Monetary Policy: Introduction to the Money Market
Summary
TLDRThis video lesson introduces monetary policy, focusing on the money market, money supply, and money demand. The money market model illustrates how the total supply and demand for money determine the equilibrium interest rate. The supply of money, controlled by the central bank, is inelastic and depicted as a vertical line, while the demand for money inversely relates to interest rates and varies with national output levels. The lesson outlines contractionary and expansionary monetary policies, explaining how changes in the money supply impact consumption, investment, and overall economic activity. Future lessons will delve into specific monetary policy tools.
Takeaways
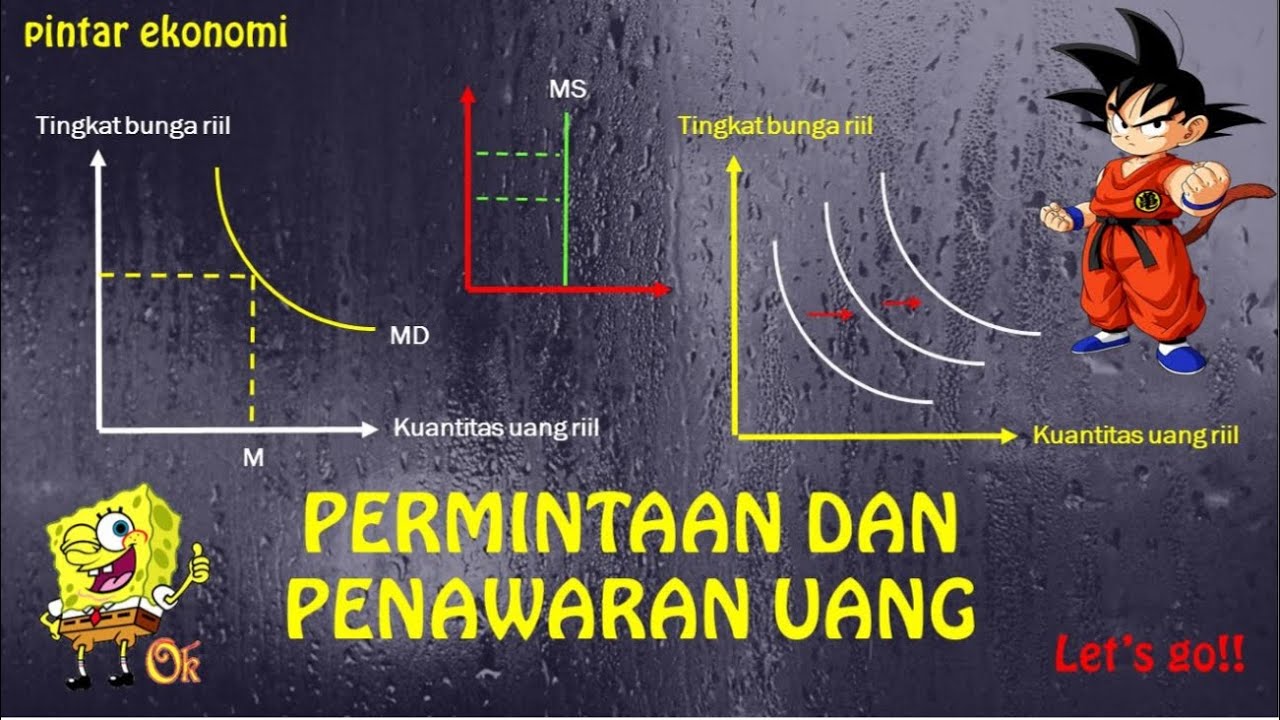
- 😀 The money market models the total supply and demand for liquid money in an economy.
- 💰 Money in this context includes cash, checkable deposits, and funds in savings accounts.
- 📉 The price of money is represented by the nominal interest rate, which reflects the opportunity cost of holding money.
- 🏦 The supply of money is determined by the central bank and is considered perfectly inelastic in the short term.
- 📊 The money supply curve is vertical and shifts left or right based on the central bank's monetary policy decisions.
- 📈 Demand for money is inversely related to the nominal interest rate; lower rates increase demand, while higher rates decrease it.
- 🌍 The demand for money also depends on the level of national output and income; higher output increases demand for money.
- 📉 At the intersection of money supply and demand, the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money are established.
- 🔼 Contractionary monetary policy reduces the money supply, raising interest rates and decreasing aggregate demand.
- 🔽 Expansionary monetary policy increases the money supply, lowering interest rates and encouraging higher aggregate demand.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of this video lesson?
-The video lesson focuses on monetary policy, which is a tool used by macroeconomic policymakers to manage the level of aggregate demand in an economy.
What does the money market model represent?
-The money market model represents the total supply and demand for money in a nation, including various forms of liquid money such as cash and checkable deposits.
How is the price of money defined in economic terms?
-In economic terms, the price of money is defined as the nominal interest rate, which represents the opportunity cost of holding onto money.
What determines the supply of money in an economy?
-The supply of money in an economy is determined by the nation's central bank, and it is not influenced by the interest rate.
How does the demand for money relate to interest rates?
-The demand for money is inversely related to interest rates; as interest rates decrease, the quantity of money demanded increases, and vice versa.
What additional factor affects the demand for money aside from interest rates?
-The level of output and income in the economy also affects the demand for money, with higher income levels leading to increased demand for money.
What happens to the equilibrium interest rate when the supply of money decreases?
-When the supply of money decreases, it leads to higher interest rates due to the increased scarcity of money in the banking system.
What is contractionary monetary policy?
-Contractionary monetary policy is a strategy used by central banks to raise interest rates by reducing the money supply, which in turn decreases aggregate demand.
What does expansionary monetary policy aim to achieve?
-Expansionary monetary policy aims to stimulate economic activity by increasing the money supply, which lowers interest rates and encourages consumption and investment.
How does economic growth affect the demand for money?
-Economic growth increases the demand for money, causing the demand curve to shift rightward, which can lead to upward pressure on interest rates.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Permintaan Uang, Kebijakan Moneter, Fungsi LM dan Keseimbangan Pasar (Man 21B)

KEBIJAKAN MONETER - Kebijakan Moneter dan Kebijakan Fiskal Part 1
Permintaan dan Penawaran Uang | Ekonomi SMA Kelas 11

The Money Market (1 of 2)- Macro Topic 4.5

PERMINTAAN DAN PENAWARAN UANG

Materi Makro M13 - Uang, Bank, dan Penawaran Uang (Bagian 3)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)