Permintaan Uang, Kebijakan Moneter, Fungsi LM dan Keseimbangan Pasar (Man 21B)
Summary
TLDRThis presentation covers key macroeconomic concepts including money demand, monetary policy, and money supply. The speaker explains Keynes' liquidity preference theory, highlighting the three motives for holding money: transaction, precautionary, and speculative. The role of monetary policy, tools like open market operations and reserve requirements, and their impact on economic stability are discussed. The LM curve is introduced as a framework to understand the equilibrium in the money market, where shifts in money supply and national income affect interest rates and economic activity. The script also highlights how monetary policies influence these dynamics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Keynes' liquidity preference theory explains the public's behavior regarding money demand, which is influenced by income, transactions, and speculative motives.
- 😀 There are three primary motives for holding money according to Keynes: transactions (based on daily needs), precautionary (for uncertain future events), and speculative (for investment in assets like stocks or bonds).
- 😀 The transaction motive for holding money is inelastic to interest rates and is driven by routine economic needs, such as food, drinks, and shopping.
- 😀 The precautionary motive relates to holding money to face uncertain future events. Factors influencing this include income level and personality type.
- 😀 The speculative motive is driven by the desire to earn profits by holding money to invest in financial assets. Lower interest rates encourage more speculation, and higher interest rates reduce it.
- 😀 Factors influencing the demand for money include real income (higher income leads to higher money demand), interest rates (higher rates reduce speculative demand), price levels (higher prices increase money demand), and credit facilities (advanced credit facilities increase money demand).
- 😀 Monetary policy is used to control the money supply to achieve desired economic outcomes like economic growth and low inflation, through tools like open market operations, reserve requirements, discount rate adjustments, and selective credit policies.
- 😀 The goal of monetary policy is to ensure internal and external equilibrium, with internal equilibrium being high employment and economic growth, and external equilibrium focusing on a stable balance of payments.
- 😀 The supply of money in modern economies is no longer determined by the amount of gold available but by the monetary authority (e.g., central banks). This includes both currency in circulation and deposits in the banking system.
- 😀 The LM curve shows the relationship between interest rates and national income where the money market is in equilibrium. Changes in income levels and interest rates shift the curve, affecting the overall economic balance.
Q & A
What is the concept of 'liquidity preference' as explained by Keynes?
-Liquidity preference refers to the demand for money, explaining people's behavior in holding cash. According to Keynes, it is influenced by three motives: transaction, precautionary, and speculative.
What are the three motives that influence people's demand for money according to Keynes?
-The three motives are: 1) Transaction motive, driven by routine needs like buying goods and services, 2) Precautionary motive, driven by the need to prepare for uncertain future events, and 3) Speculative motive, where individuals hold money to take advantage of future investment opportunities.
How does income level affect the demand for money?
-As national income increases, the demand for money for transaction purposes also rises because more economic activities lead to higher transactions that require more money.
What is the relationship between interest rates and money demand for speculation?
-When interest rates are high, people prefer saving rather than speculating, leading to a decreased demand for money for speculation. Conversely, low interest rates encourage speculation, increasing the demand for money.
What are some factors that influence the demand for money?
-Factors include real income (higher income leads to higher money demand), interest rates (higher rates reduce speculation demand), price levels (higher prices increase the need for money), and credit facilities (better access to credit can reduce cash demand).
What is the primary goal of monetary policy?
-The goal of monetary policy is to control the money supply in the economy to achieve desired economic outcomes such as low inflation, stable exchange rates, and sustained economic growth.
What are some types of monetary policy tools used by central banks?
-Central banks use tools like open market operations (buying/selling government securities), reserve requirements (mandating minimum reserves for banks), discount rates (setting interest rates for bank loans), selective credit policies, and moral suasion (encouraging banks and businesses to follow policies).
What is the difference between the classical and modern money supply theories?
-Classical money supply theory is based on the gold standard, where the supply of money is directly tied to the amount of gold available. In contrast, modern money supply theory involves central bank policies, with money supply controlled by the monetary authorities rather than physical commodities like gold.
How does a central bank's policy impact the LM curve?
-A central bank's monetary policy influences the LM curve by altering the money supply. When the money supply decreases, the LM curve shifts upward, increasing interest rates, while an increase in money supply shifts the LM curve downward, decreasing interest rates.
What does the LM curve represent in the context of the money market?
-The LM curve shows the relationship between the interest rate and the level of income that ensures equilibrium in the money market, where money supply equals money demand.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

