GCSE Biology - Genetic Diagrams #73
Summary
TLDRThis video explains genetic diagrams, focusing on how to represent allele combinations from two parent mice. It introduces dominant and recessive alleles, using capital 'A' for normal muscle and lowercase 'a' for muscular traits. The tutorial demonstrates constructing genetic diagrams and Punnett squares to predict offspring genotypes and phenotypes. Through examples, viewers learn to calculate ratios and probabilities of traits, illustrating that while single genes influence characteristics, environmental factors also play a significant role. The engaging presentation emphasizes the importance of understanding genetic inheritance.
Takeaways
- 😀 Genetic diagrams show combinations of alleles from two parents.
- 😀 Dominant alleles are represented by uppercase letters, while recessive alleles are lowercase.
- 😀 Homozygous normal mouse genotype is AA (normal phenotype), while homozygous muscular mouse genotype is aa (muscular phenotype).
- 😀 Gametes are formed by splitting parental genotypes into individual alleles.
- 😀 Offspring genotypes result from combining the gametes of both parents.
- 😀 Heterozygous offspring (Aa) express the dominant phenotype (normal muscle).
- 😀 Punnett squares provide a visual way to predict offspring genotypes and phenotypes.
- 😀 When two heterozygous mice mate, the expected genotype ratio is 1 AA : 2 Aa : 1 aa.
- 😀 The phenotype ratio from the cross of heterozygous mice is 3 normal : 1 muscular.
- 😀 Environmental factors can influence phenotypic expression alongside genetic factors.
Q & A
What is the purpose of genetic diagrams?
-Genetic diagrams illustrate the combinations of alleles that offspring can inherit from their parents.
How are dominant and recessive alleles represented in genetic diagrams?
-Dominant alleles are represented by uppercase letters (e.g., A), while recessive alleles are shown with lowercase letters (e.g., a).
What are the genotypes of the parents in the initial mouse cross example?
-One parent is homozygous normal (AA) and the other is homozygous muscular (aa).
What gametes are produced by the parents in the first example?
-The homozygous normal mouse produces gametes with the genotype A, and the homozygous muscular mouse produces gametes with the genotype a.
What is the result of crossing a homozygous normal mouse with a homozygous muscular mouse?
-All offspring are heterozygous (Aa) and exhibit the normal phenotype due to the dominance of the A allele.
What is a Punnett square, and how is it used?
-A Punnett square is a diagram used to predict the genotype and phenotype combinations of offspring from parental gametes. It is laid out in a grid format.
What outcomes can occur when two heterozygous mice are crossed?
-When two heterozygous mice (Aa x Aa) are crossed, the expected genotypes are 1 homozygous dominant (AA), 2 heterozygous (Aa), and 1 homozygous recessive (aa), resulting in a 3:1 phenotype ratio of normal to muscular.
What does a 3:1 ratio in offspring phenotypes indicate?
-A 3:1 ratio indicates that for every four offspring, three are expected to have the normal phenotype and one the muscular phenotype.
How do environmental factors influence genetic traits?
-While genes play a crucial role in determining traits, environmental factors, such as nutrition and upbringing, can significantly affect the expression of these traits.
What should viewers do if they enjoyed the video?
-Viewers are encouraged to like the video and subscribe for more educational content.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

POLA-POLA HEREDITAS part 3 (PENYIMPANGAN SEMU HUKUM MENDEL-interaksi antaralel)| Biologi XII SMA

GCSE Biology - DNA Part 2 - Alleles / Dominant / Heterozygous / Phenotypes and more! #64

Inherited Genetic Disorders | Genetics | Biology | FuseSchool

GENETICS 101 (Part 3) | Definitions, Albinism, Sickle Cell Anaemia| CXC Biology Tutor

Chromosomal Basis
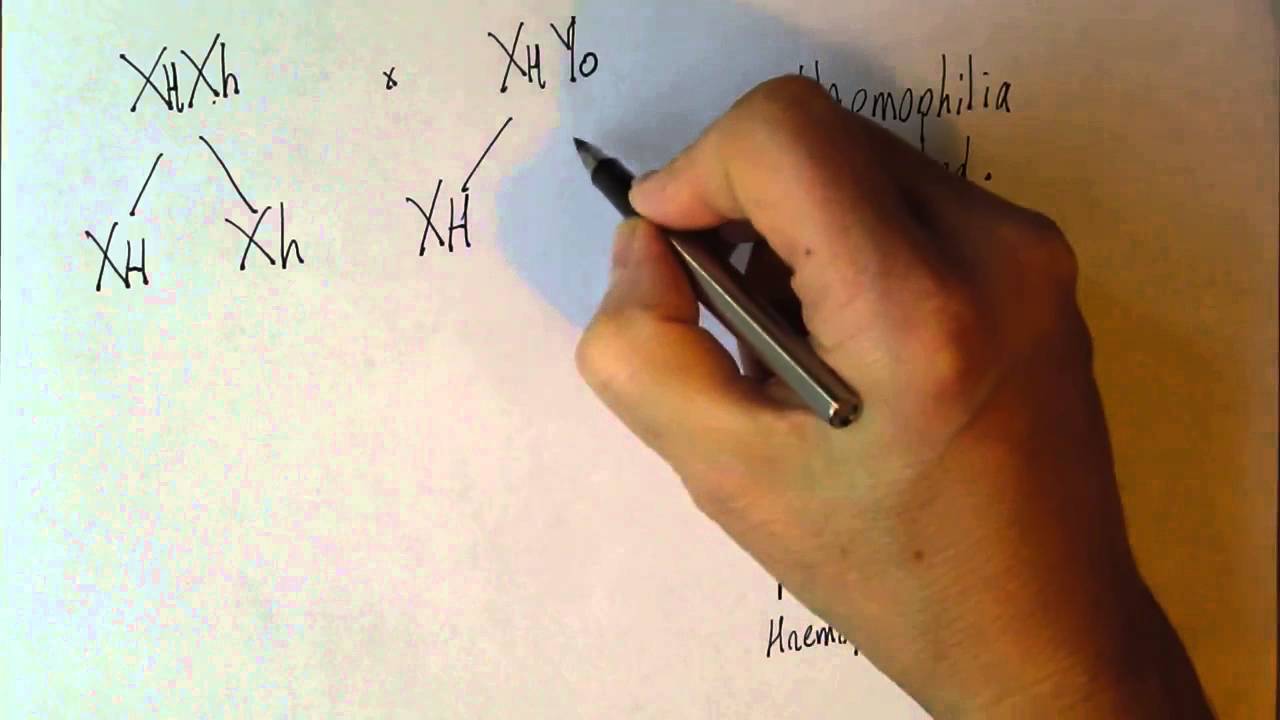
Hemophilia genetics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
