Biomolecules | Classification of Biomolecules | Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic Acids
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Teacher Issa Maria introduces biomolecules, exploring their four main categories: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. She explains their structures, functions, and roles in sustaining life, such as energy provision, cellular support, and genetic information storage. The video covers essential concepts like monomers, polymers, and the classification of each biomolecule. Through clear explanations, viewers gain insight into how these organic compounds are integral to cellular processes and overall health. Perfect for students and anyone curious about the foundational elements of life.
Takeaways
- 😀 Biomolecules are organic compounds that are produced by cells and living organisms and are essential for life.
- 😀 Biomolecules are classified into four main categories: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
- 😀 Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body, providing 4 calories per gram.
- 😀 Proteins are made up of amino acids and serve various functions such as building tissues, catalyzing reactions, and transporting molecules.
- 😀 Lipids, including fats and oils, are hydrophobic molecules that store energy, protect organs, and act as messengers in the body.
- 😀 Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, carry genetic information and are essential for protein synthesis and inheritance.
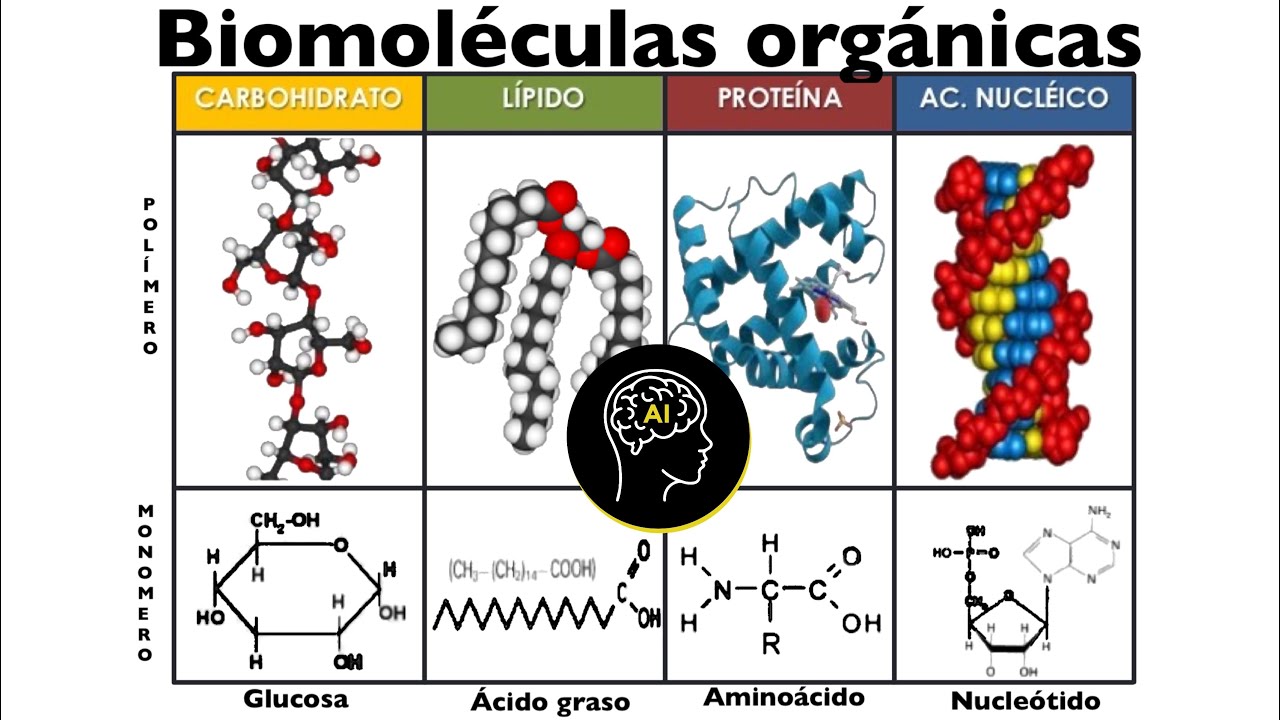
- 😀 Monomers are the building blocks of biomolecules, with examples like glucose for carbohydrates, amino acids for proteins, and nucleotides for nucleic acids.
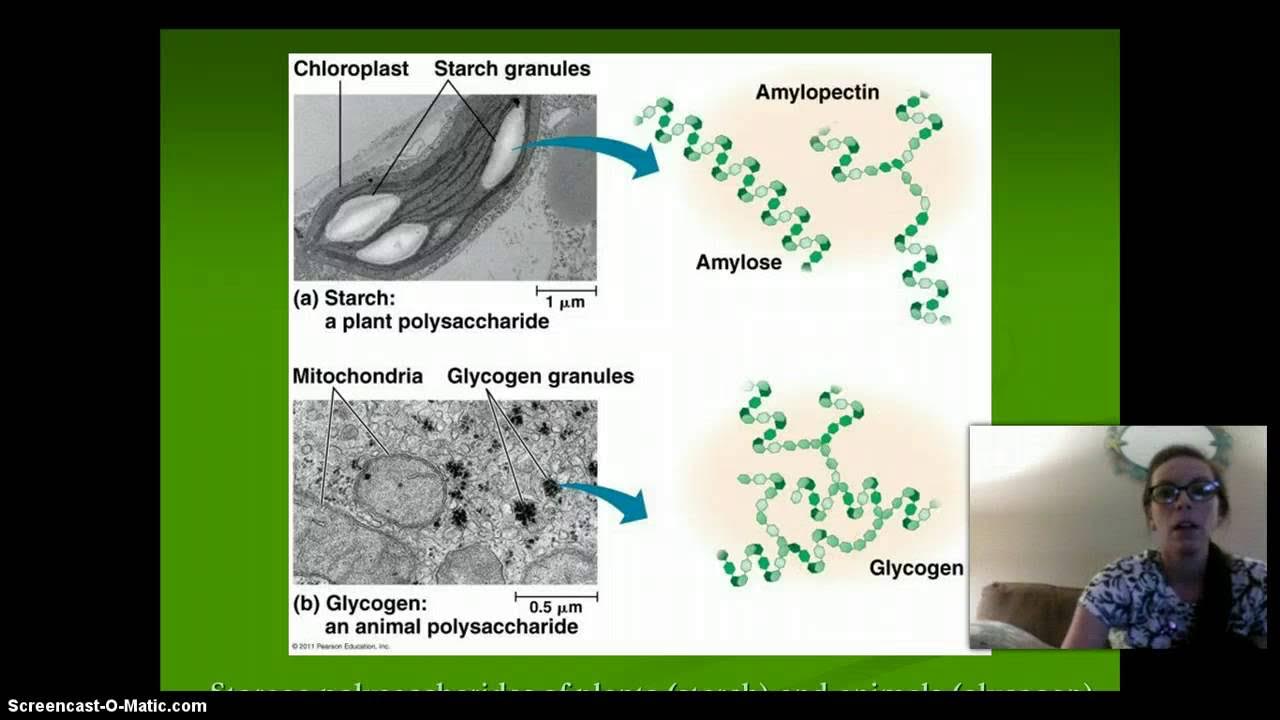
- 😀 Carbohydrates can be classified into monosaccharides (simple sugars), disaccharides (two monosaccharides), and polysaccharides (complex carbs like starch and glycogen).
- 😀 Proteins are composed of 20 amino acids, 9 of which are essential and must be obtained through diet.
- 😀 Lipids include fatty acids, triglycerides, steroids, and waxes, and they help store energy, protect organs, and maintain cell membranes.
- 😀 Nucleotides are the monomers that make up nucleic acids and consist of a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Q & A
What are biomolecules?
-Biomolecules, also known as biological molecules, are substances produced by cells and living organisms. They play vital roles in various biological functions and are typically classified into four major categories: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Why is carbon important in biomolecules?
-Carbon is essential in biomolecules because it forms strong covalent bonds with other elements, making it highly versatile and the backbone of organic compounds. This versatility is critical for the structure and function of biomolecules in living organisms.
What is the difference between monomers and polymers?
-Monomers are the smallest functional units of biomolecules, while polymers are larger molecules formed by linking multiple monomers together. For example, amino acids are monomers that form proteins, and nucleotides are monomers that form nucleic acids.