PERMINTAAN DAN PENAWARAN UANG
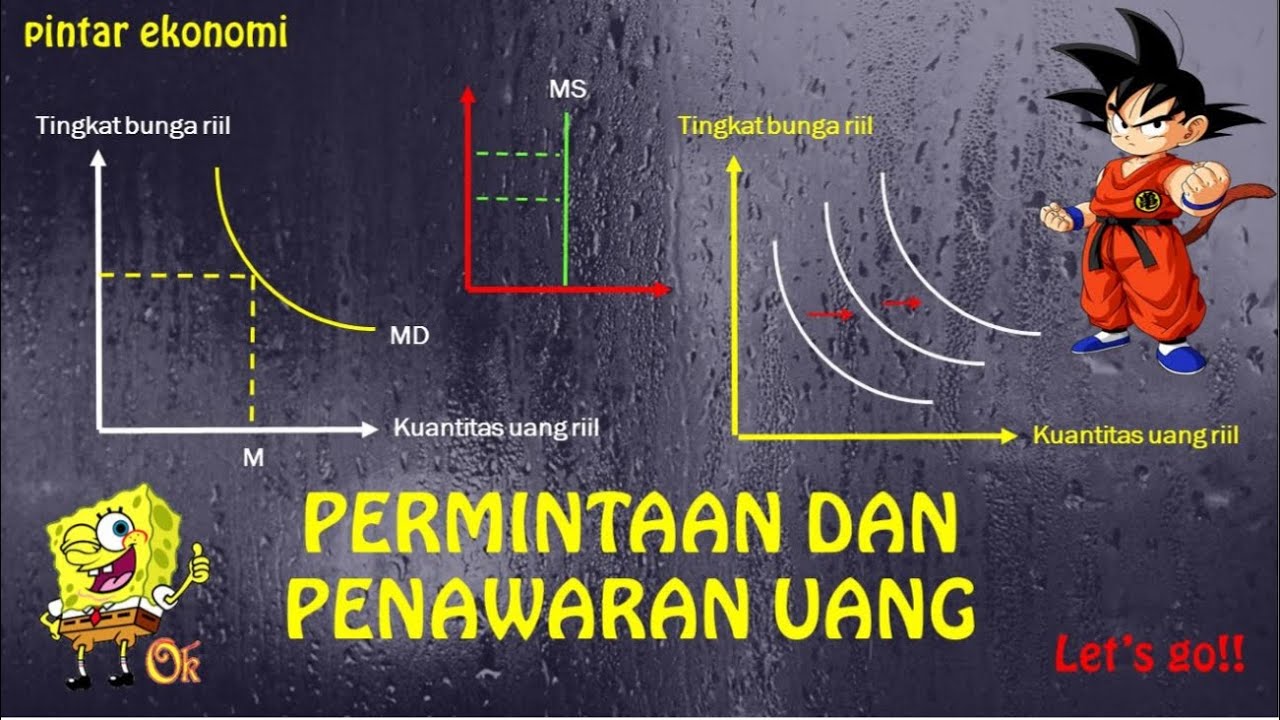
Permintaan dan Penawaran Uang | Ekonomi SMA Kelas 11

Monetary Policy: Introduction to the Money Market

The Money Market (1 of 2)- Macro Topic 4.5

A Permintaan dan Penawaran Uang

Monetary and fiscal policy | Aggregate demand and aggregate supply | Macroeconomics | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
