GCSE Biology - DNA Part 2 - Alleles / Dominant / Heterozygous / Phenotypes and more! #64
Summary
TLDRThis video continues the discussion on DNA by explaining key genetic terms such as allele, dominant and recessive traits, homozygous and heterozygous, as well as genotype and phenotype. It describes how genes code for proteins, and how different versions of these genes, called alleles, determine traits. Using an example of fur color in mice, it shows how dominant and recessive alleles affect physical traits. The video also distinguishes between genotype, the genetic makeup, and phenotype, the observable characteristics, preparing viewers for the next topic on genetic diagrams.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Genes are segments of DNA that code for specific proteins, determining traits we develop.
- 👥 Traits can be influenced by a single gene or multiple genes interacting together.
- 🔄 Alleles are different versions of the same gene, which can lead to variations in traits.
- 👫 We inherit two alleles for each gene, one from each parent, which can be the same or different.
- 🎭 If both alleles are the same, the organism is homozygous for that trait, and if they are different, it's heterozygous.
- 🏆 In cases of heterozygosity, the dominant allele is expressed, while the recessive one remains unexpressed.
- 🐭 A mouse with one purple allele (dominant) and one green allele (recessive) will be purple.
- 🌈 The only way for the mouse to be green is if it inherits two green (recessive) alleles, which is homozygous recessive.
- 🧬 Genotype refers to the collection of alleles an organism has.
- 👀 Phenotype refers to the physical traits or characteristics expressed by the genotype, like fur color.
Q & A
What is an allele?
-An allele is a different version or form of the same gene. Each individual has two alleles for every gene, one from each parent.
How do dominant and recessive alleles affect traits?
-A dominant allele will always be expressed in an organism's appearance if present, while a recessive allele will only be expressed if both alleles are recessive.
What does it mean to be homozygous for a gene?
-Being homozygous means having two of the same alleles for a particular gene, either both dominant or both recessive.
What does it mean to be heterozygous for a gene?
-Being heterozygous means having two different alleles for a particular gene, one dominant and one recessive.
If a mouse is heterozygous for fur color with one purple allele (dominant) and one green allele (recessive), what color will the mouse be?
-The mouse will be purple because the purple allele is dominant and will be expressed over the recessive green allele.
What is the only way for a mouse to have green fur if green is the recessive allele?
-The mouse must have two green alleles (homozygous recessive) for green fur to be expressed.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
-Genotype refers to the collection of alleles an organism has, while phenotype refers to the physical traits or characteristics that are expressed as a result of the genotype.
Can two mice with different genotypes have the same phenotype?
-Yes, a heterozygous mouse (one dominant, one recessive allele) and a homozygous dominant mouse (two dominant alleles) can both have the same phenotype, as the dominant trait will be expressed in both.
What is an example of a trait determined by a single gene?
-Fur color in mice and red-green color blindness in humans are examples of traits determined by a single gene.
Why are characteristics like height determined by multiple genes?
-Height is influenced by several genes that interact with each other, which is why people vary greatly in height. It is an example of a polygenic trait.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
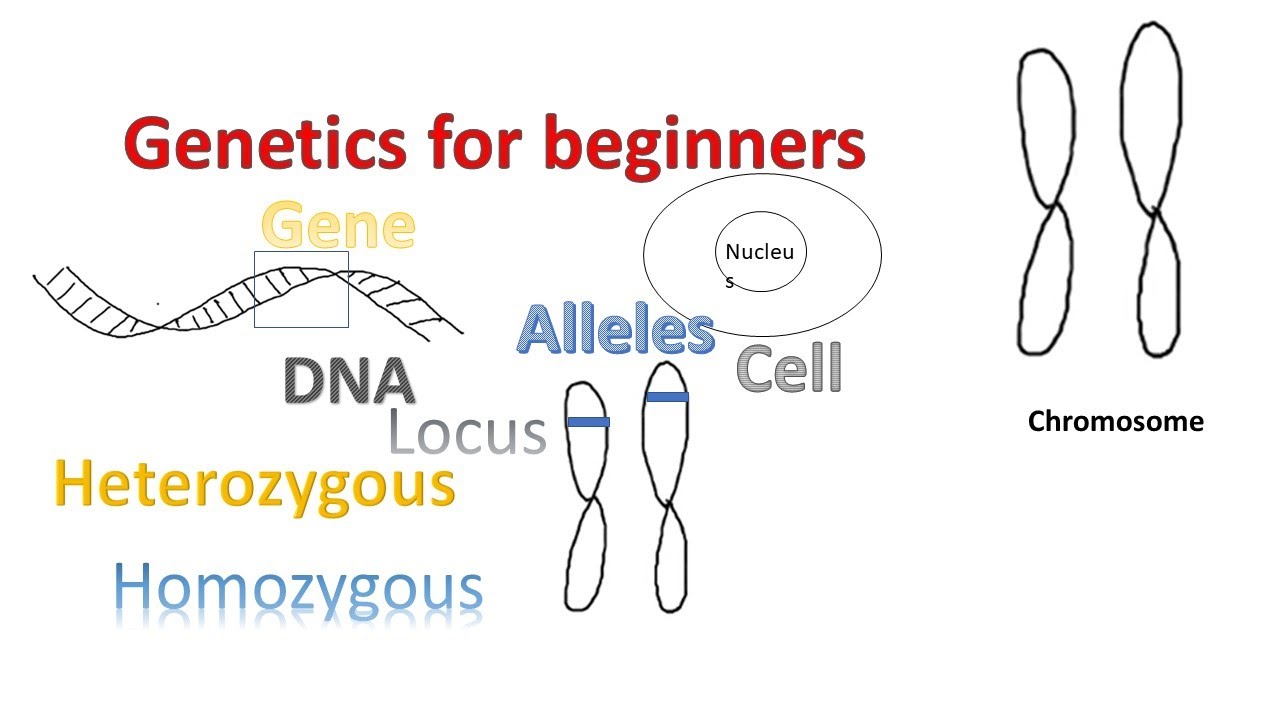
Genetics for beginners | Genes Alleles Loci on Chromosomes |

Conceitos básicos de genética - Biologia - Ensino Médio

Introduction to Cytogenetics (Filipino) Genes Alleles Chromosomes

Co-dominance and Incomplete Dominance | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy

Genotypic Ratios and Phenotypic Ratios for Punnett Squares

An Introduction to Mendelian Genetics | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)