OSMOSE - CÉLULA ANIMAL X CÉLULA VEGETAL | Biologia com Samuel Cunha
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the teacher explains the concept of osmosis, a passive transport process where water moves through a semipermeable membrane from a hypotonic to a hypertonic solution without using energy. The video covers how osmosis affects animal and plant cells, with detailed examples and practical applications for understanding the process in biology. The teacher also distinguishes between hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic solutions and explains the role of water movement in maintaining cellular balance. Additionally, the video emphasizes the importance of these concepts in exams, using real-life analogies and student-friendly explanations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Osmosis is a passive transport process where the solvent (typically water) moves across a semi-permeable membrane from a hypotonic to a hypertonic solution without the use of energy (ATP).
- 😀 Osmosis often confuses students because vestibular exams frequently test this concept using examples of animal and plant cells in different types of solutions (hypotonic, isotonic, hypertonic).
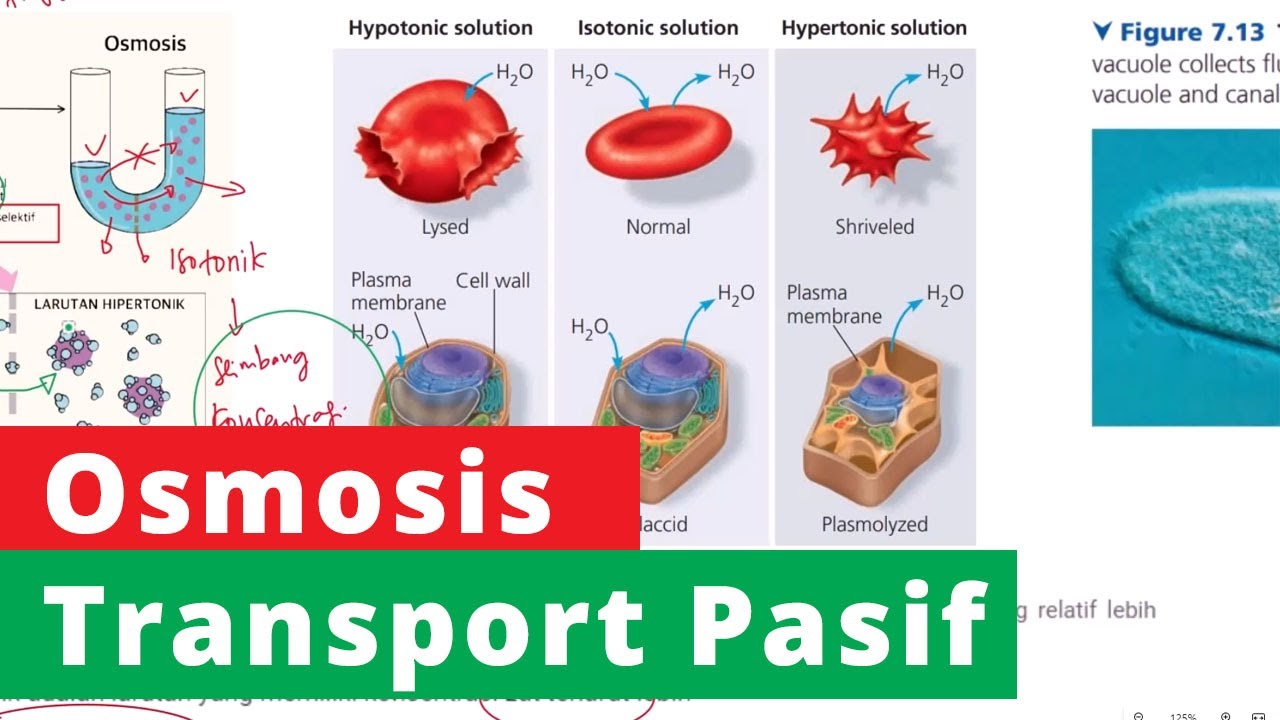
- 😀 A hypotonic solution has a lower solute concentration compared to the inside of a cell, leading to water moving into the cell.
- 😀 An isotonic solution has the same solute concentration as the inside of the cell, meaning water moves in and out at an equal rate, keeping the cell unchanged.
- 😀 A hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration than inside the cell, causing water to move out of the cell, potentially leading to cell shrinkage.
- 😀 Animal cells in a hypotonic solution will swell and may burst because water enters the cell. In an isotonic solution, the cell remains stable. In a hypertonic solution, the cell will shrink.
- 😀 Plant cells have a cell wall, which means they behave differently than animal cells during osmosis. In a hypotonic solution, the plant cell becomes turgid (firm), but it won't burst due to the cell wall.
- 😀 When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, it undergoes plasmolysis, where the cell shrinks away from the cell wall, but the cell wall remains intact.
- 😀 Osmosis is important in biology and often tested in exams, so understanding how water moves in and out of cells in various solutions is crucial for students.
- 😀 The instructor emphasizes the importance of studying different types of cell transport (passive, active, vesicular) and encourages students to learn about osmotic pressure and related concepts like endocytosis and exocytosis.
Q & A
What is osmosis and how is it different from other forms of passive transport?
-Osmosis is a type of passive transport where the solvent, usually water, passes through a semi-permeable membrane from a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution, without the use of energy. This differs from other forms of passive transport like simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion, where solutes move instead of solvents.
What is the significance of osmosis in biology, especially in exams like vestibular?
