Introduction to Force
Summary
TLDRIn this engaging lesson, the teacher explores the concept of force as the ability to change an object's state of motion, clarifying the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. Through hands-on demonstrations, students observe how varying the applied force and mass affects acceleration. The lesson emphasizes that force is a vector with both magnitude and direction, and distinguishes between contact and field forces, such as friction and gravity. With practical examples and student interactions, the lesson highlights the critical role of forces in understanding motion and the dynamics of objects.
Takeaways
- 😀 A force is defined as the ability to cause a change in the state of motion of an object.
- 😀 Force, mass, and acceleration are interconnected concepts essential to understanding motion.
- 😀 Increasing the mass on a mass hanger increases the force applied to a block, leading to greater acceleration.
- 😀 If the mass of a block increases while keeping the force constant, its acceleration decreases due to increased resistance to motion.
- 😀 The presence of a force does not always guarantee a change in motion; factors like friction can prevent acceleration.
- 😀 Forces are vector quantities, meaning they have both magnitude and direction.
- 😀 There are two main categories of forces: contact forces (e.g., friction, applied force) and field forces (e.g., gravity, magnetic force).
- 😀 Friction plays a significant role in determining whether an object will accelerate or remain stationary.
- 😀 The force of gravity is an example of a field force, acting at a distance without direct contact.
- 😀 Understanding these principles of force is foundational for further studies in physics.
Q & A
What is the definition of force according to the transcript?
-Force is defined as the ability to cause a change in the state of motion of an object.
How are force, mass, and acceleration related?
-Force, mass, and acceleration are interconnected; force can cause acceleration, and mass is a measure of an object's resistance to that acceleration.
What happens to the acceleration of the block when mass is added to the mass hanger?
-Adding mass to the mass hanger increases the force applied to the block, resulting in greater acceleration of the block.
What effect does increasing the mass of the block have on its acceleration?
-Increasing the mass of the block raises its resistance to acceleration, thus decreasing its acceleration if the applied force remains constant.
What role does friction play when increasing the mass of the block?
-Friction increases as the mass of the block increases, which can balance the applied force and prevent acceleration.
What is a vector, and how does it relate to force?
-A vector has both magnitude and direction. Force is considered a vector because it involves both the strength of the force and the direction in which it acts.
What are contact forces?
-Contact forces are interactions between two objects that touch each other, such as applied force, friction force, and tension force.
What distinguishes field forces from contact forces?
-Field forces do not require the two interacting objects to be in direct contact; for example, gravity acts over a distance.
What are some examples of field forces mentioned in the transcript?
-Examples of field forces include the force of gravity, magnetic force, and electric force.
How does increasing inertia affect the necessary force to accelerate an object?
-While more inertia increases resistance to acceleration, it does not mean that a new minimum force is always required. Instead, factors like friction also influence the needed force.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

What is Newton's 2nd Law Of Motion? | F = MA | Newton's Laws of Motion | Physics Laws | Dr. Binocs

Newton's Laws of Motion (Tagalog)
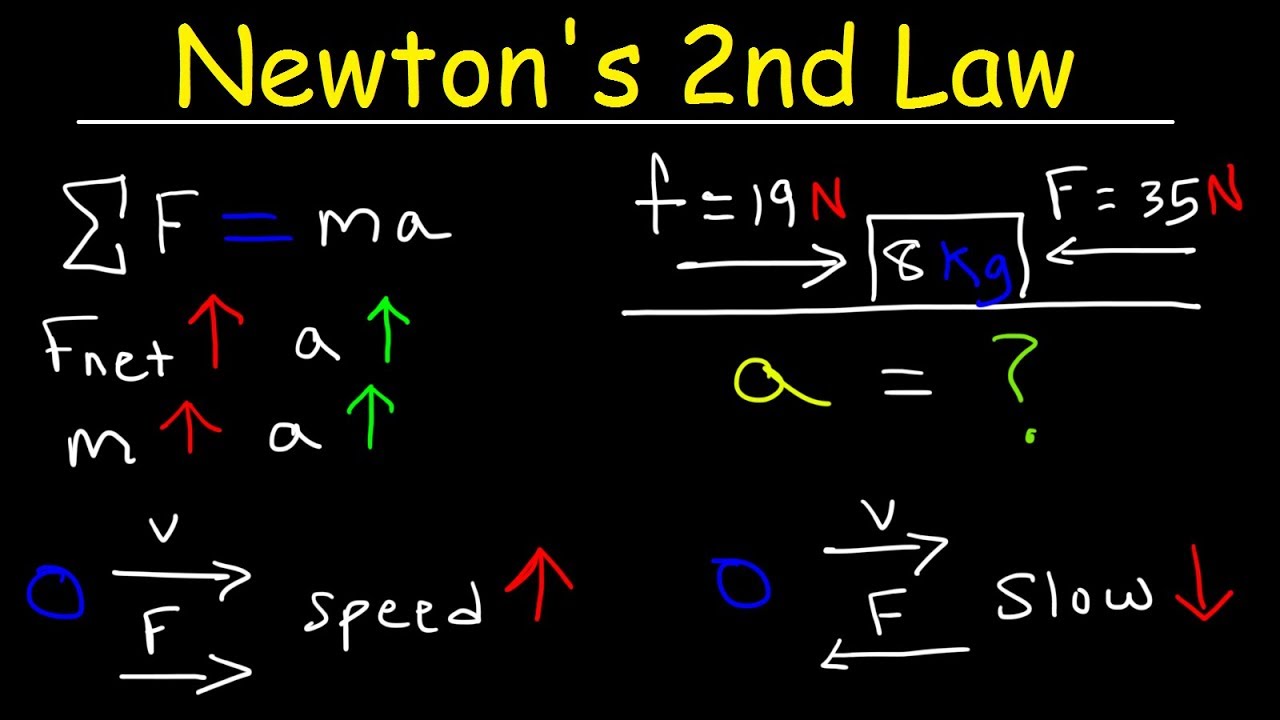
Newton's Second Law of Motion - Force, Mass, & Acceleration

BAB 4 GERAK DAN GAYA || Gaya dan Hukum Newton – IPA Kelas 7 Kurikulum Merdeka

GCSE Physics Revision "Newton's Second Law of Motion"

Newton's Laws of Motion: Law of Acceleration | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 1 Module 1 Part 2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
