5. Understanding balance sheet
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth explanation of a company's consolidated balance sheet, focusing on the breakdown of assets, liabilities, and equity. The balance sheet is divided into non-current and current assets, with examples like property, machinery, inventories, and receivables. Similarly, liabilities are categorized into non-current and current, highlighting obligations like loans and provisions. The equity section, which includes share capital and reserves, is also discussed. The video emphasizes the importance of analyzing associated notes to understand the details behind significant balance sheet items, offering valuable insights into a company's financial health.
Takeaways
- 😀 The consolidated balance sheet is a year-on-year snapshot of a company's financial position, unlike the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, which focuses on a specific year.
- 😀 The balance sheet is divided into two main sections: assets and liabilities, with assets and liabilities further divided into non-current and current categories.
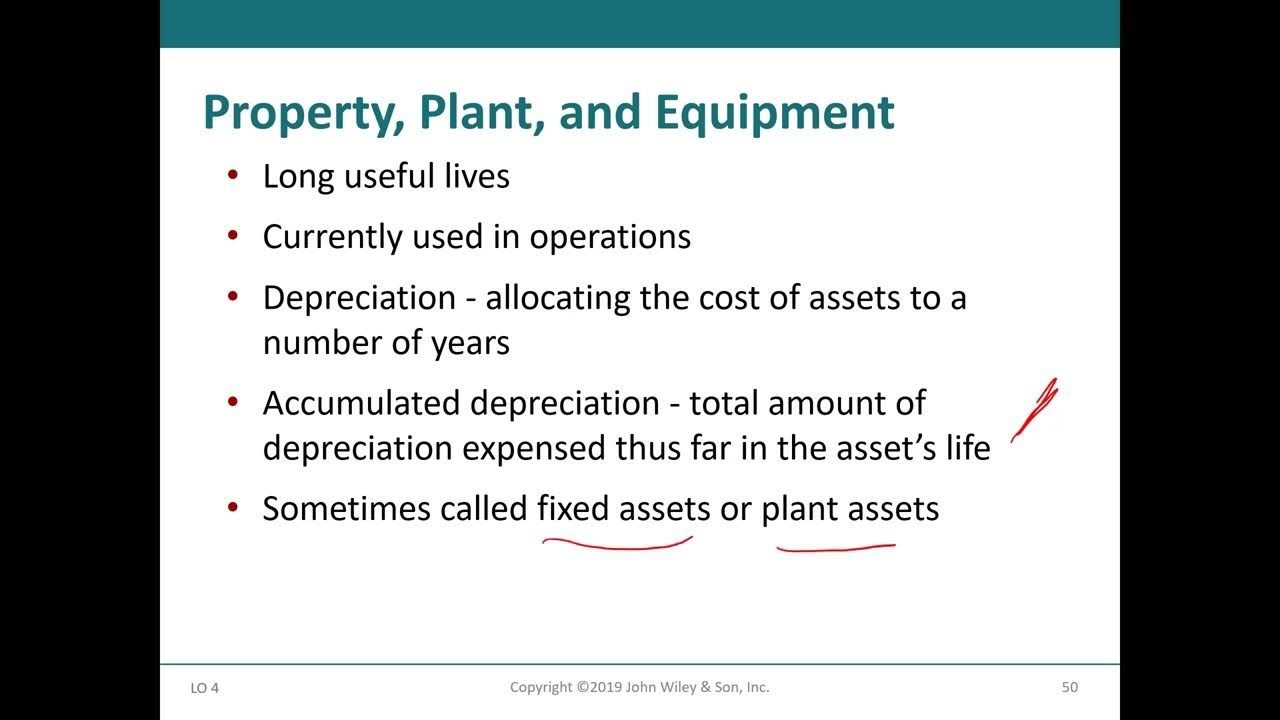
- 😀 Non-current assets are long-term investments or items like property, plant, machinery, intangible assets, and long-term financial investments.
- 😀 Current assets are those expected to be converted into cash or used within one year, such as inventories, trade receivables, loans, and cash balances.
- 😀 The total assets of a company are calculated by adding current and non-current assets together.
- 😀 Large line items in the balance sheet, such as financial investments or property, plant, and equipment, should be further explored by consulting the associated notes.
- 😀 Liabilities are financial obligations of the company, divided into non-current liabilities (long-term obligations) and current liabilities (due within one year).
- 😀 Non-current liabilities include long-term financial obligations like loans or provisions, while current liabilities cover short-term obligations like payables or credit.
- 😀 The equity section of the balance sheet consists of share capital (initial investment) and other equity, which includes reserves and surpluses.
- 😀 Reserves and surpluses represent profits accumulated over time and are earmarked for various purposes, reflecting the company's financial health and growth.
- 😀 To fully understand the nuances of line items in the balance sheet, it is essential to refer to the associated notes, which provide detailed explanations of each item.
Q & A
What is the main difference between a balance sheet and a profit & loss (P&L) statement?
-The main difference is that a balance sheet shows the financial position of a company at a specific point in time, whereas a P&L statement details the company’s performance over a specific period, typically a year.
What are non-current assets and can you give examples from the Bajaj Auto balance sheet?
-Non-current assets are long-term assets that provide economic benefits over a period of more than one year. Examples from Bajaj Auto include property, plant and equipment, intangible assets like trademarks and patents, and long-term financial investments.
What defines current assets, and what are some examples from Bajaj Auto's balance sheet?
-Current assets are assets expected to be converted into cash or used within a year. Examples from Bajaj Auto’s balance sheet include inventories, trade receivables, loans receivable within a year, and cash and cash equivalents.
How do non-current liabilities differ from current liabilities?
-Non-current liabilities are long-term financial obligations that the company must fulfill over a period greater than one year, while current liabilities are obligations due within the next year.
What are provisions under non-current liabilities in Bajaj Auto's balance sheet?
-Provisions under non-current liabilities refer to funds set aside for long-term financial obligations, such as welfare schemes, compensated absences, and warranties on products sold.
What are the key components of the equity section in the balance sheet?
-The equity section consists of share capital, which represents the money invested by the company’s founders and early investors, and reserves and surpluses, which are profits retained by the company for future use.
Why should one pay attention to heavy line items in the balance sheet?
-Heavy line items often represent significant parts of the company's financial position, and understanding them can provide deeper insights into the company’s financial health and strategy. For example, non-current investments or property, plant, and equipment may require further analysis.
How can you investigate large line items in the balance sheet?
-To investigate large line items, you should refer to the associated notes in the financial statements, as they provide detailed explanations and breakdowns of these items.
What does the term 'other equity' in the balance sheet refer to?
-'Other equity' represents reserves and surpluses, which are funds accumulated from profits and earmarked for various purposes, such as reinvestment or to cover future liabilities.
How do you differentiate between non-current and current financial obligations?
-Non-current financial obligations are long-term debts or commitments due over several years, while current financial obligations are those that must be settled within the next year, such as short-term loans, payables, or credit card debt.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
Financial Accounting 1: 13- Sections Of A Classified Statement Of Financial Position (شرح بالعربي)

Statement of Financial Position (SOFP) | Laporan Posisi Keuangan | Akuntansi Keuangan Menengah

How to Analyze a Balance Sheet Like a Hedge Fund Analyst

The KEY to Understanding Financial Statements

Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet)

Bilanzen einfach erklärt (explainity® Erklärvideo)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
