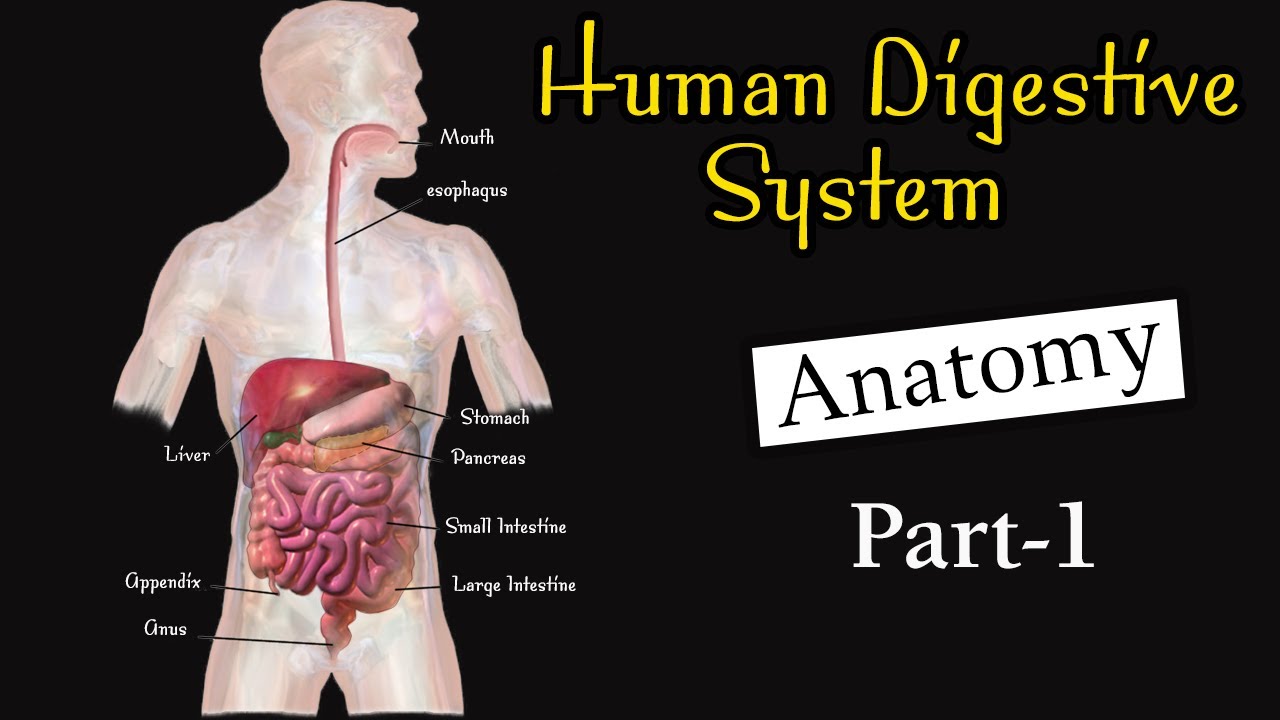
Sistem pencernaan Manusia : Struktur dan fungsi sistem pencernaan makanan pada manusia
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the human digestive system, detailing the four main stages of food processing: ingestion, digestion, absorption, and defecation. It explains the mechanical and chemical digestion that begins in the mouth and continues through the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine. Key organs involved, such as the liver and pancreas, contribute essential enzymes for breaking down food. The video also discusses the role of the large intestine in water absorption and the formation of waste, emphasizing the importance of beneficial bacteria in digestion. Overall, it provides a comprehensive overview of how our bodies process food.
Takeaways
- 😀 Digestion occurs in four stages: ingestion, digestion, absorption, and defecation.
- 😀 Mechanical digestion begins in the mouth, where food is chewed and mixed.
- 😀 Chemical digestion involves enzymes breaking down complex molecules into smaller ones.
- 😀 The digestive system includes the alimentary canal and accessory organs like the liver and pancreas.
- 😀 Saliva contains enzymes, such as amylase, that start breaking down starches in the mouth.
- 😀 The food bolus moves from the mouth to the esophagus, aided by peristaltic movements.
- 😀 In the stomach, gastric juices, including hydrochloric acid and pepsin, further digest food.
- 😀 The small intestine is where most chemical digestion and nutrient absorption occur.
- 😀 The large intestine absorbs water and compacts waste into feces, which is excreted through the anus.
- 😀 Beneficial bacteria in the large intestine help digest remaining food and produce essential vitamins.
Q & A
What are the four main stages of food processing in the human digestive system?
-The four main stages are ingestion, digestion, absorption, and defecation.
What begins the digestion process in the mouth?
-The digestion process begins with mechanical digestion through chewing and chemical digestion aided by saliva, which contains enzymes like amylase.
How does food travel from the mouth to the stomach?
-After being chewed in the mouth, the food forms a bolus, which travels through the pharynx to the esophagus, where peristaltic movements push it into the stomach.
What role does hydrochloric acid (HCl) play in the stomach?
-HCl creates an acidic environment in the stomach, which helps to kill pathogens and activates digestive enzymes like pepsin that break down proteins.
What is chyme, and where does it go after the stomach?
-Chyme is the semi-liquid mass formed in the stomach after digestion. It then moves into the small intestine, specifically the duodenum.
What are the main functions of the small intestine in digestion?
-The small intestine is primarily responsible for the chemical digestion of nutrients and the absorption of those nutrients into the bloodstream.
What is the role of bile in digestion?
-Bile, produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, helps emulsify fats in the small intestine, making them easier to digest and absorb.
How do nutrients from the small intestine enter the bloodstream?
-Nutrients are absorbed through the walls of the ileum in the small intestine and are transported into the bloodstream.
What happens to undigested materials in the large intestine?
-Undigested materials move into the large intestine, where water is reabsorbed, and waste is formed into feces.
What is the significance of bacteria like Escherichia coli in the large intestine?
-Bacteria such as Escherichia coli help in the fermentation of undigested food and produce essential vitamins like K and B12.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)