Structured and Unstructured Storage in the Cloud
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the distinctions between structured and unstructured data storage in the cloud. Structured data, organized in rows and columns, is easy to analyze and manipulate, with examples including names and addresses. In contrast, unstructured data, comprising emails, videos, and documents, poses challenges for processing and requires advanced analytics for insights. The video outlines various storage solutions for both data types, recommending cloud storage for unstructured data and specific tools like Google BigQuery and Cloud SQL for structured data, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right solution based on the use case.
Takeaways
- 😀 Structured data is organized into columns and rows, commonly found in spreadsheets or relational databases.
- 😀 Examples of structured data include names, addresses, contact numbers, dates, and billing information.
- 😀 Structured data is easy to capture, access, and analyze, making it user-friendly for programming languages.
- 😀 Approximately 80% of all data is unstructured, which is more challenging to process using traditional methods.
- 😀 Unstructured data includes text and multimedia content, such as emails, documents, photos, videos, and presentations.
- 😀 Organizations are increasingly focused on mining unstructured data to gain competitive insights.
- 😀 When choosing a storage solution, consider the use case: unstructured solutions are suitable for files, backups, and blobs.
- 😀 Cloud storage is a recommended option for holding unstructured data.
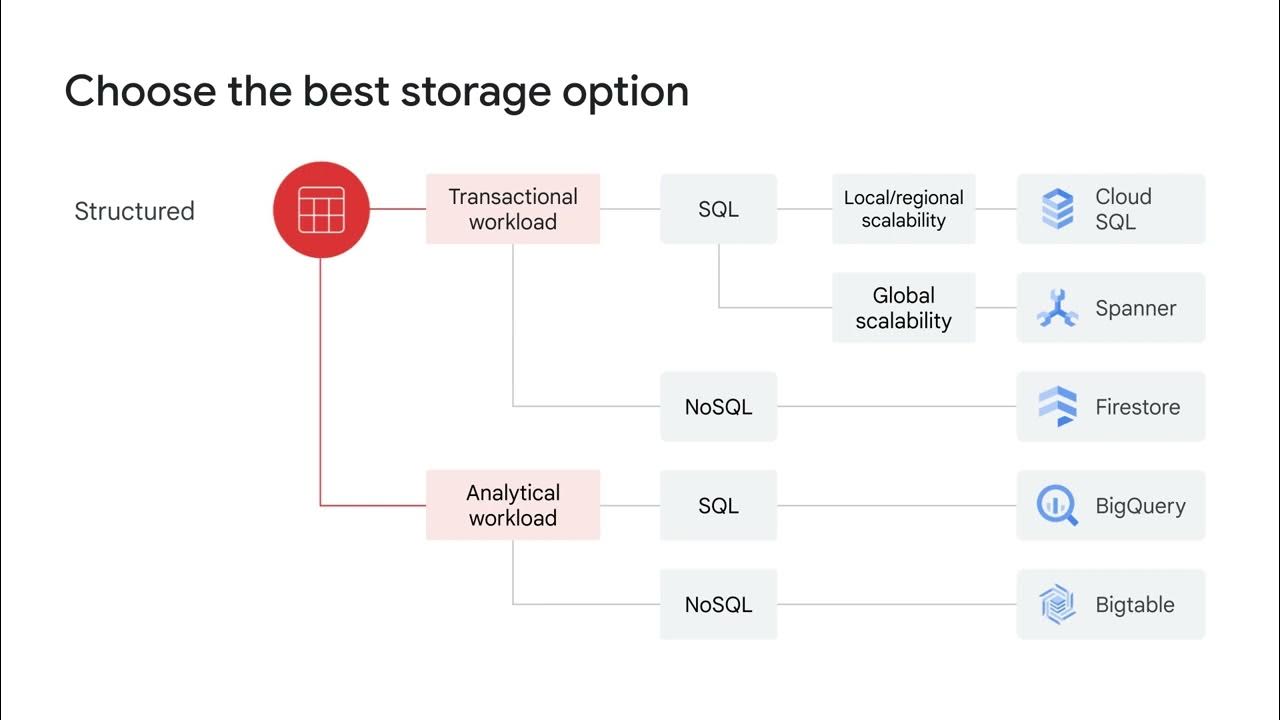
- 😀 For structured data needs, options like BigQuery and Cloud BigTable are suitable for workload analytics.
- 😀 Relational databases can be managed using MySQL or PostgreSQL through Cloud SQL, or you can opt for horizontally scalable options like Cloud Spanner.
Q & A
What is structured data?
-Structured data is organized in a predefined manner, typically fitting into columns and rows in spreadsheets or relational databases, making it easy to capture, access, and analyze.
Can you provide examples of structured data?
-Examples of structured data include names, addresses, contact numbers, dates, and billing information.
Why is structured data beneficial?
-Structured data can be easily understood by programming languages, allowing for quick manipulation and analysis.
What percentage of all data is estimated to be unstructured?
-It's estimated that around 80% of all data is unstructured.
What challenges are associated with unstructured data?
-Unstructured data is difficult to process or analyze using traditional methods due to the lack of internal identifiers, making it hard to search and identify.
What types of content are considered unstructured data?
-Unstructured data often includes text and multimedia content, such as email messages, documents, photos, videos, presentations, and webpages.
Why are organizations focusing on unstructured data?
-Organizations are increasingly mining unstructured data for insights that can provide a competitive edge in their operations.
What storage solution is recommended for holding files, backups, and logs?
-For holding files, backups, and logs, a good unstructured solution would be cloud storage.
Which options are available for structured data solutions?
-For structured data solutions, options include BigQuery, Cloud Bigtable, traditional managed MySQL or PostgreSQL databases using Cloud SQL, and horizontally scalable databases like Cloud Spanner.
What is a recommended noSQL option for applications?
-Cloud Datastore is a solid choice for a simple noSQL option to use for applications.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)