What is TIG Welding? (GTAW)
Summary
TLDRTIG welding, or Tungsten Inert Gas welding, is a process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create an electric arc for melting the base metal. The heat generated by the arc is controlled via a foot pedal or thumb wheel. Direct current (DC) is typically used for most metals, while alternating current (AC) is employed for aluminum to clean oxides from the workpiece. TIG welding can be done with or without filler metal, using a filler rod when necessary. The molten metal is protected by shielding gases like argon, ensuring a clean weld. This versatile welding method provides precise control over the welding process.
Takeaways
- 😀 TIG welding stands for Tungsten Inert Gas welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW).
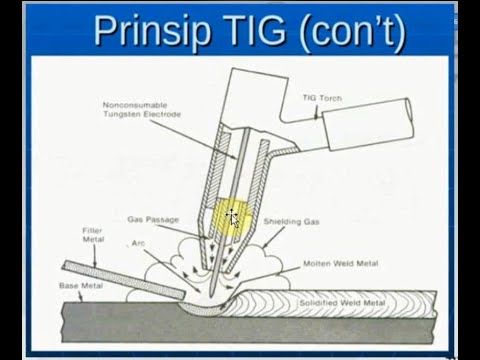
- 😀 The process uses a tungsten electrode that doesn't melt, making it a non-consumable electrode.
- 😀 Unlike other welding methods, where the electrode melts and becomes part of the weld, TIG welding keeps the electrode separate from the weld material.
- 😀 The tungsten electrode is inserted into a TIG torch and held in place by a collet that allows adjustment of the electrode's length.
- 😀 TIG welding generates heat through an electric arc between the tungsten electrode and the base metal.
- 😀 The heat can be controlled using a foot pedal or a thumb wheel on the torch.
- 😀 Direct Current (DC) is typically used for most metals, with the electrode being negative and the workpiece positive (DCEN).
- 😀 For aluminum welding, alternating current (AC) is used, which switches between positive and negative, helping to clean oxides off the surface of the workpiece.
- 😀 The welding circuit is completed through a work lead clamped to the workpiece, connecting it back to the machine.
- 😀 TIG welding can be done with or without filler metal; filler rods are used when additional metal is required to strengthen the weld.
- 😀 Shielding gas, typically argon, is used to protect the molten metal from contaminants like oxygen and water vapor in the atmosphere.
Q & A
What does TIG stand for in welding?
-TIG stands for Tungsten Inert Gas welding. It's also referred to as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW).
What is unique about the tungsten electrode used in TIG welding?
-The tungsten electrode used in TIG welding has an extremely high melting point. It is non-consumable, meaning it doesn't melt or become part of the weld, unlike other welding electrodes.
How does TIG welding differ from other welding processes in terms of the electrode?
-In TIG welding, the electrode does not melt, unlike in other welding processes where the electrode melts and becomes part of the weld. This makes the tungsten electrode non-consumable.
What are the main components of a TIG welding setup?
-A typical TIG welding setup includes a tungsten electrode, a TIG torch, a collet to hold the electrode, a regulator for shielding gas, a foot pedal or thumb wheel to control heat, and a filler rod if needed.
How is heat controlled during TIG welding?
-Heat in TIG welding is controlled using a foot pedal or a thumb wheel on the torch, which adjusts the amount of heat generated by the electric arc.
What is the difference between DCEN and AC in TIG welding?
-DCEN (Direct Current Electrode Negative) puts most of the heat on the workpiece and is common in welding metals like steel. AC (Alternating Current) switches between positive and negative, helping control oxides, especially when welding aluminum.
Why is AC current preferred for welding aluminum?
-AC current is used for welding aluminum because it helps control oxides that form on the surface of the metal. The alternating current helps clean the weld pool by shifting heat between the electrode and the workpiece.
What is the role of shielding gas in TIG welding?
-Shielding gas, typically argon or sometimes helium, protects the molten metal from reacting with oxygen and water vapor in the atmosphere, preventing contamination and ensuring a strong weld.
How is the shielding gas provided to the weld in TIG welding?
-The shielding gas is stored in high-pressure cylinders, and its pressure is reduced to a usable level by a regulator. The gas then flows through a hose and exits at the point of the weld.
Can filler metal be used in TIG welding, and how is it applied?
-Yes, filler metal can be used in TIG welding. It is added separately in the form of a filler rod, which is a metal rod with a specific alloy that is compatible with the base metal and provides the necessary strength.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)