Osmose - Resumo
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of osmosis is explained through a detailed overview of solvent movement across a semipermeable membrane. The video covers the difference between hypotonic and hypertonic solutions and how water moves between them. It describes key biological concepts such as plasmolysis, turgidity, and lysis in cells, with comparisons between animal and plant cells. The process of osmosis is illustrated with examples, including the effects of placing cells in different solutions. The video concludes by highlighting the unique features of plant and animal cells during osmosis and offers a call to action for viewers to follow the channel for more educational content.
Takeaways
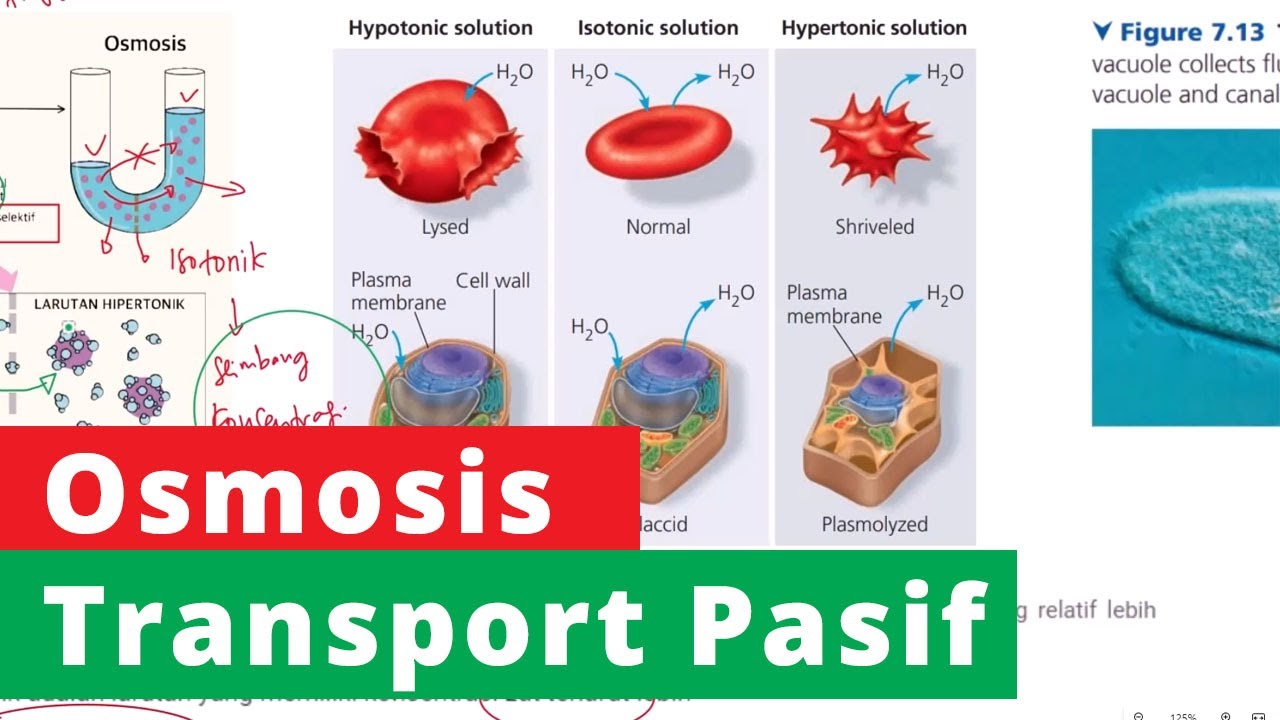
- 😀 Osmosis is the movement of a solvent (usually water) from a hypotonic environment to a hypertonic one through a semipermeable membrane.
- 😀 A semipermeable membrane allows only the solvent (like water) to pass through, not the solute.
- 😀 In an experiment, one side is more concentrated with solute (hypertonic), while the other side has a lower concentration (hypotonic).
- 😀 Water moves from the hypotonic side (low solute concentration) to the hypertonic side (high solute concentration) to balance the concentrations.
- 😀 When water enters the hypertonic side, it increases the volume of that side, while the hypotonic side loses water, balancing the solute concentrations.
- 😀 Once the concentrations equalize, the water stops moving, and the system reaches an isotonic state.
- 😀 If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, it will lose water, causing it to shrink. This process is called plasmolysis.
- 😀 If a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, it will absorb water, leading to an increase in volume and making the cell turgid (firm and swollen).
- 😀 In extreme cases, if too much water enters a cell in a hypotonic solution, the cell may rupture, a process known as plasmoptysis.
- 😀 A key difference between animal and plant cells during osmosis: animal cells may burst in hypotonic solutions due to lack of structural support, but plant cells are protected by their rigid cell walls.
Q & A
What is osmosis?
-Osmosis is the movement of solvent (typically water) from a hypotonic solution (low solute concentration) to a hypertonic solution (high solute concentration) through a semi-permeable membrane.
What is the role of the semi-permeable membrane in osmosis?
-The semi-permeable membrane allows only the passage of solvent (such as water) but not solutes, ensuring that water moves to balance the concentration of solutes between two solutions.
What is the difference between a hypotonic and a hypertonic solution?
-A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes (more water), while a hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solutes (less water).
What happens when water moves from a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic one?
-Water moves from the hypotonic solution (lower solute concentration) to the hypertonic solution (higher solute concentration) in an attempt to equalize the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane.
What occurs when two solutions become isotonic?
-When two solutions become isotonic, their solute concentrations are equal, and the movement of water across the semi-permeable membrane stops.
What happens to an animal cell placed in a hypertonic solution?
-An animal cell placed in a hypertonic solution will lose water and shrink due to the higher solute concentration outside the cell, a process known as plasmolysis.
What happens to an animal cell placed in a hypotonic solution?
-An animal cell placed in a hypotonic solution will gain water, causing it to swell, and if too much water enters, it can burst, a phenomenon known as plasmoptysis.
How do plant cells react differently in a hypotonic solution compared to animal cells?
-Plant cells in a hypotonic solution also gain water, but their rigid cell wall prevents them from bursting. Instead, the cell becomes turgid, or swollen, due to internal pressure from the water entering the cell.
What is the role of the plant cell wall in osmosis?
-The plant cell wall provides structural support and prevents the cell from bursting when it takes in water. It creates a counteracting pressure that balances the osmotic pressure from water entering the cell.
What is the key difference between plasmolysis and plasmoptysis?
-Plasmolysis occurs when a cell loses water and shrinks, often seen in animal cells in hypertonic solutions, while plasmoptysis refers to the bursting of a cell due to excessive water intake, typically in animal cells in hypotonic solutions.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)