What is Segment Reporting?
Summary
TLDRThis video on segment reporting explores the importance of understanding how large companies, like Pepsico, break down their operations into different segments based on products, regions, or other factors. It explains the key criteria for identifying reportable segments, including the 10% revenue, profit, and asset tests. The video also covers the significance of major customer disclosures and corporate expenses. Segment reporting is crucial for assessing a company's performance, risks, and potential growth areas. The information is vital for accounting students and CPA candidates looking to understand segment reporting in depth.
Takeaways
- 😀 Segment reporting helps companies provide a clear picture of their performance in different business areas (e.g., beverages, snacks, etc.).
- 😀 Companies like PepsiCo operate in multiple segments, and segment reporting breaks down financial information for better analysis and understanding.
- 😀 Knowing a company's segments helps assess risks (e.g., geopolitical issues like the Russian-Ukrainian war can affect certain regions).
- 😀 Segment reporting allows for a deeper understanding of growth opportunities and the profitability of specific business areas (e.g., comparing soda versus snacks).
- 😀 An operating segment must generate revenue and incur expenses, have a chief operating officer, and produce financial information.
- 😀 To be considered a reportable segment, a division must meet one of the three 10% tests: revenue, operating profit/loss, or assets.
- 😀 The 10% tests are used to identify significant segments for reporting purposes based on revenue, profit, or asset size relative to the company.
- 😀 In segment reporting, companies must disclose information about segment profits, losses, assets, and liabilities, as well as any risks associated with the segments.
- 😀 Corporate assets (used for general purposes) and corporate expenses (benefiting the whole company) are excluded from segment reporting.
- 😀 Major customers must be disclosed if they account for 10% or more of total company revenue, as losing a major customer could significantly affect the company's financials.
Q & A
Why is segment reporting important for companies?
-Segment reporting is important because it helps stakeholders understand a company's performance across different business segments, such as different product lines or geographic areas. This transparency allows for better risk assessment, decision-making, and forecasting of future cash flows.
What is an operating segment?
-An operating segment is a part of a company that generates revenue and incurs expenses independently. It has its own chief operating officer and is regularly reviewed by management to assess performance. Operating segments can be defined by industry, geography, or customer type.
What are the three tests used to determine if a segment is reportable?
-The three tests to determine if a segment is reportable are the revenue test, the operating profit or loss test, and the asset test. A segment must meet at least one of these tests, where the segment's revenue, operating profit or loss, or assets should represent 10% or more of the company's total.
How does the revenue test for reportable segments work?
-The revenue test examines whether the segment's total revenue, including both internal and external revenue, represents 10% or more of the company's total revenue. If a segment meets this threshold, it is considered reportable.
What does the operating profit or loss test measure?
-The operating profit or loss test measures whether a segment's operating profit or loss represents 10% or more of the total operating profits or losses (in absolute value). The segment’s profit is added to the profit of other profitable segments, and losses are summed similarly, and the greater of the two is used to calculate the 10% threshold.
What does the asset test determine for reportable segments?
-The asset test determines if a segment's total assets (both tangible and intangible) represent 10% or more of the company's total assets. If a segment exceeds this threshold, it is considered reportable.
What is the 75% rule in segment reporting?
-The 75% rule requires that the total revenue from reportable segments must represent at least 75% of the company's total revenue. If reportable segments fall short of this threshold, additional segments must be included until the 75% threshold is met.
What are corporate assets and why are they not included in segment reporting?
-Corporate assets are those assets that are maintained for general corporate purposes and are not specifically tied to any individual operating segment. These assets are excluded from segment reporting as they do not contribute directly to the operations of a specific segment.
What defines a major customer in segment reporting?
-A major customer is one whose sales account for 10% or more of a company's total revenue. If a segment relies heavily on a single customer, this must be disclosed, as the loss of such a customer could have a significant impact on the company’s performance.
What type of information must be disclosed in segment reporting?
-In segment reporting, companies must disclose general information about the operating segments, their profits and losses, assets, geographical areas, depreciation, interest expenses, and sales to major customers. Additionally, a reconciliation between segment data and the company's overall financial statements is required.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Segmenting, Targeting, dan Positioning (Pemasaran Internasional)

Pelaporan Segmen - AKUNTANSI KEUANGAN LANJUTAN

Manajemen Modal Kerja atau Working Capital Management !

Business Model Canvas: Customer Segments

Kesalahan Target Market Ini Bisa Bikin Bisnismu Gagal! The Insight Factory#3
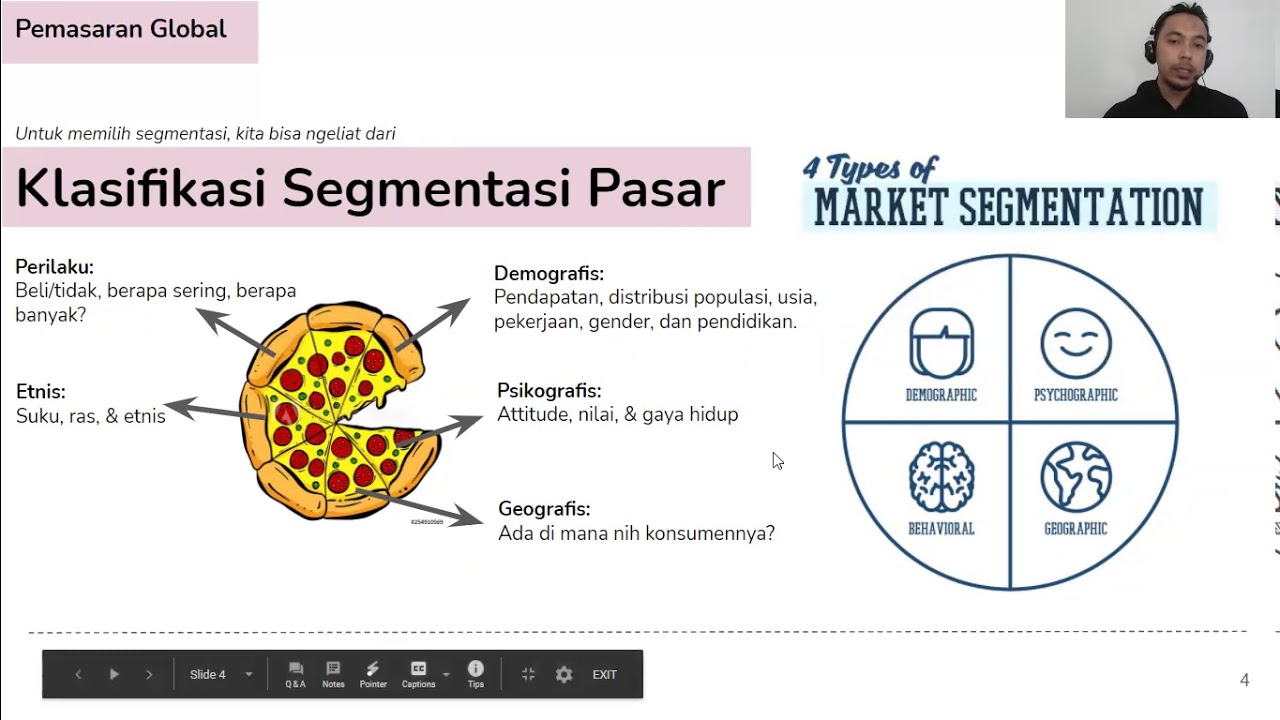
Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