What are the main categories of biomolecules?
-The four main categories of biomolecules are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Each category has distinct structures and functions crucial for various biological processes.
What are carbohydrates and what functions do they serve in the body?
-Carbohydrates, also known as saccharides or carbs, provide energy for the body. They are broken down into glucose, which is the primary energy source for the brain and muscles. Carbohydrates also help in energy storage, nerve tissue regulation, and preventing constipation.
What are the types of carbohydrates?
-Carbohydrates are classified into three types: monosaccharides (simple sugars like glucose), disaccharides (two monosaccharides combined, like sucrose), and polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates, like starch and glycogen).
What is the role of proteins in the body?
-Proteins play a critical role in the body by providing structural support (e.g., hair, nails), acting as enzymes to catalyze biochemical reactions, transporting molecules, and supporting immune function. They are made of amino acids and are involved in nearly every cellular process.
What are essential and non-essential amino acids?
-Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through diet, while non-essential amino acids are produced by the body. There are 9 essential amino acids, and 11 non-essential amino acids, some of which are conditional and needed in specific circumstances.
What are lipids and what roles do they play in the body?
-Lipids are organic molecules that are largely hydrophobic (water-repelling). They are used by the body for energy storage, forming cell membranes, acting as chemical messengers (hormones), and protecting internal organs with insulation.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids?
-Saturated fatty acids lack carbon-carbon double bonds and are typically solid at room temperature. Unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more double bonds and are usually liquid at room temperature. Saturated fats are found in animal products, while unsaturated fats are more common in plant-based oils.
What are nucleic acids and why are they important?
-Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, are essential biomolecules that store and transmit genetic information. DNA contains the blueprint for the synthesis of proteins, while RNA helps in protein synthesis and gene expression.
How do nucleic acids store genetic information?
-Nucleic acids store genetic information through sequences of nucleotides. DNA encodes genetic instructions for protein production, while RNA serves as a template for protein synthesis. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Beginners Guide to MACROMOLECULES
AP Biology Macromolecules Carbs, Lipids and DNA
Biomoléculas presentes en células (orgánicas): carbohidratos, lípidos, proteínas y ácidos nucleicos

La Química de los Alimentos: Cómo los Compuestos Influyen en tu Nutrición y Salud

Biomolecules (Older Video 2016)

Biomoléculas (atualizado em 2023)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
