AP Psychology | Myers’ Unit 3A
Summary
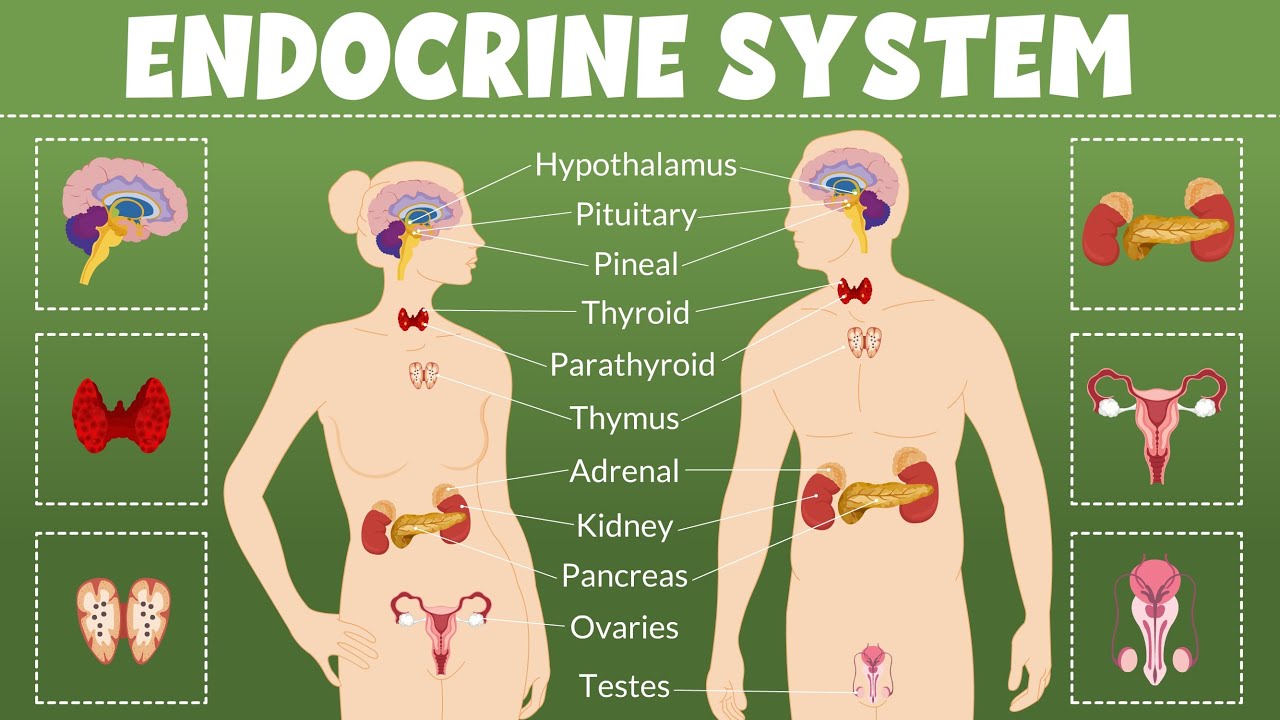
TLDRIn this video, Abe and Frank explore key topics from unit 3a of the AP Psychology textbook, focusing on neural processes and the endocrine system. They discuss the basics of neurons, including their structure and function, types (sensory, motor, and interneurons), and neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and acetylcholine. The video also explains the nervous system, differentiating between the central and peripheral systems, and touches on reflex actions. The endocrine system's role in controlling hormones, with a focus on glands like the pituitary and adrenal, is also examined.
Takeaways
- 🧠 Psychology and biology are closely linked fields, emphasizing the importance of understanding the biological basis of psychological phenomena.
- 🗝️ Phrenology, although initially incorrect, contributed to the understanding that different brain regions have specific functions.
- 🌐 Humans are biopsychosocial systems, composed of interconnected subsystems at various levels, from cells to organs.
- 👨🏫 Neurons are the fundamental units of the nervous system, with different types like sensory, motor, and interneurons, each playing a distinct role.
- 🌿 Myelin sheaths are crucial for the speed of neural communication by insulating axons and facilitating faster transmission of information.
- 🔄 Synapses are the junctions where neurons communicate, involving neurotransmitters and receptor sites to transmit signals between neurons.
- 🔄 Reuptake is a process where the sending neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters to regulate neurotransmitter levels.
- 💊 Neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and acetylcholine play critical roles in various psychological processes, with imbalances potentially leading to conditions like depression or schizophrenia.
- 🚫 GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that prevents other neurotransmitters from binding to dendrites and sending signals.
- 🌀 Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter involved in memory, and excessive levels can lead to migraines or seizures due to heightened brain activity.
- 💊 Endorphins act as natural painkillers released by the brain to alleviate pain signals from specific areas of the body.
Q & A
What is the relationship between psychology and biology as mentioned in the script?
-Psychology and biology are closely linked fields, with everything psychological also being biological, indicating that psychological processes have a biological basis.
What did Franz Gall originally propose with phrenology, and what was the ultimate outcome of this theory?
-Franz Gall originally proposed that bumps on the skull could reveal mental abilities. However, this theory was proven false, but it did contribute to the understanding that various brain regions have particular functions.
What are the three main types of neurons and their functions?
-There are sensory neurons, which receive information from the senses; motor neurons, which send signals to muscles to create movement; and interneurons, which connect neurons within the brain and spinal cord.
