Kelainan Pada Manusia Akibat Mutasi - Biologi Kelas 12
Summary
TLDRIn this biology lesson, the teacher introduces the concept of mutations and their effects on humans, focusing on genetic disorders caused by changes in chromosome number and structure. The lesson covers various syndromes like Down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and Turner syndrome, explaining the genetic causes behind each disorder. The teacher also explains how mutations lead to conditions such as trisomy and monosomy, and discusses the structural changes that result in syndromes like Cri-du-chat and Wolff syndrome. The lesson aims to help students understand these genetic mutations and their implications for human health.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lesson begins with a prayer, followed by a greeting and check on students' well-being.
- 😀 The topic of the lesson is 'Mutations and Genetic Disorders,' focusing on human mutations.
- 😀 The learning objective is for students to be able to identify examples of genetic disorders caused by mutations.
- 😀 The script introduces the concept of a karyotype, which is a visual representation of human chromosomes.
- 😀 Human beings have 46 chromosomes, consisting of 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes, XX for females and XY for males.
- 😀 The lesson explains how to write karyotypes for humans, including correct notation for autosomes and sex chromosomes.
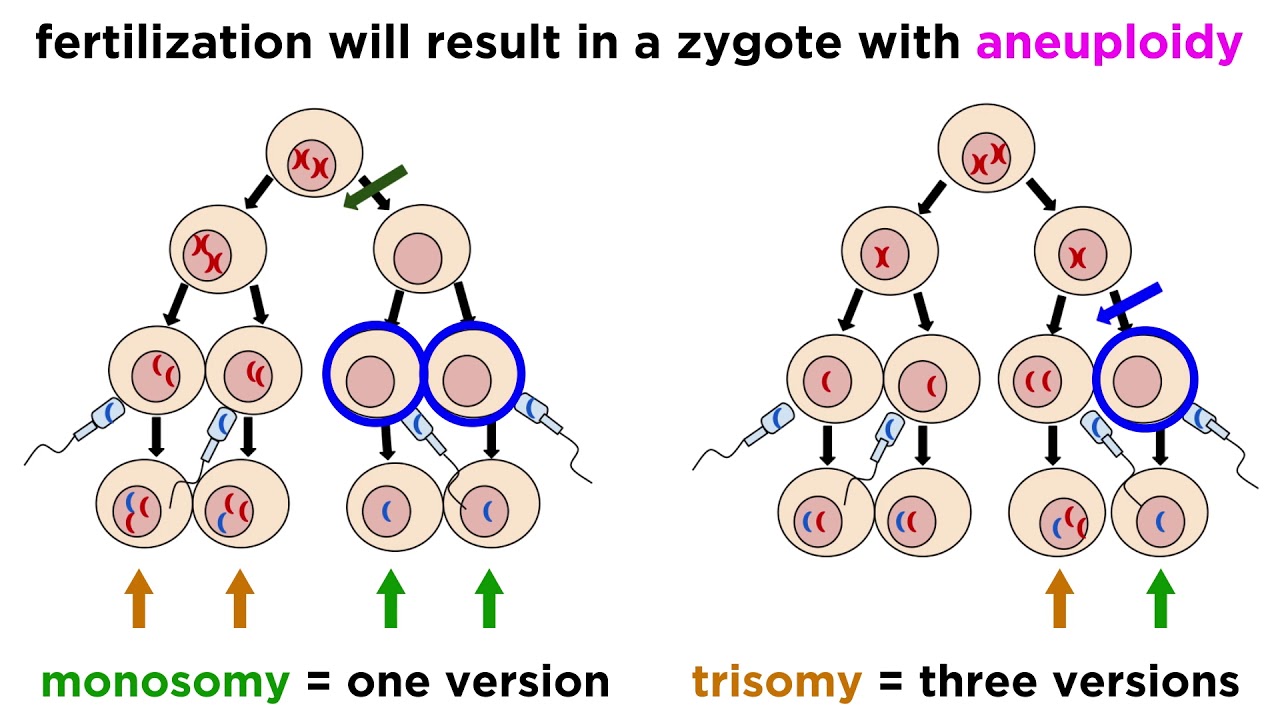
- 😀 Two main categories of mutations are discussed: changes in chromosome number (aneuploidy) and changes in chromosome structure.
- 😀 Nine examples of genetic disorders caused by mutations are presented: Down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, Jacob's syndrome, Turner syndrome, Patau syndrome, Edward's syndrome, Cri-du-chat syndrome, and Wolf syndrome.
- 😀 Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 21, where an extra chromosome 21 results in developmental and physical characteristics such as a small head and intellectual delays.
- 😀 Klinefelter syndrome is caused by an extra X chromosome in males (XXY), leading to symptoms like enlarged breasts, infertility, and low testosterone.
- 😀 Turner syndrome results from monosomy X (only one X chromosome in females), causing short stature, undeveloped ovaries, and infertility.
- 😀 Other conditions like Patau syndrome, Edward's syndrome, Cri-du-chat syndrome, and Wolf syndrome involve trisomy or deletions in specific chromosomes, leading to severe developmental issues.
Q & A
What is a karyotype, and how does it differentiate males and females?
-A karyotype is a photograph or diagram of an individual's chromosomes. It shows 46 chromosomes, arranged in 23 pairs. The differentiation between males and females is found in the gonosomes, where females have XX chromosomes and males have XY chromosomes.
What are the two main categories of mutations discussed in the script?
-The two main categories of mutations discussed are changes in the number of chromosomes (such as aneuploidy, trisomy, and monosomy) and changes in the structure of chromosomes (such as deletions).
