Sistem Pernapasan Manusia - Biologi kelas 11
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the human respiratory system, covering key topics like the structure and function of respiratory organs, the process of inhalation and exhalation, and the exchange of gases in the alveoli. It also highlights the different lung volumes, including tidal and reserve volumes, and introduces respiratory disorders such as asthma and tuberculosis. The video includes interactive questions to reinforce learning and provides a comprehensive understanding of how our body breathes, processes oxygen, and eliminates carbon dioxide.
Takeaways
- 😀 The human respiratory system consists of a series of organs and passages that allow air to flow into the body, starting from the nose and ending in the alveoli, where gas exchange takes place.
- 😀 The nose plays a key role in filtering, warming, and humidifying the air before it reaches the lungs, with the help of nose hairs and mucus membranes.
- 😀 The respiratory path includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx (voice box), trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli, with each segment playing a specific role in the process of breathing.
- 😀 In the alveoli, oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide through diffusion, and oxygen is then transported via the bloodstream to the cells throughout the body.
- 😀 Breathing consists of two main types of respiration: external respiration (gas exchange between alveoli and capillaries) and internal respiration (gas exchange between capillaries and body cells).
- 😀 Oxygen is transported in the blood, primarily bound to hemoglobin, while carbon dioxide is transported in different forms including as bicarbonate ions and carbaminohemoglobin.
- 😀 Breathing can be categorized into chest (thoracic) and abdominal (diaphragmatic) breathing. Chest breathing involves contraction of intercostal muscles, expanding the chest cavity, while abdominal breathing involves diaphragm movement.
- 😀 Lung volumes include tidal volume (the amount of air we breathe in and out during normal breathing), inspiratory reserve volume (extra air inhaled after normal inhalation), and expiratory reserve volume (extra air exhaled after normal exhalation).
- 😀 Vital capacity is the maximum amount of air that can be moved in and out of the lungs, and total lung capacity includes both vital capacity and residual volume (the air left in the lungs after exhalation).
- 😀 Respiratory disorders like asthma, tuberculosis, bronchitis, and emphysema can affect the proper functioning of the respiratory system, often due to infections, allergens, or environmental factors like pollution and smoking.
Q & A
What is the main organ responsible for respiration in humans?
-The main organ responsible for respiration in humans is the lungs. They are protected by a thin membrane called pleura.
What are the key functions of the hair and mucous membranes in the nasal cavity?
-The hair in the nasal cavity helps filter dust and other particles from the air, while the mucous membranes warm, moisten, and protect the air by trapping microbes.
How does the pharynx contribute to the respiratory process?
-The pharynx is a junction between the respiratory and digestive systems. It helps direct air into the larynx and prevents food from entering the respiratory tract by pushing the epiglottis to close during swallowing.
What is the role of the trachea in the respiratory system?
-The trachea is a tube that directs air into the lungs. It is made of flexible cartilage rings and is lined with cilia and mucous membranes that filter the air, trapping foreign particles.
Where does the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occur in the respiratory system?
-The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs in the alveoli, tiny air sacs in the lungs that are surrounded by capillaries.
What are the two types of respiration, and where do they occur?
-There are two types of respiration: external respiration, which occurs between the alveoli and the capillaries, and internal respiration, which takes place between the capillaries and the body’s cells.
How is oxygen transported in the blood?
-Around 97% of oxygen is transported by hemoglobin in the red blood cells, forming oxyhemoglobin. The rest is carried by the plasma.
What is the role of diaphragm and intercostal muscles in the process of breathing?
-During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward while the intercostal muscles between the ribs contract, causing the rib cage to expand, increasing the lung volume and allowing air to enter the lungs. During expiration, these muscles relax, and the lung volume decreases, pushing air out.
What are some of the main diseases that can affect the respiratory system?
-Common respiratory diseases include asthma (due to airway contraction), tuberculosis (which affects the alveoli), bronchiitis (inflammation of the bronchi), and pneumonia (inflammation of the lungs caused by infection).
What is emphysema and what causes it?
-Emphysema is a condition where the alveoli lose elasticity, causing the lungs to over-expand. It is often caused by smoking, air pollution, or genetic factors and leads to the trapping of carbon dioxide in the lungs.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Alat Peraga Sistem Pernapasan Manusia

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman IPA Kelas 8 Bab 2: Sistem Pernapasan

Quiz on Respiratory System || Interactive MCQ on Respiratory System

Struktur Dan Fungsi Sistem Pernapasan Manusia : Organ Pernapasan Manusia

BAB 2 Struktur dan Fungsi Tubuh Makhluk Hidup || Sistem Pernapasan - Kelas 8 Kurikulum Merdeka
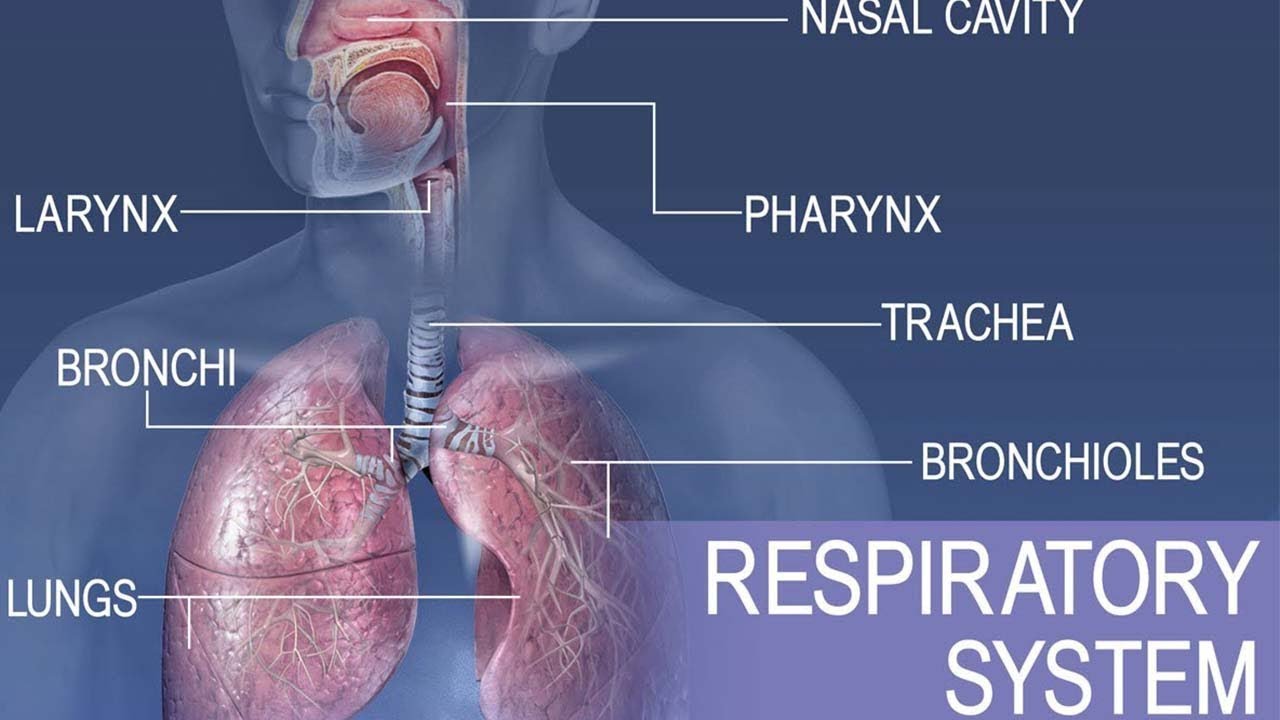
Anatomy and physiology of Respiratory system
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
