Menghidupkan Kembali Hewan yang Sudah Mati Lewat Kloning | #PlanetA
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the groundbreaking science of cloning endangered species to preserve biodiversity. It highlights the successful cloning of a wild horse, the challenges faced in cloning extinct animals, and the controversial nature of such experiments. Researchers use genetic material to revive species that have disappeared, potentially reversing biodiversity loss and enhancing ecosystem stability. The video delves into the ethical concerns, the technological advancements, and the global efforts to conserve genetic diversity, emphasizing the urgency of saving species from extinction due to environmental threats and human activity.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cloning technology has been successfully used to revive extinct species, such as the wild horse *Gold*, offering hope for biodiversity restoration.
- 😀 The process of cloning involves using frozen genetic material from extinct species and combining it with domestic animals for reproduction.
- 😀 Cloning can help preserve species at risk of extinction by maintaining genetic diversity and supporting stronger populations.
- 😀 The first successful cloning of the wild horse is a major breakthrough, though cloning still faces challenges, such as high failure rates and short-lived clones.
- 😀 The loss of biodiversity is a growing crisis, with around 60% of species disappearing since 1970 and around 150 species being lost every day.
- 😀 The preservation of genetic material from endangered species is becoming more important, allowing for future cloning or restoration efforts.
- 😀 Cloning is controversial, with concerns over the ethical implications and potential ecological risks of creating genetically identical animals.
- 😀 Efforts to preserve DNA and create clones are being conducted worldwide, from Western countries to India, China, and the Amazon region.
- 😀 While cloning shows promise, it cannot replace the importance of protecting existing species and ecosystems from further decline.
- 😀 The future of cloning will likely focus on both the revival of extinct species and the genetic preservation of currently endangered animals.
Q & A
What is the significance of the cloned wild horse, Gold?
-Gold, the cloned wild horse, is significant because it represents a major breakthrough in cloning technology. It is the first successful clone of a wild horse, produced through genetic cloning, which could help preserve biodiversity and slow the extinction of endangered species.
How does cloning contribute to biodiversity conservation?
-Cloning can contribute to biodiversity conservation by reintroducing genetic diversity into populations of endangered species. By using genetic samples that would otherwise be lost, cloning can help strengthen populations and ensure their survival against threats like disease, inbreeding, and environmental changes.
What are the challenges of cloning endangered species?
-Challenges include the difficulty of obtaining genetic material from endangered species, the complexity of successful cloning procedures, and the risk of low survival rates for clones. Additionally, cloned animals may face health problems, and their long-term impact on ecosystems is still uncertain.
What other species, besides the wild horse, has been attempted for cloning?
-Besides the wild horse, cloning attempts have been made with the extinct Iberian ibex, a mountain goat. However, this cloning effort was unsuccessful, with the cloned animal dying shortly after birth.
What is the role of genetic banking in species preservation?
-Genetic banking plays a crucial role in species preservation by storing genetic material from endangered species. This material can be used for future cloning or breeding efforts, helping to protect genetic diversity and prevent the extinction of species.
How can cloning help in the fight against climate change?
-Cloning can help species adapt to climate change by maintaining healthy, genetically diverse populations that are more resilient to environmental shifts. It could also help restore extinct species that played important ecological roles, potentially contributing to ecosystem stability.
What are the ethical concerns surrounding cloning technology?
-Ethical concerns include the potential for humans to overstep natural boundaries, creating clones for commercial or recreational purposes rather than conservation. Additionally, there is worry that cloning could disrupt natural ecosystems or result in cloned animals that suffer from health problems.
What is the purpose of genetic editing in conservation efforts?
-Genetic editing is used to enhance the genetic resilience of endangered species by correcting harmful mutations or improving traits that are critical for survival. This technology can also aid in preserving genetic diversity and adapting species to environmental challenges.
How many species have been successfully cloned so far?
-As of now, very few species have been successfully cloned, and even fewer have survived long-term. The success rate remains low, and only a small fraction of cloned animals, such as certain domesticated species, have shown long-term viability.
What is the main criticism of cloning as a method for species conservation?
-The main criticism of cloning for species conservation is its high cost and uncertain long-term effects. Critics argue that efforts should instead focus on protecting existing species and their natural habitats, rather than relying on cloning as a last resort.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Could cloning help save biodiversity?

Conservation and the race to save biodiversity

What is an endangered species?
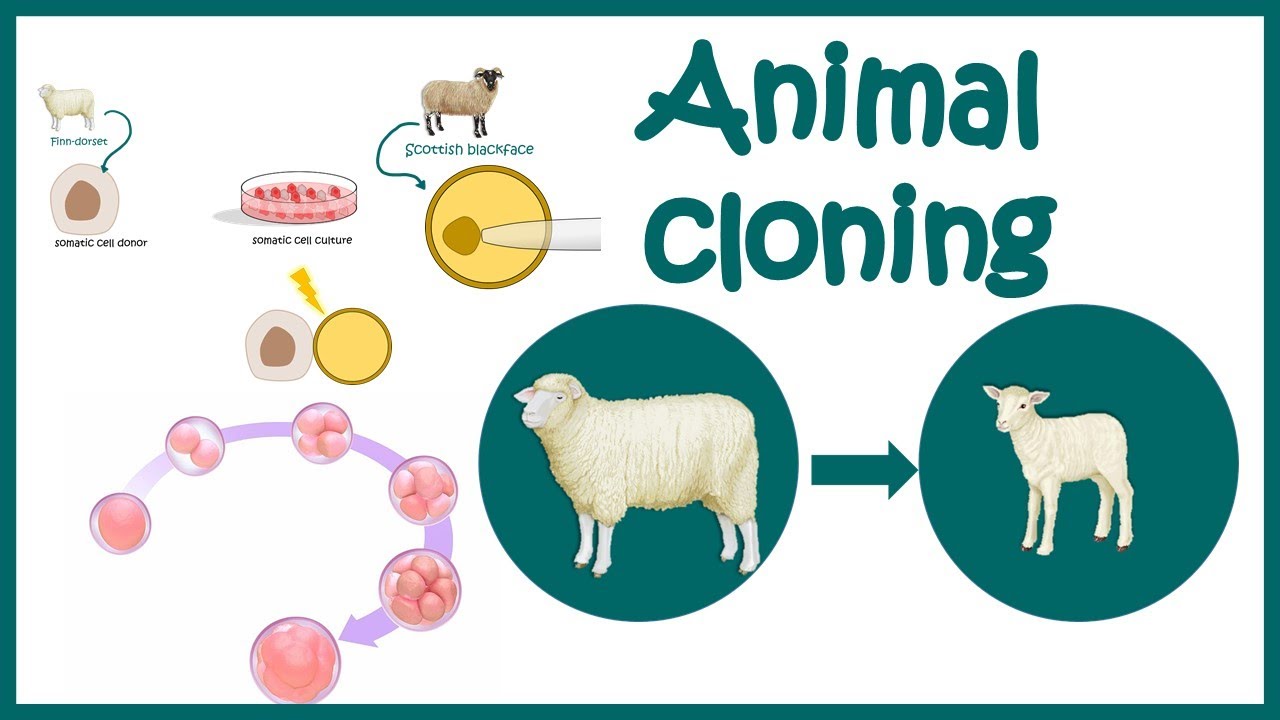
Animal cloning : Story of Dolly the sheep | The world of animal cloning | Animated biology

Biodiversity and Evolution | Population Distribution | Causes of Extinction

Endangered species and Extinct species | Endangered species | Extinct species | Info Biodiversity
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