Describe the structure of a neuron and its role in transmitting information.
-A neuron has a dendrite, which receives information; a soma or cell body, which processes the information; an axon, which carries the information; and an axon terminal, which sends the information to other neurons via neurotransmitters.
What is the function of myelin sheaths in neurons?
-Myelin sheaths are insulating layers along the axon that speed up communication by allowing faster transmission of information or energy from one part of the body to another.
How do neurons communicate with each other through synapses?
-Neurons communicate through synapses where the terminal branches of one axon meet the dendrite of another neuron. Neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal and bind to receptor sites on the dendrite to transmit messages.
What is the role of reuptake in the process of neurotransmission?
-Reuptake involves the reabsorption of excess neurotransmitters by the sending neuron that were not absorbed by the receiving neuron, ensuring that the signal is terminated and preventing continuous stimulation.
What are some key neurotransmitters and their functions as discussed in the script?
-Key neurotransmitters include acetylcholine, which enables muscle learning and memory; dopamine, which influences movement, learning, and emotion; serotonin, which affects sleep, arousal, hunger, and mood; GABA, which inhibits other neurotransmitters; glutamate, which is involved in memory and can cause migraines or seizures when overactive; and endorphins, which act as natural painkillers.
How does the central nervous system differ from the peripheral nervous system?
-The central nervous system, consisting of the brain and spinal cord, can trigger reflexes without conscious thought, while the peripheral nervous system involves all other nerves outside the CNS and is responsible for voluntary movements and responses.
What is the role of the autonomic nervous system and its two branches?
-The autonomic nervous system is responsible for involuntary bodily functions like heartbeat and digestion. It has two branches: the sympathetic nervous system, which expends energy and prepares the body for action (fight or flight), and the parasympathetic nervous system, which conserves energy and promotes rest and digestion.
How does the endocrine system interact with the nervous system?
-The endocrine system secretes hormones that influence various bodily functions like hunger and sex drive, and it interacts with the nervous system by producing molecules that act on receptors, similar to neurotransmitters, but with slower and longer-lasting effects.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Neuroplasticity & Effects Of Psychoactive Drugs [AP Psychology Unit 2 Topic 8]

Agonists & Antagonists Drugs [AP Psychology Unit 2 Topic 5]

PSY 1001 : Introduction to Psychology
Endocrine System: What Is It, Functions & Organs | Video for Kids

AP Psych (2024)Key Terms 1.3 The Neuron and Neural Firing

AP Psychology Unit 7 Motivation, Emotion, Personality Review Video with Mandy Rice
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)