-Osmosis is a crucial concept in biology, often tested in exams like vestibular. It involves understanding how cells behave in different solutions, such as hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic solutions. The movement of water across the cell membrane can greatly impact cell size and function, making it a frequent subject in exams.
What happens to an animal cell placed in a hypotonic solution?
-When an animal cell is placed in a hypotonic solution (where the concentration of solute outside the cell is lower than inside), water will enter the cell via osmosis. This can cause the cell to swell and eventually burst, as the water enters to balance the concentration.
How does an animal cell behave in an isotonic solution?
-In an isotonic solution, the concentration of solute inside and outside the animal cell is the same. Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate, so the cell remains stable and does not change in size.
What occurs when an animal cell is placed in a hypertonic solution?
-In a hypertonic solution (where the outside solute concentration is higher than inside the cell), water moves out of the animal cell to balance the concentration. This causes the cell to shrink or crenate as it loses water.
How do plant cells react to a hypotonic solution?
-In a hypotonic solution, plant cells absorb water through osmosis, causing the cell to become turgid or swollen. However, the cell wall prevents the cell from bursting, unlike animal cells. The cell becomes rigid and maintains its shape.
What happens to plant cells in a hypertonic solution?
-In a hypertonic solution, water moves out of plant cells, causing them to lose turgor pressure. This leads to a process called plasmolysis, where the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall as the cell shrinks.
What is the role of the cell wall in plant cells during osmosis?
-The cell wall in plant cells provides structural support and prevents the cell from bursting when it absorbs water in a hypotonic solution. It also limits the extent of plasmolysis when water moves out in a hypertonic solution, allowing the cell to maintain its shape.
What is the difference between osmotic pressure and turgor pressure?
-Osmotic pressure is the pressure exerted by a solvent, such as water, as it moves through a semi-permeable membrane to balance solute concentrations. Turgor pressure is the pressure exerted by the cell wall in plant cells to resist the entry of water, maintaining the cell's rigidity.
Why is it important to understand osmosis for vestibular exams?
-Osmosis is a frequent topic in vestibular exams because it is fundamental to understanding how cells interact with their environment. The behavior of cells in different osmotic environments is key to many biological processes and is frequently tested in various question formats.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

TRANSPORTE PASSIVO: Difusão Simples | Difusão Facilitada | Osmose
Proses Terjadinya Osmosis - Transport Pasif

Osmosis | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children

Osmose - Resumo

Osmosis | Osmolarity | Osmotic Equilibrium | Transport Across the Cell Membrane | Cell Physiology

Osmosis in Potato Strips - Bio Lab
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)