Free CCNA | DHCP | Day 39 Lab | CCNA 200-301 Complete Course
Summary
TLDRIn this comprehensive video, Jeremy walks viewers through the process of configuring DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) in a Cisco environment. He covers setting up a DHCP server (R2), configuring R1 as both a DHCP client and relay agent, and troubleshooting common DHCP issues. The tutorial offers practical, hands-on examples using Cisco routers and switches, explaining key commands and configurations. Additionally, Jeremy introduces a bonus lab from Boson NetSim, providing further opportunities for practice and deepening understanding. This video is perfect for CCNA students looking to master DHCP configuration and troubleshooting techniques.
Takeaways
- 😀 Jeremy’s IT Lab offers a free, comprehensive course for the CCNA, with videos, lab files, and a link to a network simulator called Boson NetSim.
- 😀 Boson NetSim for CCNA is recommended for hands-on practice, including guided labs to enhance understanding of the exam topics.
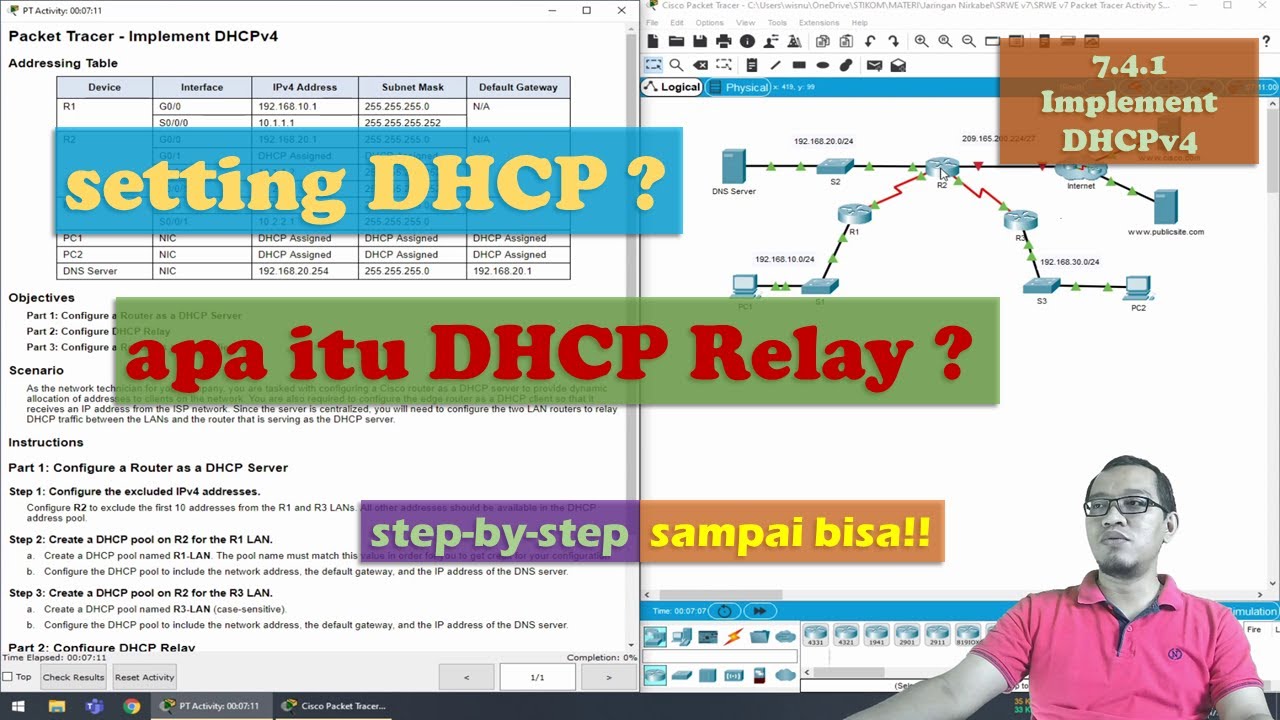
- 😀 In the lab, the DHCP server (R2) is configured with three pools for different subnets, and the first 10 IP addresses are excluded from assignment.
