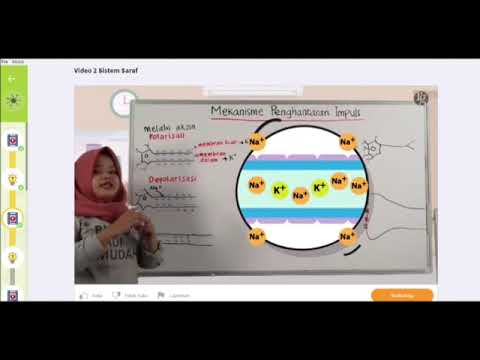
Mekanisme Penghantaran Impuls ( Sistem Saraf )
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host discusses the mechanisms of impulse transmission within the nervous system, focusing on the process of depolarization and the role of neurotransmitters like acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin. The lesson covers how sensory stimuli are received by receptors, processed by the nervous system, and transmitted through neurons to trigger responses in effectors. The video also explains the difference between voluntary and reflexive movements, highlighting the fast, automatic nature of reflexes that bypass the brain. A thorough overview of the central nervous system and its functions is also included.
Takeaways
- 😀 The nervous system is responsible for processing stimuli and transmitting impulses throughout the body.
- 😀 Receptors are parts of the body that receive or respond to stimuli, while effectors are responsible for reacting to those stimuli.
- 😀 In the absence of stimuli, nerve cells (neurons) are in a polarized or resting state.
- 😀 When a stimulus is received, the nerve cell undergoes depolarization, reversing the charge of the cell by allowing Na+ ions to enter.
- 😀 Depolarization generates an action potential, which travels along the nerve cell.
- 😀 After an action potential passes, the cell restores its charge by releasing K+ ions, returning to a polarized state.
- 😀 Nerve cells enter a refractory period after an action potential, during which they are less responsive to new stimuli as they recover.
- 😀 Synapses are junctions between nerve cells, where neurotransmitters are released to transmit impulses across cells.
- 😀 Neurotransmitters include acetylcholine, noradrenaline, serotonin, and dopamine, each playing different roles in the nervous system.
- 😀 The process of voluntary movement involves the brain processing a stimulus, sending signals through motor neurons to initiate a response.
- 😀 Reflex actions are involuntary and rapid movements that occur without brain processing, usually in response to sudden stimuli, with the spinal cord coordinating the response.
Q & A
What is an impulse in the context of the nervous system?
-An impulse is a change detected by the body, either from external or internal stimuli, which is transmitted in the form of an electrical signal by nerve cells or neurons.
What is the function of receptors in the nervous system?
-Receptors are parts of the body that detect or respond to stimuli. They play a key role in receiving the signals that are sent to the nervous system for processing.
What are effectors in the nervous system?
-Effectors are parts of the body that react to the stimuli received from the nervous system. They carry out the response or action based on the processed signal.
How does the process of depolarization occur in a nerve cell?
-Depolarization occurs when a nerve cell experiences a stimulus that leads to the reversal of the cell's charge by increasing membrane permeability. This allows sodium ions (Na+) to enter the cell.
What is the significance of an action potential in nerve signal transmission?
-An action potential is the electrical signal that is generated during depolarization. It travels along the nerve cell and is crucial for transmitting the impulse to other neurons or effectors.
What happens to the nerve cell after an impulse has passed through?
-After an impulse has passed through a nerve cell, the region that was depolarized recovers its charge by releasing potassium ions (K+), and the cell enters a refractory period where it is not responsive to further stimuli.
What are neurotransmitters and what role do they play in nerve signal transmission?
-Neurotransmitters are chemical substances produced by nerve cells that facilitate the transmission of signals across synapses between nerve cells. They are essential for communication within the nervous system.
What is the function of synaptic vesicles in nerve cells?
-Synaptic vesicles are small sacs that store neurotransmitters before they are released into the synaptic cleft during nerve signal transmission. They help in ensuring the proper delivery of neurotransmitters to the post-synaptic membrane.
What are the differences between voluntary movement and reflex movement?
-Voluntary movement is conscious and occurs after the brain processes the stimulus. Reflex movement is automatic and fast, occurring without the brain's involvement, typically in response to sudden or harmful stimuli.
How does the reflex arc function in reflex movements?
-In reflex movements, a stimulus is received by the receptors, which then send the signal through sensory nerves to the spinal cord (instead of the brain). The signal is quickly relayed to motor neurons, resulting in an immediate response or movement.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)