Big Data Training | Data Structures Explained | EBDP Module 1.5
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the different types of data structures, focusing on structured, unstructured, semi-structured data, and metadata. Structured data is highly organized in predefined formats like tables, ideal for relational databases. Unstructured data lacks a set structure and requires advanced techniques like NLP and machine learning for analysis. Semi-structured data lies between the two, offering some flexibility with formats like XML and JSON. Finally, metadata provides valuable context and characteristics about the data, aiding in data governance and discovery. Understanding these distinctions is essential for effective data management.
Takeaways
- 😀 Structured data is the most organized and easily recognizable type of data, arranged in rows and columns for easy processing and analysis.
- 😀 Unstructured data lacks a predefined format, making it challenging to store and analyze directly, and includes text, images, audio, and video files.
- 😀 Semi-structured data has some organization, using tags, attributes, or metadata, making it more flexible than structured data but still easier to manage than unstructured data.
- 😀 Metadata is data about data, providing essential information about a data set's characteristics, attributes, and properties, such as creation date and author.
- 😀 Structured data is typically used in relational databases, spreadsheets, and SQL databases, where it can be easily accessed and modified.
- 😀 Unstructured data requires advanced techniques like natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to extract valuable insights.
- 😀 Semi-structured data formats, such as XML and JSON, allow for variations in the number and types of fields while maintaining some structure.
- 😀 Understanding metadata is crucial for data governance, data discovery, and data management processes.
- 😀 Structured data is highly suitable for databases, making it easy to store, process, and analyze data with clear formats.
- 😀 Unstructured data is diverse and includes sources like social media posts, audio, video files, and documents, all of which require advanced processing techniques.
- 😀 The key difference between structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data lies in how organized and flexible their formats are, impacting how easily they can be stored and analyzed.
Q & A
What is the main characteristic of big data discussed in the previous module?
-The main characteristic of big data discussed is its ability to process unstructured data.
Why is there a difference in data structures?
-The difference in data structures is due to the need for computers to efficiently store and organize data on storage devices.
What is a data structure?
-A data structure is a way of organizing and storing data in a computer so that it can be accessed and modified efficiently.
What is the most organized and easily recognizable type of data?
-Structured data is the most organized and easily recognizable type of data.
How is structured data typically organized?
-Structured data is organized in a predefined format with well-defined rows and columns.
Where is structured data commonly found?
-Structured data is commonly found in spreadsheets, SQL databases, and other organized data sets.
What makes unstructured data more challenging to process?
-Unstructured data lacks a predefined format, making it more difficult to store, analyze, and extract insights from directly.
What are some examples of unstructured data?
-Examples of unstructured data include text documents, images, audio files, video files, and social media posts.
What techniques are required to extract insights from unstructured data?
-Advanced techniques such as natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning are required to extract insights from unstructured data.
What is semi-structured data, and how does it differ from structured data?
-Semi-structured data has some organizational structure, often using tags, attributes, or metadata, making it more flexible than structured data but less organized than fully structured data.
What are some common formats for semi-structured data?
-Common formats for semi-structured data include XML and JSON.
What is metadata?
-Metadata is data about data, providing information about a dataset's characteristics, attributes, and properties.
Why is metadata important in data management?
-Metadata is crucial in data governance, data discovery, and data management as it helps users understand the context and characteristics of the data.
How does metadata aid in understanding a dataset?
-Metadata acts as a description or label for a dataset, including details such as the data source, creation date, author, data format, and other relevant information.
What are the key differences between structured, unstructured, semi-structured data, and metadata?
-Structured data is highly organized with rows and columns, unstructured data lacks a predefined format, semi-structured data has some organizational structure with tags or metadata, and metadata provides descriptive information about a dataset.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
2. What is data? Different types of data? Structured | Semi-structured | Unstructured data
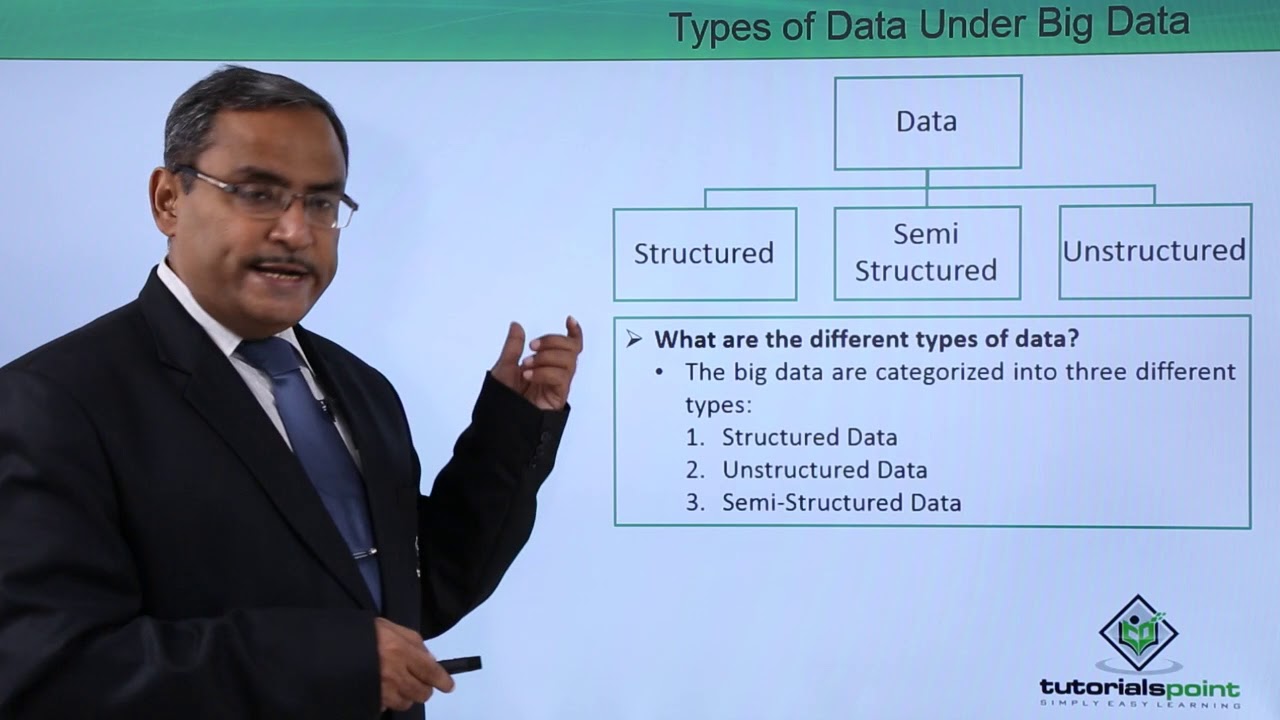
Types of Data Under Big data

51. Databricks | Pyspark | Delta Lake: Introduction to Delta Lake

What Is Big Data? Types, Structure & Why It Matters! 🚀 | upGrad KnowledgeHut

The 5Vs of Big Data (characteristics) #BigData #bigdataanalytics

Kuliah Metodologi Komunikasi: WAWANCARA - PROF RK (RACHMAT KRIYANTONO)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)