What is Down Syndrome, and what causes it?
-Down Syndrome is a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21, leading to trisomy 21. It results in intellectual disability and physical features like a smaller head and upward-slanting eyes.
What is Klinefelter Syndrome, and how does it affect males?
-Klinefelter Syndrome occurs when a male has an extra X chromosome (XXY instead of XY). This condition results in symptoms like enlarged breasts, reduced testosterone levels, infertility, and sometimes cognitive delays.
What causes Jacob's Syndrome, and what are its main characteristics?
-Jacob's Syndrome is caused by an extra Y chromosome in males (XYY). Individuals with this syndrome tend to be taller than average, have an aggressive or antisocial personality, but are typically fertile.
What is Triple X Syndrome, and how does it affect females?
-Triple X Syndrome is a condition where a female has an extra X chromosome (XXX). It can lead to developmental delays, learning disabilities, irregular menstruation, and infertility, though some individuals may show few symptoms.
What is Turner Syndrome, and how does it affect females?
-Turner Syndrome occurs when a female has only one X chromosome (X0), leading to short stature, underdeveloped ovaries, and infertility. Affected individuals may also have a characteristic 'webbed' neck and other physical anomalies.
What is Patau Syndrome, and what are its primary symptoms?
-Patau Syndrome is caused by trisomy 13, where there is an extra copy of chromosome 13. It leads to severe developmental and physical abnormalities such as cleft lip and palate, small head size, and organ defects. The condition often results in early death.
What causes Edwards Syndrome, and what are its key characteristics?
-Edwards Syndrome is caused by trisomy 18, where an individual has three copies of chromosome 18. Symptoms include a small, elongated head, overlapping fingers, and developmental delays. Individuals with this syndrome often live only a few months.
What are Cri-du-chat and Wolf-Hirschhorn syndromes, and how do they differ?
-Both Cri-du-chat and Wolf-Hirschhorn syndromes are caused by deletions in chromosomes. Cri-du-chat results from a deletion on chromosome 5, while Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome is caused by a deletion on chromosome 4. Both syndromes are associated with intellectual disability, but they have distinct physical features like a cat-like cry in Cri-du-chat and a prominent nose in Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

MUTASI KROMOSOM

Aula Biologia - Mutações Gênicas - Origens e Consequências para o Enem e Vestibulares - STOODI
Alteration of Chromosome Number and Structure

Genetics - Mutations and their Types - Lesson 20 | Don't Memorise

GenBio1 Lesson 5.3: Genetics and Cell-Cycle Related Illnesses and Disorders

Grade 10 SCIENCE | Quarter 3 Module 4C | Mutations
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
