RMS Value of AC Circuits
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of RMS (Root Mean Square) value in AC circuits, detailing its significance for power dissipation equivalent to DC circuits. It covers the relationship between peak and RMS voltage, providing formulas for calculation, including the integral approach. The presenter demonstrates how to derive the RMS value from peak voltage and discusses the importance of understanding these concepts for effective circuit analysis. The video aims to clarify how to compute RMS values, enhancing comprehension of AC power dynamics.
Takeaways
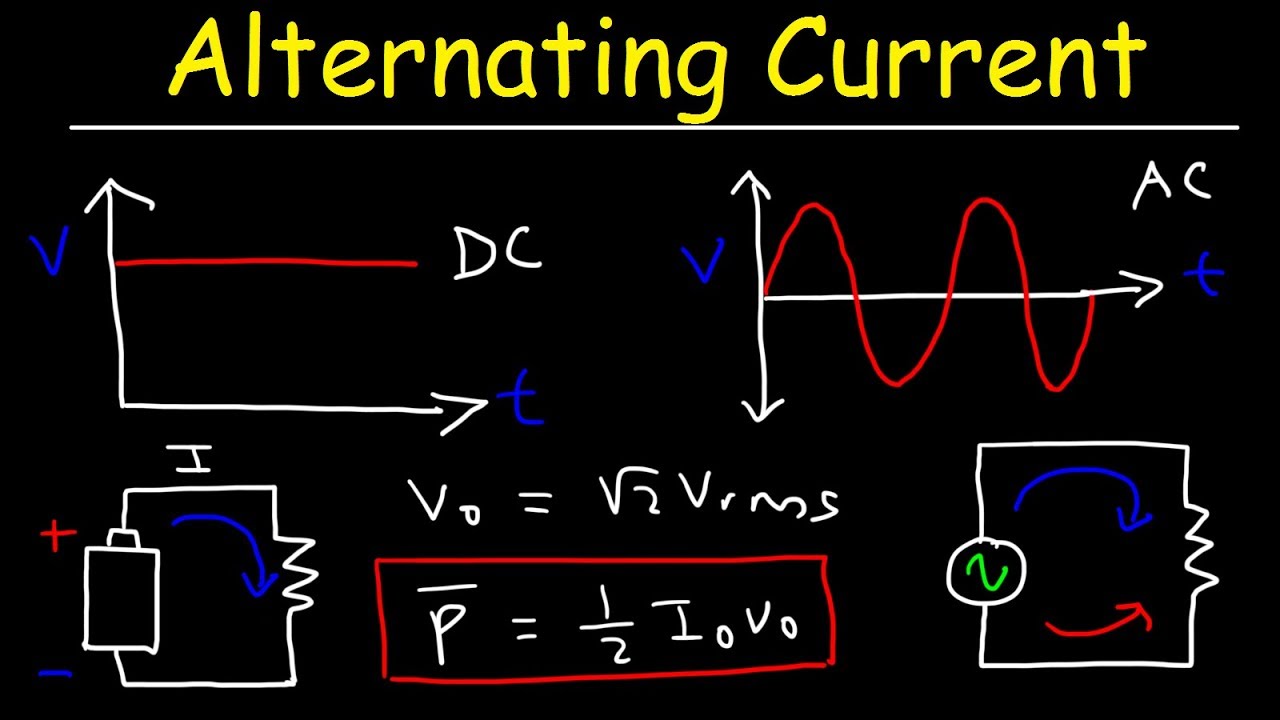
- 😀 RMS (Root Mean Square) value indicates the effective voltage or current in AC circuits, equivalent to DC power dissipation.
- 🔌 The power dissipation formula for a DC circuit is P = V² / R, which also applies to AC using RMS voltage.
- 📈 The peak voltage (V_peak) of a sine wave is higher than the RMS voltage (V_RMS) and is calculated as V_peak = V_RMS × √2.
- 📉 To find RMS from peak voltage, use the formula V_RMS = V_peak / √2, approximately equal to 0.7071 × V_peak.
- 🔍 Understanding the difference between peak and RMS voltage is essential for accurate power calculations in AC circuits.
- 📊 An example shows that for a peak voltage of 1V, the RMS voltage is approximately 0.7071V.
- 📏 The general formula for calculating RMS voltage from any voltage function involves integrating the square of the function over a period.
- 🧮 For sine waves, the integral of sine squared over one period leads to the RMS value of √2/2, reaffirming the peak-to-RMS relationship.
- 📐 When calculating RMS, it's crucial to take the arithmetic mean of the squared voltages before taking the square root.
- 📚 The concepts of RMS and peak voltage are fundamental in electrical engineering for analyzing AC circuits and ensuring proper design.
Q & A
What does RMS stand for and why is it important in AC circuits?
-RMS stands for Root Mean Square. It is important in AC circuits because it represents the equivalent DC voltage that would produce the same power dissipation in a resistor.
How is the RMS voltage calculated from the peak voltage?
-The RMS voltage is calculated by dividing the peak voltage by the square root of 2. Alternatively, it can also be expressed as the peak voltage times the square root of 2 over 2.
What is the peak voltage if the RMS voltage is 30 volts?
-The peak voltage would be approximately 42.4 volts, calculated as 30 times the square root of 2 (about 1.4142).
What is the value of the square root of 2 over 2?
-The value of the square root of 2 over 2 is approximately 0.7071.
How do you calculate the RMS voltage using a sine wave?
-To calculate the RMS voltage of a sine wave, square the voltage values at equal intervals, find the average of those squares, and then take the square root of that average.
What is the general formula for calculating the RMS voltage using calculus?
-The general formula is 1/T times the integral from 0 to T of the square of the voltage function dt, where T is the period of the wave.
What is the significance of the sine wave's period in calculating RMS voltage?
-The period of a sine wave (2π) is crucial for determining the intervals over which voltage values are calculated, ensuring accurate RMS computation.
What happens to the RMS voltage if the peak voltage increases?
-If the peak voltage increases, the RMS voltage will also increase proportionally, as it is derived from the peak voltage.
Why is it necessary to ensure your calculator is in radian mode when calculating sine values?
-Calculating sine values requires the input of angles in the correct unit; sine functions in physics typically use radians, and using degrees would yield incorrect results.
What method is suggested to find the integral of sine squared?
-The method involves using power-reducing formulas for integration, which can simplify the process of finding the integral of sine squared.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Meaning of RMS value in AC Supply | What is Rms value in hindi
Alternating Current vs Direct Current - Rms Voltage, Peak Current & Average Power of AC Circuits

Rangkaian Resistif, Induktif, dan Kapasitif | Rangkaian AC | Part 1 | Fisika Dasar

Simulasi Arus dan Tegangan Bolak-Balik dengan Phet

W3_L4_The Sinusoid

8.1. Gelombang Alternating Current (AC) - Rangkaian Listrik
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
