Analysing, interpreting and presenting data
Summary
TLDRThis video presents five essential tips for effectively analyzing, interpreting, and presenting data. The tips emphasize keeping your aim and audience in mind, organizing data to identify patterns, using visuals like charts for clarity, and labeling data correctly in text. It highlights the importance of using analytical language and making recommendations based on data. Practical examples are provided, such as evaluating attendance trends and qualitative feedback, to guide viewers in presenting data in a way that maximizes clarity and impact while ensuring meaningful interpretation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Keep your aim and audience in mind when analyzing data to stay focused on your objectives.
- 😀 Develop a list of guiding questions before analyzing the data to help you stay on track.
- 😀 Use data to identify trends, patterns, and relationships, and manipulate it to enhance clarity.
- 😀 Organize raw data in tables or charts, using functions like sum and average to extract insights.
- 😀 Use visual formats like charts to present trends more clearly than raw data tables.
- 😀 Analyze both quantitative (numbers) and qualitative (words, observations) data for a more holistic view.
- 😀 Identify themes or categories in qualitative data to better understand the underlying patterns.
- 😀 Present data in formats that maximize clarity and impact, such as tables, charts, or text.
- 😀 Ensure that all data is properly labeled, referred to, and explained within the text to avoid confusion.
- 😀 Use language that indicates analysis and interpretation, avoiding just describing the data without providing context.
- 😀 Signal analysis and interpretation to your reader, helping them understand the meaning, importance, or implications of the data.
Q & A
Why is it important to keep your aim and audience in mind when analyzing data?
-Keeping your aim and audience in mind ensures that the data analysis stays focused and relevant. It helps to prioritize the right questions and avoid unnecessary distractions.
What is the first step in analyzing data effectively?
-The first step is to develop a list of questions to guide your thinking. This helps to define the scope and focus of your analysis.
What kinds of questions might you ask when tasked with evaluating staff satisfaction with a program?
-Some examples of questions you might ask include: 'Has attendance gone up, down, or stayed the same?' 'Has participant satisfaction improved?' 'Are these changes significant?' and 'Does qualitative data support quantitative data?'
What are some common tools used to organize and summarize data?
-Common tools for organizing and summarizing data include spreadsheets, databases, tables, and graphs. These tools help identify relationships, patterns, and trends.
How can you manipulate data to notice trends?
-You can manipulate data by using functions like sum, average, or mean to calculate totals or changes over time. Visualizing data in formats like bar charts can also help reveal trends more clearly.
What trend did the data reveal in the example regarding workshop attendance?
-The data showed that overall attendance remained stable, but two workshops became more popular, while two others saw a decline in attendance.
What is a useful approach when analyzing qualitative data like survey responses?
-A useful approach for qualitative data is to categorize it by themes or labels, such as grouping responses based on topics, time periods, or personal characteristics, like geography.
Why is it important to present data in the right format?
-Presenting data in the right format maximizes clarity and impact. For example, a well-designed chart may highlight trends more effectively than a table, making it easier for the audience to understand the key points.
How should data be referred to and explained in text?
-Data should be referred to clearly, placed close to the relevant text, and explained with language that indicates analysis, interpretation, or implications, rather than just describing the data.
What language should be used when reporting data analysis?
-When reporting data, use language that highlights trends, changes, or comparisons, such as 'dropped significantly,' 'suggesting a decline,' or 'indicating that these topics lack relevance.' This helps convey the meaning and implications of the data.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Kurikulum Merdeka Materi Informatika Kelas 7 Bab 6 Analisis Data Bagian 1

Geo X. 52. Teknik Pengumpulan & Pengolahan Data

Video Pembelajaran Matematika Kelas 7 SMP ( Pengolahan Data )
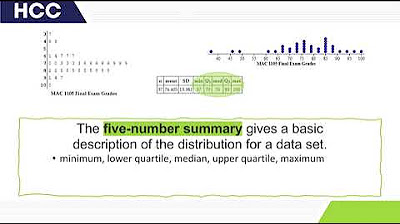
How Do I Compare to the Group?
Top Data Visualizations Explained | Know When to Use Each!

5 Projects for a Data Analyst Job | All Materials Included
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
