pembuatan hormon insulin sintetis / buatan - bioteknologi modern materi sma biologi kelas 12
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the modern biotechnology process used to create synthetic insulin for diabetes patients. It covers the steps of genetic engineering, including DNA recombination, gene isolation, plasmid manipulation, and bacterial transformation. The process is broken down into stages such as isolating the target gene, ligating it with a plasmid, transforming bacteria, and screening for successful recombinant colonies. The video also explains how synthetic insulin is harvested and purified for medical use. The process relies on advanced biotechnology methods to address the needs of diabetes patients.
Takeaways
- 😀 Insulin plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels, and its production is vital for people with diabetes.
- 😀 People with Type 1 diabetes cannot produce insulin naturally, requiring them to inject synthetic insulin.
- 😀 The process of creating synthetic insulin involves modern biotechnology, specifically genetic engineering and recombinant DNA technology.
- 😀 Key components required for recombinant DNA include a target gene, restriction enzymes, ligase enzymes, a vector (plasmid), and a host cell (bacteria).
- 😀 The first step in recombinant DNA technology is isolating the target gene (the insulin gene), which is taken from human mRNA rather than DNA to avoid non-coding sequences (introns).
- 😀 The mRNA is converted into cDNA using reverse transcriptase, which is then used for further amplification through PCR.
- 😀 Plasmids are isolated from bacteria and then cut using restriction enzymes, which allows the insertion of the target gene.
- 😀 The ligase enzyme is used to join the target gene (cDNA) with the plasmid to create recombinant plasmids.
- 😀 The recombinant plasmids are transformed into bacterial cells, which are then cultured to multiply.
- 😀 A blue-white screening method is used to identify which bacterial colonies have successfully taken up the recombinant plasmids, with successful colonies turning white due to the disruption of the lacZ gene.
- 😀 Once the correct bacterial colonies are identified, they are cultured to produce insulin, which is then harvested, purified, and packaged for use in diabetes treatment.
Q & A
What is synthetic insulin, and why is it needed?
-Synthetic insulin is a lab-produced form of insulin used to treat people with diabetes, especially those with Type 1 diabetes. In Type 1 diabetes, the pancreas cannot produce insulin, so synthetic insulin is injected to help regulate blood sugar levels.
How does insulin work in the body?
-Insulin helps regulate blood sugar by promoting the uptake of glucose into cells for energy. It lowers the level of glucose in the blood, which is essential for maintaining balance and preventing high blood sugar (hyperglycemia).
Why can't Type 1 diabetes patients produce insulin?
-In Type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, known as beta cells. As a result, the body is unable to produce insulin naturally.
What is recombinant DNA technology, and how is it used to produce insulin?
-Recombinant DNA technology involves combining DNA from different sources to create new genetic combinations. In insulin production, the gene responsible for insulin production is isolated, inserted into bacterial plasmids, and transformed into bacteria. The bacteria then produce insulin, which can be harvested and purified for use.
Why is mRNA used to create synthetic insulin?
-mRNA is used because it is a direct copy of the gene that codes for insulin. mRNA is more stable and easier to manipulate in the laboratory than DNA. Once isolated, mRNA is converted into cDNA (complementary DNA) to be inserted into bacterial plasmids.
What is the role of plasmids in recombinant DNA technology?
-Plasmids are small, circular DNA molecules found in bacteria. In recombinant DNA technology, plasmids serve as vectors to carry the gene of interest (such as the insulin gene) into bacterial cells, where it can be expressed and produce the desired protein (insulin).
What is the purpose of using restriction enzymes in the process?
-Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA at specific sequences. In the insulin production process, they cut both the plasmid and the target gene to create sticky ends that allow for the insertion of the insulin gene into the plasmid.
What is blue-white colony screening, and how does it help identify successful DNA recombination?
-Blue-white colony screening is a method used to identify bacterial colonies that contain the recombinant plasmid. The presence of the insulin gene disrupts the lacZ gene in the plasmid, preventing the production of a blue-colored product. Colonies that are white indicate successful recombination, as they contain the insulin gene.
What happens after the bacteria are transformed with the recombinant plasmid?
-After the bacteria are transformed with the recombinant plasmid, they are cultured in a growth medium. The bacteria reproduce, and as they do, they produce insulin. The insulin is then harvested, purified, and prepared for use in medical treatments.
How is the synthetic insulin purified before it is used?
-The synthetic insulin is purified through a series of steps, including filtration and chromatography, to remove any impurities and ensure that the insulin is of the highest quality before it is packaged and administered to patients.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

