PENGERTIAN DAN JENIS-JENIS GAYA DALAM PADA STRUKTUR - MUDAH
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the fundamentals of Engineering Mechanics, focusing on internal forces within structures caused by external loads. Key concepts discussed include moments, shear forces, and axial forces, with clear definitions and examples. The video explains how positive and negative moments affect the behavior of structures, alongside the significance of shear and normal forces. This foundational knowledge is essential for civil engineering students, providing a basis for further analysis and design in structural engineering. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of understanding these internal forces for effective engineering practice.
Takeaways
- 👷♂️ Engineering mechanics focuses on understanding internal forces within structures caused by external loads.
- 🔍 Internal forces can be classified into three types: moments, shear forces, and normal forces.
- ⚖️ A moment is the product of a force and the perpendicular distance from the point of interest to the line of action of the force.
- 👍 Positive moments compress the upper fibers of a structure and elongate the lower fibers, while negative moments do the opposite.
- 📏 The calculation of moments is crucial for determining the placement of reinforcement bars in structural elements.
- 🌀 Shear forces act perpendicular to the main axis of the structure and are essential for understanding how loads are distributed.
- 🔄 Shear forces can be categorized into positive (left side moves up) and negative (right side moves up) shear forces.
- 🌟 The design of shear reinforcement depends on the shear force distribution along the length of the structure.
- ⬆️ Normal forces act parallel to the main axis of the structure, indicating whether it is in tension or compression.
- 🔄 Normal forces can also be positive (indicating tension) or negative (indicating compression), affecting the overall stability of the structure.
Q & A
What is the definition of internal forces in structures?
-Internal forces are forces that arise within a structure due to the application of external loads.
What happens to internal forces if no external forces are acting on a structure?
-If there are no external forces acting on a structure, the internal forces will be equal to zero.
What are the three types of internal forces discussed in the transcript?
-The three types of internal forces discussed are moments, shear forces, and normal forces.
How is a moment defined and calculated?
-A moment is defined as the product of a force and the perpendicular distance from the line of action of that force to the point of interest.
What distinguishes a positive moment from a negative moment?
-A positive moment compresses the upper fibers of a structure and elongates the lower fibers, while a negative moment elongates the upper fibers and compresses the lower fibers.
What are shear forces, and how do they function in a structure?
-Shear forces are forces that act perpendicular to the main axis of a structure, affecting how the structure reacts to vertical loads.
Can you explain the difference between positive and negative shear forces?
-Positive shear forces cause the left side of a structure to move upward relative to the right side, while negative shear forces cause the right side to move upward relative to the left side.
What is a normal force, and how is it oriented in relation to a structure?
-A normal force is a force that acts parallel to the main axis of a structure, indicating tension or compression depending on its sign.
What does a positive normal force indicate about a structure?
-A positive normal force indicates that the structure is being pulled apart, suggesting tension.
Why is it important to understand internal forces in structural design?
-Understanding internal forces is crucial for determining where to place reinforcements in a structure to ensure it can withstand applied loads safely.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

MACAM GAYA DALAM STRUKTUR BANGUNAN

Statika/Mekanika Teknik #4: Gaya Dalam
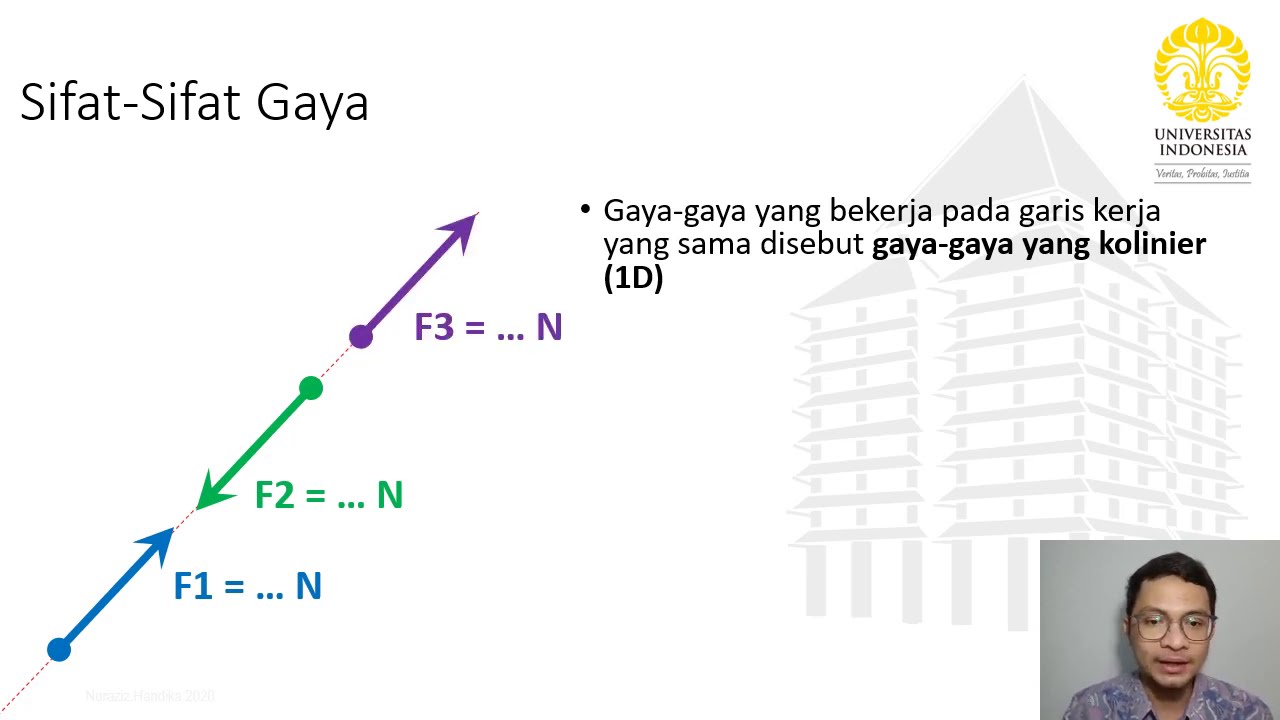
Kuliah Sifat-Sifat Gaya - Statika Kuliah 2(1) Vid
Introduction to Engineering Mechanics
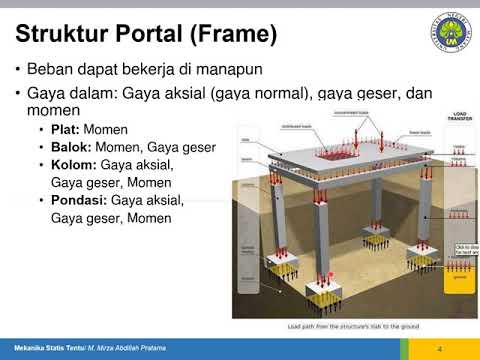
Mekanika Statis Tentu: Klasifikasi Struktur Bangunan

Structural Theory 1 Chapter 1 Structural Elements & Types of Structure Part 1 (with Subtitles)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)