- 😀 The configuration of the DHCP pools on R2 includes specifying DNS, domain names, and default routers for each subnet.
- 😀 PC2 successfully receives an IP address (192.168.2.11) from R2's DHCP server, and the correct network details such as domain name and default gateway are displayed.
- 😀 R1 is configured as a DHCP client on its G0/0 interface using the command 'IP ADDRESS DHCP', and it receives an IP address from R2 (203.0.113.2).
- 😀 R1 is also configured as a DHCP relay agent on its G0/1 interface to relay DHCP requests from clients to R2, which is the actual DHCP server.
- 😀 PC1 is able to receive an IP address via R1, confirming that R1 is properly relaying DHCP requests to R2.
- 😀 The Boson NetSim lab preview demonstrates troubleshooting a DHCP issue where clients cannot obtain IP addresses, suggesting the issue is with the DHCP configuration on Router1.
- 😀 The 'no service dhcp' command was identified as the cause of Router1 not responding to DHCP requests, and it was resolved by enabling DHCP service with 'service dhcp'.
Q & A
What is the main objective of the lab demonstrated in the video?
-The main objective of the lab is to configure DHCP on Cisco devices, specifically setting up R2 as a DHCP server, R1 as both a DHCP client and relay agent, and ensuring that DHCP clients (PC1 and PC2) receive IP addresses.
How does the process of DHCP assignment work in this lab?
-In this lab, R1 is configured as a DHCP client to obtain an IP address from R2, while R2 is set up as the DHCP server. R1 also acts as a DHCP relay agent for the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet, allowing PC1 to obtain an IP address via R2, even though they are not on the same subnet.
What is the purpose of the IP DHCP EXCLUDED-ADDRESS command?
-The IP DHCP EXCLUDED-ADDRESS command is used to exclude specific IP addresses from being assigned by the DHCP server. In this lab, the first 10 addresses of each subnet are reserved, so they are not assigned to DHCP clients.
What is the significance of the NO SERVICE DHCP command in this lab?
-The NO SERVICE DHCP command disables the DHCP service on a router. In the troubleshooting section of the lab, this command was found to be the cause of DHCP issues on Router1, preventing it from responding to DHCP requests.
What commands are used to configure a router interface as a DHCP client?
-To configure a router interface as a DHCP client, the commands used are: 'IP ADDRESS DHCP' under the interface configuration mode, followed by 'NO SHUTDOWN' to bring the interface up.
What is the role of R1 in this DHCP setup?
-R1 serves multiple roles: it acts as a DHCP client on its G0/0 interface to receive an IP address from R2, and as a DHCP relay agent on its G0/1 interface, forwarding DHCP requests from clients on the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet to the DHCP server (R2).
How is the DNS server configured in this lab's DHCP pools?
-The DNS server is configured as '8.8.8.8' in both DHCP pools (POOL1 and POOL2) on R2, ensuring that the clients receive this DNS address along with their IP configuration.
What steps were taken to ensure PC1 could receive an IP address from R2 through R1?
-To ensure PC1 receives an IP address from R2 via R1, R1 was configured as a DHCP relay agent with the 'IP HELPER-ADDRESS' command pointing to R2's IP address (203.0.113.1). This allowed DHCP requests from PC1 to be forwarded to R2 for assignment.
What is the purpose of using the 'SHOW RUN | SECTION DHCP' command?
-The 'SHOW RUN | SECTION DHCP' command is used to filter and display only the DHCP-related configurations from the running configuration on the router. This makes it easier to review and troubleshoot DHCP settings.
What issues were identified during the troubleshooting phase related to DHCP on Router1?
-During troubleshooting, it was discovered that the 'NO SERVICE DHCP' command had been applied to Router1, disabling the DHCP service. This prevented Router1 from responding to DHCP requests, which was the root cause of the issue.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)