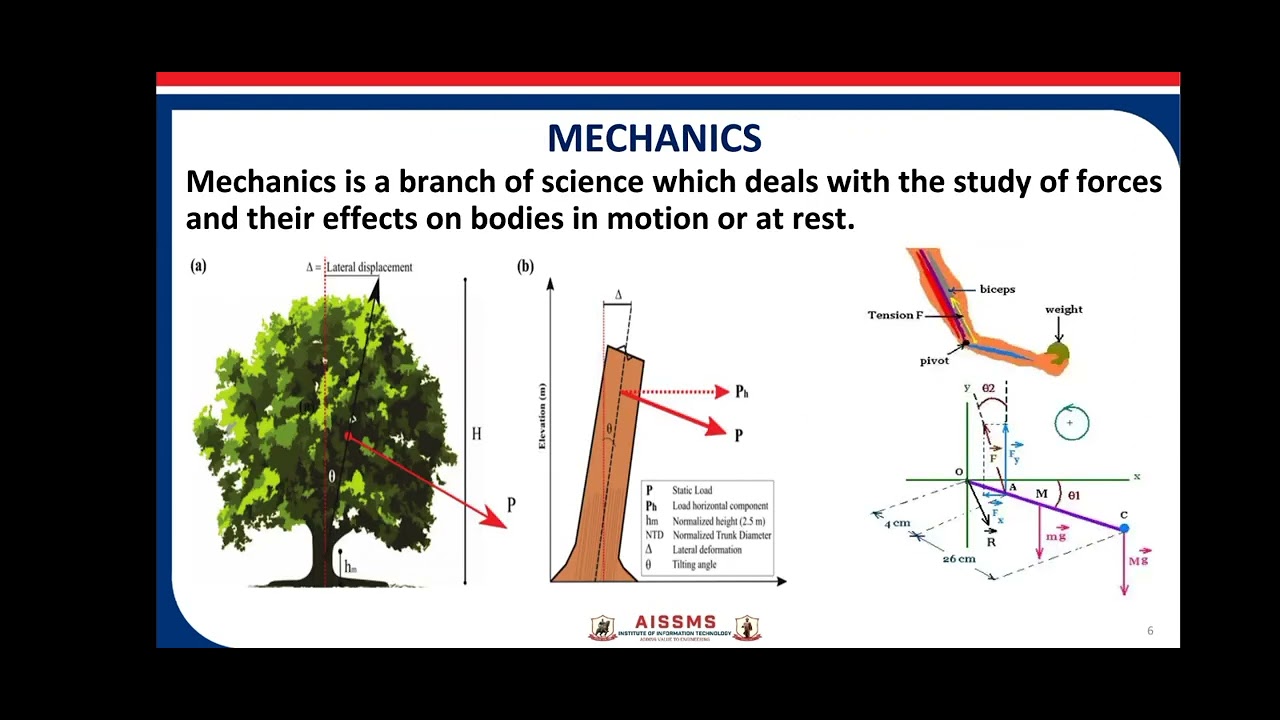
Introduction to Engineering Mechanics

ANALISA STRUKTUR 2 KONSEP DASAR MATRIKS FLEKSIBILITAS#flexibilitymatrix#Flexibility#matrix
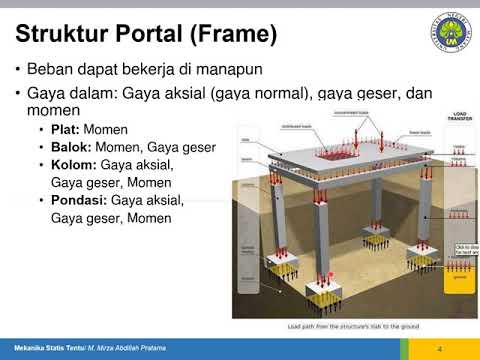
Mekanika Statis Tentu: Klasifikasi Struktur Bangunan

Praktikum Geomorfologi 2021 Acara 4 - Bentuklahan Asal Proses Struktural
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