INOVASI TEKNOLOGI BIOLOGI | FASE A DAN B | KELAS X SMA / MA | KURIKULUM MERDEKA

Hibridoma dan Teknologi Plasmid ( Bioteknologi Modern )

BIOTEKNOLOGI MODERN

How synthetic Insulin is made using Recombinant DNA Technology From Bacteria
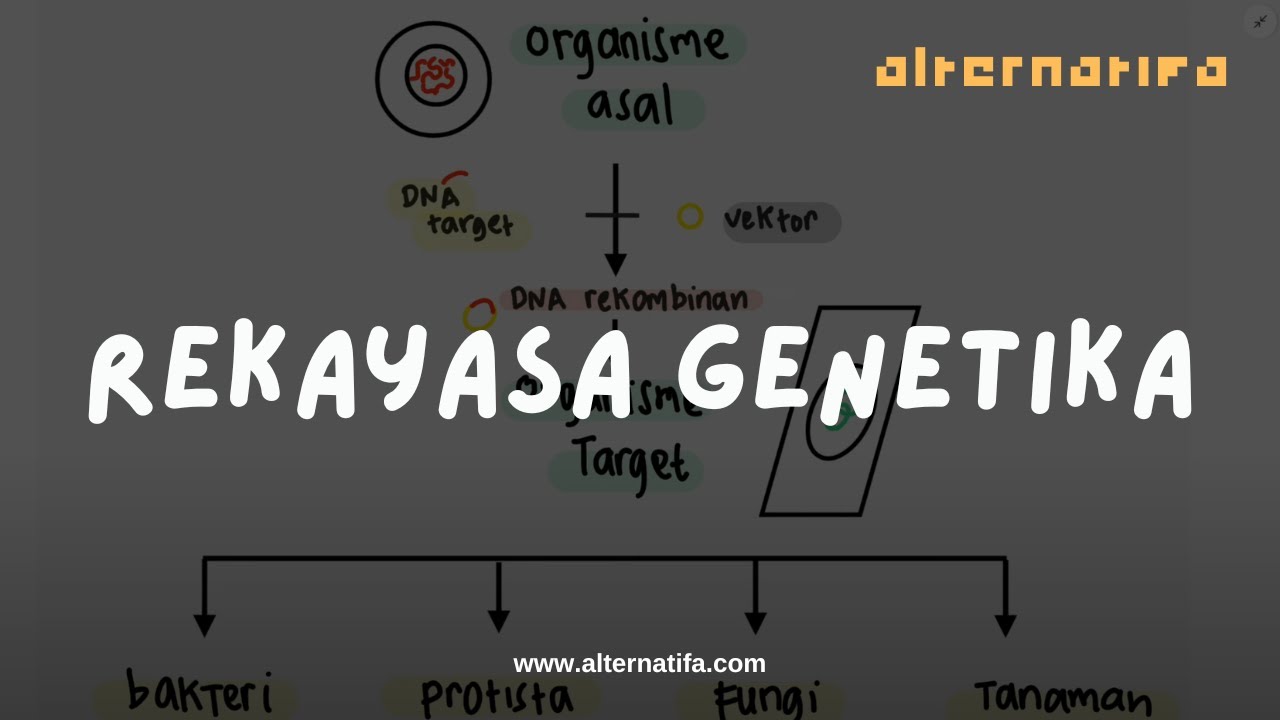
Bioteknologi: Rekayasa Genetika | Biologi SMA | Alternatifa
Production of Insulin Throuhg Genetic Engineering
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
