Airbus A320 CBT # 19 AUTO FLIGHT FMS 2 FLIGHT MANAGEMENT
Summary
TLDRThe Flight Management and Guidance Computer (FMGC) plays a crucial role in aviation, managing navigation, flight planning, performance predictions, and optimization. It calculates the aircraft's position using a mix of IRS, GPS, and radio data, updating the flight plan dynamically. Pilots can input and revise flight routes and altitudes, with real-time adjustments based on operational needs. The system utilizes two key databases for navigation and performance, ensuring fuel efficiency and accurate predictions. Alerts and predictions for top of climb, descent, and fuel consumption are provided to optimize the flight, enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Flight Management and Guidance Computer (FMGC) handles key functions: navigation, flight planning, performance prediction, and display management.
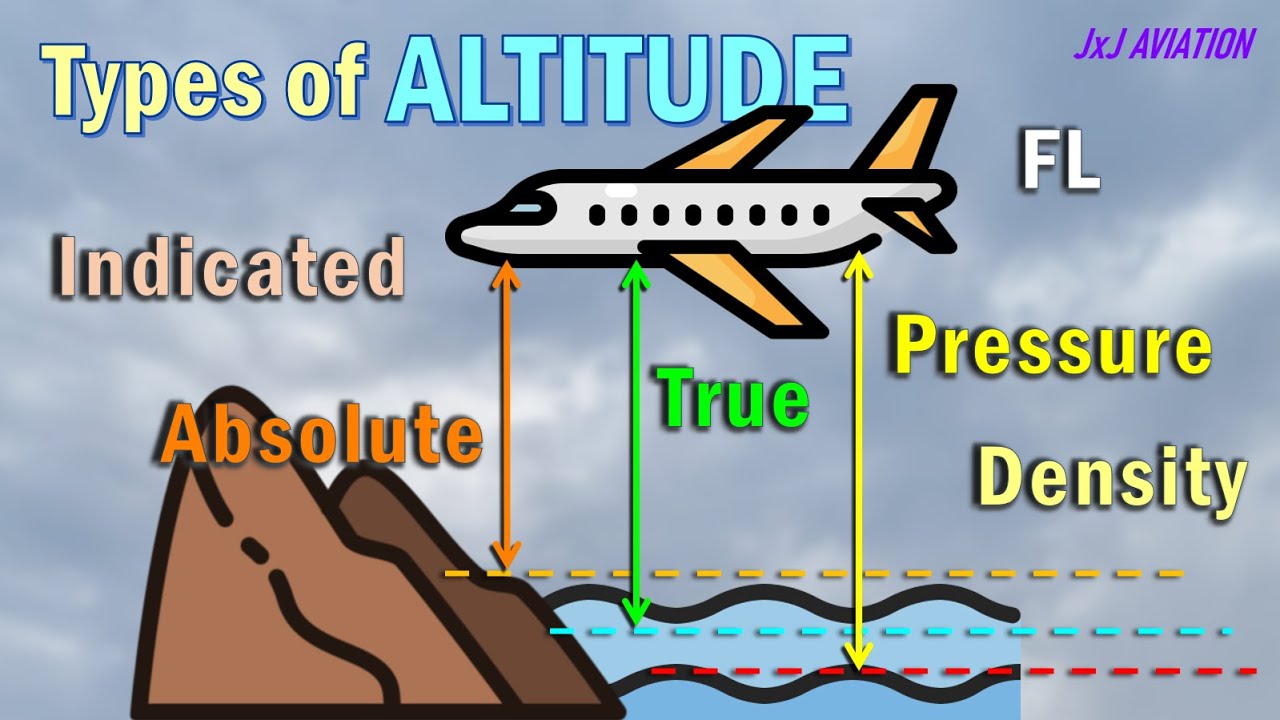
- 😀 Accurate position computation is essential for the FMGC, which combines IRS, GPS, and radio positions to determine the aircraft's location.
- 😀 The FMGC prioritizes the most accurate position source based on integrity criteria, with IRS and GPS positions being critical for accurate flight management.
- 😀 If GPS data fails, the FMGC uses radio position updating or memorizes bias to maintain position accuracy until GPS or radio positions are restored.
- 😀 The FMGC computes the Estimated Position Error (EPE) and compares it to Required Navigation Performance (RNP) to ensure flight accuracy and compliance with airworthiness standards.
- 😀 The flight plan includes both a primary (active) and secondary (alternate) plan, with navigation and performance data critical for optimization.
- 😀 Two key databases are used by the FMGC: the navigation database (for lateral flight planning) and the performance database (for optimization and fuel prediction).
- 😀 The FMGC provides tools for lateral revisions to the flight plan, such as inserting or modifying waypoints, airways, or creating flight plan discontinuities.
- 😀 Vertical flight planning involves defining altitude and speed constraints at waypoints, managing fuel policies, and optimizing operational costs with factors like cost index (CI).
- 😀 The FMGC computes various predictions like top of climb (TC), top of descent (TD), fuel consumption, and speed changes, providing these data to the navigation display and autopilot systems for real-time guidance.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the FMGC in an aircraft?
-The FMGC (Flight Management and Guidance Control) system is responsible for navigation, flight planning, performance prediction, and optimization, ensuring the aircraft follows the planned route efficiently and accurately.
How does the FMGC calculate the aircraft's position?
-The FMGC calculates the aircraft's position using a mix of IRS (Inertial Reference Systems), GPS, and radio-based positions. The system continuously selects the most accurate position based on data integrity and precision.
What happens when one IRS fails in the FMGC system?
-If one IRS fails, the FMGC uses the remaining IRS, or switches to the radio or GPS-based position. The system updates the position based on whichever data source is most accurate.
What role do the navigation and performance databases play in the FMGC?
-The navigation database (NavDB) contains information about waypoints, routes, and airports, while the performance database (PerfDB) contains data about aircraft performance, used to optimize the flight plan and predict fuel consumption, ETAs, and other performance parameters.
How is the flight plan initialized in the FMGC?
-The flight plan is initialized through the MCDU (Multi-Function Control Display Unit) by inserting the origin and destination, selecting departure and arrival waypoints, or using a company route. It can also be initialized by sending a request for an active flight plan.
What is the significance of the Cost Index (CI) in flight planning?
-The Cost Index (CI) is used to optimize flight speed and altitude by balancing fuel consumption with flight time. A lower CI corresponds to fuel efficiency, while a higher CI prioritizes reducing flight time.
What is the role of lateral revisions in flight planning?
-Lateral revisions allow the pilot to modify the active flight plan by adding or removing waypoints, adjusting routes, and even selecting alternative airports or holding patterns. These revisions can be made during the flight and immediately impact the aircraft's trajectory.
What does the system do when GPS function is lost?
-When GPS is lost, the FMGC will display a 'GPS Primary Lost' message on the ND and MCDU scratchpad. The crew must then verify the position accuracy using available raw data and cross-check it periodically during the flight.
How does the FMGC handle flight plan discontinuities?
-Flight plan discontinuities occur when waypoints are added or deleted. These changes may lead to a break in the active flight plan, which must be addressed by the crew to avoid navigation issues. Discontinuities are shown on the MCDU and must be resolved by revising the flight plan.
What is the purpose of the vertical flight plan in the FMGC?
-The vertical flight plan manages altitude and speed constraints for different flight phases (takeoff, climb, cruise, descent, approach). It also incorporates weather data and aircraft performance factors to ensure the aircraft operates efficiently during each phase of the flight.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)