INOVASI TEKNOLOGI BIOLOGI | FASE A DAN B | KELAS X SMA / MA | KURIKULUM MERDEKA
Summary
TLDRThis educational video introduces 10th-grade students to biotechnology, explaining its principles and distinctions between conventional and modern biotechnology. The video covers the definition of biotechnology, its historical use in food production (e.g., fermentation), and its evolution with advancements in genetic engineering. It highlights the differences between conventional biotechnology, which uses simple techniques like fermentation, and modern biotechnology, which utilizes advanced genetic engineering, sterility, and more efficient methods to create products like genetically modified organisms and synthetic insulin. The video concludes with a preview of the next topic on the use of microorganisms in biotechnology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Biotech is the application of scientific principles to process materials using biological agents to create goods and services for human benefit.
- 😀 Biotechnology is derived from the Greek words 'bios' (life), 'technos' (application), and 'logos' (knowledge).
- 😀 Biotechnology plays a crucial role in managing both organic and inorganic materials with the help of living organisms like microorganisms, animals, and plants.
- 😀 Living organisms are used in biotechnology because they are readily available in nature, can be genetically modified, and can reproduce offspring with consistent traits.
- 😀 Conventional biotechnology dates back to early human civilizations and involved simple techniques like food fermentation.
- 😀 Modern biotechnology advanced significantly after the discovery of DNA structure and function, leading to genetic engineering techniques.
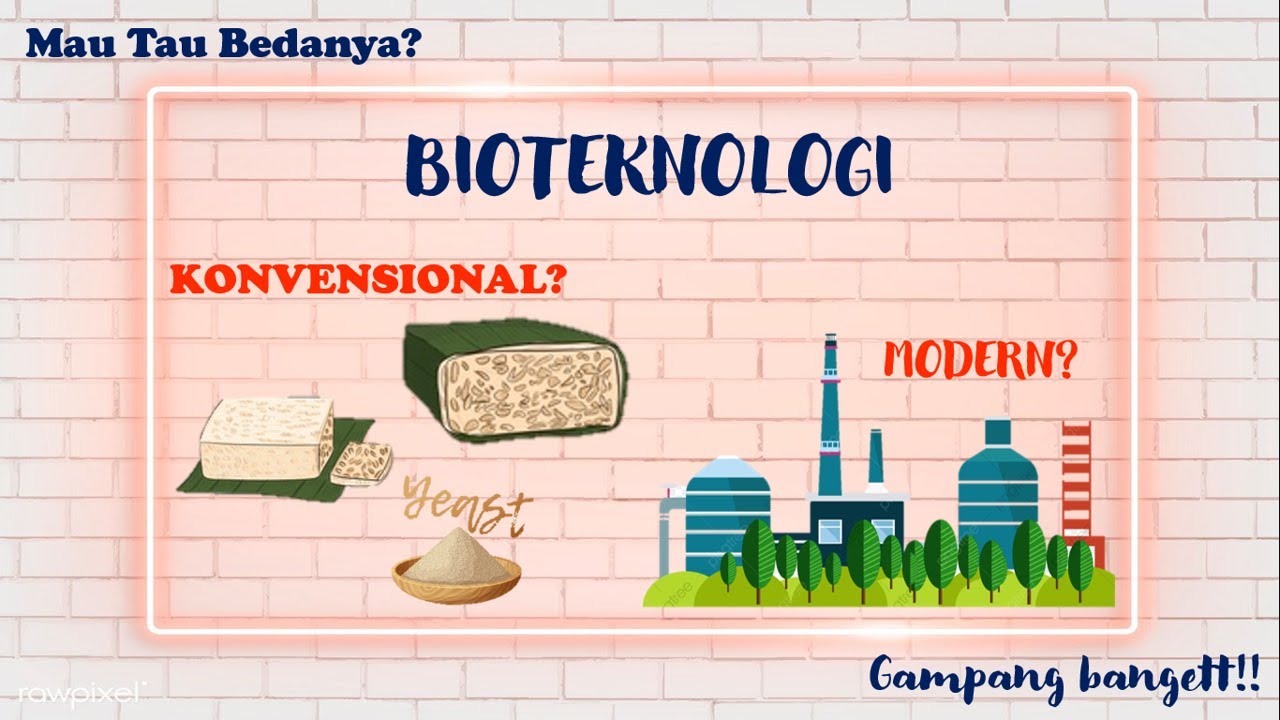
- 😀 The main difference between conventional and modern biotechnology lies in the tools and methods used: conventional relies on basic techniques, while modern uses advanced equipment and genetic modification.
- 😀 Conventional biotechnology produces fewer results with less consistency, while modern biotechnology ensures sterilized environments, faster production, and standardized quality.
- 😀 Examples of conventional biotechnology include the production of tempe, tape, yogurt, cheese, and nata de coco.
- 😀 Modern biotechnology includes innovations like transgenic organisms, cloned animals, and the production of synthetic insulin.
- 😀 The discovery of DNA's structure significantly impacted biotechnology, leading to the development of new and more advanced biotechnological products.
Q & A
What is biotechnology?
-Biotechnology is a field of science that applies scientific principles and engineering techniques to process materials with the help of biological agents, such as microorganisms, cells, animals, and plants, to improve products and services for human needs.
What are the key components involved in the production of biotechnological products?
-The key components include inputs such as raw materials, microorganisms, or living cells, as well as scientific principles that guide the process of biotechnology to produce goods and services.
Why are living organisms used in biotechnology?
-Living organisms are used because they are easily available, can be modified through genetic engineering techniques, and can produce products that are beneficial to humans. Additionally, their characteristics can be passed down to future generations.
What is the difference between conventional and modern biotechnology?
-Conventional biotechnology involves simple methods, such as fermentation, and uses microorganisms directly or through chemical compounds. Modern biotechnology, on the other hand, uses advanced techniques, such as genetic engineering, and employs genetically modified microorganisms, animals, or plants.
When did biotechnology begin to be practiced, and what were its early uses?
-Biotechnology began with the discovery of food fermentation processes, which were used in the production of food products like tempeh, yogurt, and bread. This practice dates back to ancient civilizations.
What triggered the advancement of modern biotechnology?
-The advancement of modern biotechnology was triggered by the discovery of the structure and function of DNA, which enabled the development of genetic engineering techniques and the creation of more sophisticated biotechnological products.
How does conventional biotechnology differ in terms of sterilization and product quality compared to modern biotechnology?
-Conventional biotechnology tends to have less sterile conditions, produces smaller quantities, and may have inconsistent quality. Modern biotechnology, however, is highly sterilized, can produce larger quantities in shorter times, and ensures standardized quality.
Can you provide examples of conventional biotechnology products?
-Examples of conventional biotechnology products include tempeh, tape, bread, yogurt, cheese, and nata de coco.
What are some examples of products from modern biotechnology?
-Examples of modern biotechnology products include cultured tissues, transgenic organisms, cloned animals, and synthetic insulin.
What role does genetic engineering play in modern biotechnology?
-Genetic engineering plays a crucial role in modern biotechnology by enabling the modification of the genetic makeup of organisms, which can result in the creation of new, more efficient products and improvements in existing processes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)