How Were The Elements Made?
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the origin of elements, beginning with the Big Bang and the formation of the first protons that led to hydrogen, helium, and tiny amounts of lithium. It delves into stellar nucleosynthesis, where stars fuse elements until iron is formed, marking a limit. When massive stars explode in supernovae, they produce heavier elements up to plutonium. Elements like lithium, beryllium, and boron are created by cosmic ray spallation. Finally, elements beyond plutonium are man-made. The video highlights how all these processes create the atoms that make up the universe and everything within it.
Takeaways
- 😀 The periodic table of elements represents the building blocks of matter, defined by the number of protons in an atom's nucleus.
- 😀 Atoms consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons define the element, while neutrons determine isotope variation.
- 😀 Isotopes are variations of elements with differing numbers of neutrons, and can be stable or unstable.
- 😀 Some nuclei are stable, while others spontaneously decay or require external energy to change into different elements or isotopes.
- 😀 The origins of elements trace back to the Big Bang, where the first protons and elements like hydrogen and helium were created.
- 😀 Early stars synthesized elements by fusing hydrogen into helium. Larger stars fused heavier elements until they reached iron.
- 😀 Iron-56 is the most stable nucleus, and when stars reach this point, they can no longer fuse elements to produce energy.
- 😀 When a star with sufficient mass exhausts its hydrogen, it collapses and explodes in a supernova, producing heavy elements.
- 😀 Supernova explosions create heavy elements (past iron) through neutron capture and decay, spreading these atoms throughout the universe.
- 😀 Elements like lithium, beryllium, and boron are mostly formed through cosmic ray spallation rather than stellar fusion.
- 😀 Elements heavier than plutonium are typically man-made in laboratories, with plutonium itself also being synthetically created.
Q & A
What defines an element?
-An element is defined by the number of protons in the nucleus of its atoms. This number is called the atomic number.
What are isotopes?
-Isotopes are variations of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, which affects their stability.
How does the stability of an atom's nucleus affect its behavior?
-Some atomic nuclei are stable, while others are unstable. Stable nuclei don’t spontaneously change, whereas unstable nuclei decay or transform into other elements or isotopes.
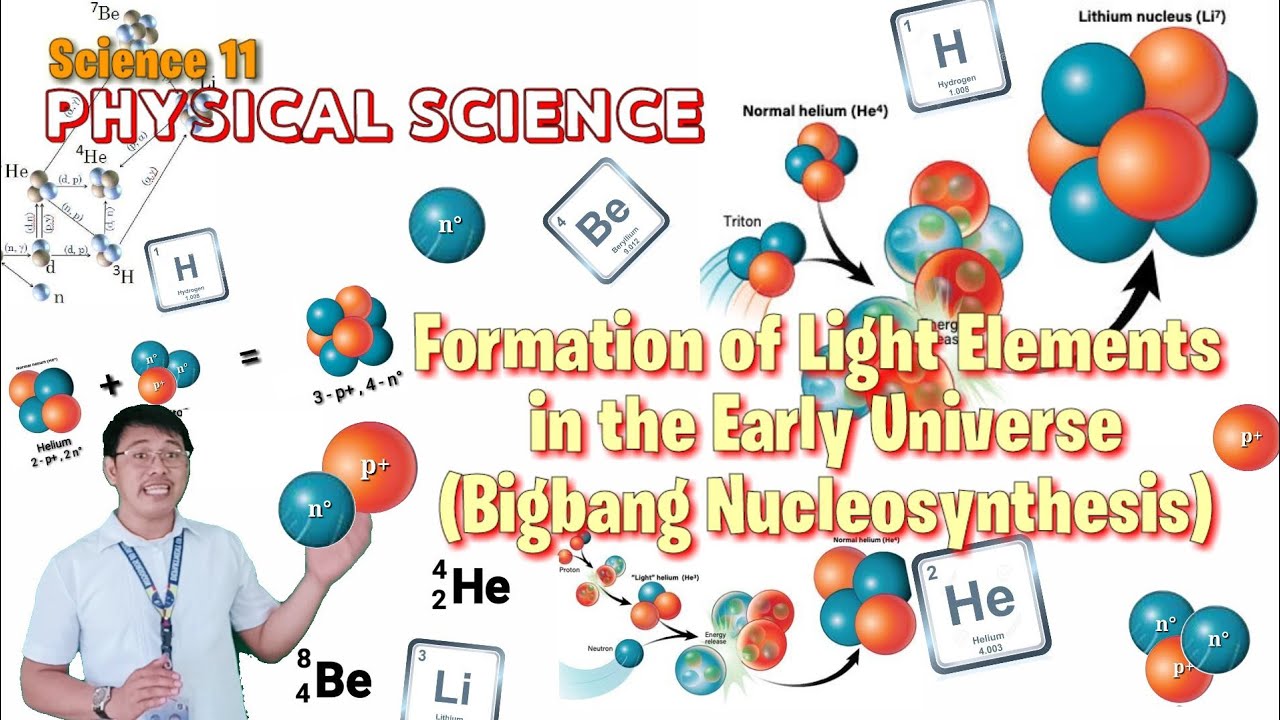
How were the first protons and elements formed in the universe?
-In the first few minutes after the Big Bang, as the universe expanded and cooled, fundamental particles came together to form protons. These protons then formed the first element, hydrogen.
Why was the synthesis of larger elements halted after the formation of hydrogen, helium, and lithium?
-After the formation of hydrogen, helium, and a tiny amount of lithium, the temperature and conditions in the early universe weren’t conducive to forming larger elements until stars began to form.
How do stars contribute to the creation of elements?
-Stars create elements through nuclear fusion, where lighter elements like hydrogen fuse to form heavier elements like helium. Larger stars can continue fusing heavier elements until iron is produced.
Why do stars stop producing elements beyond iron?
-Iron-56 has the most stable nucleus in nature. When a star produces iron, the nuclear reactions no longer release enough energy to support the star, leading to a collapse, and the star eventually explodes in a supernova.
What happens during a supernova that contributes to element creation?
-During a supernova, intense heat and gamma rays break apart iron nuclei, producing large quantities of neutrons. These neutrons are captured by iron and other elements, creating new, heavier elements up to plutonium.
How are elements like lithium, beryllium, and boron created?
-These elements are primarily created through cosmic ray spallation, where high-energy particles collide with heavier elements like carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, causing them to break into smaller nuclei.
How are elements heavier than plutonium created?
-Elements heavier than plutonium are created synthetically by scientists in laboratories through nuclear reactions, although plutonium itself can also be produced synthetically.
Why is the study of nuclear processes and stellar life cycles important?
-Understanding nuclear processes and stellar life cycles helps explain the origin of elements in the universe, including those that make up everything in existence, from stars to planets to living organisms.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)