vid 2
Summary
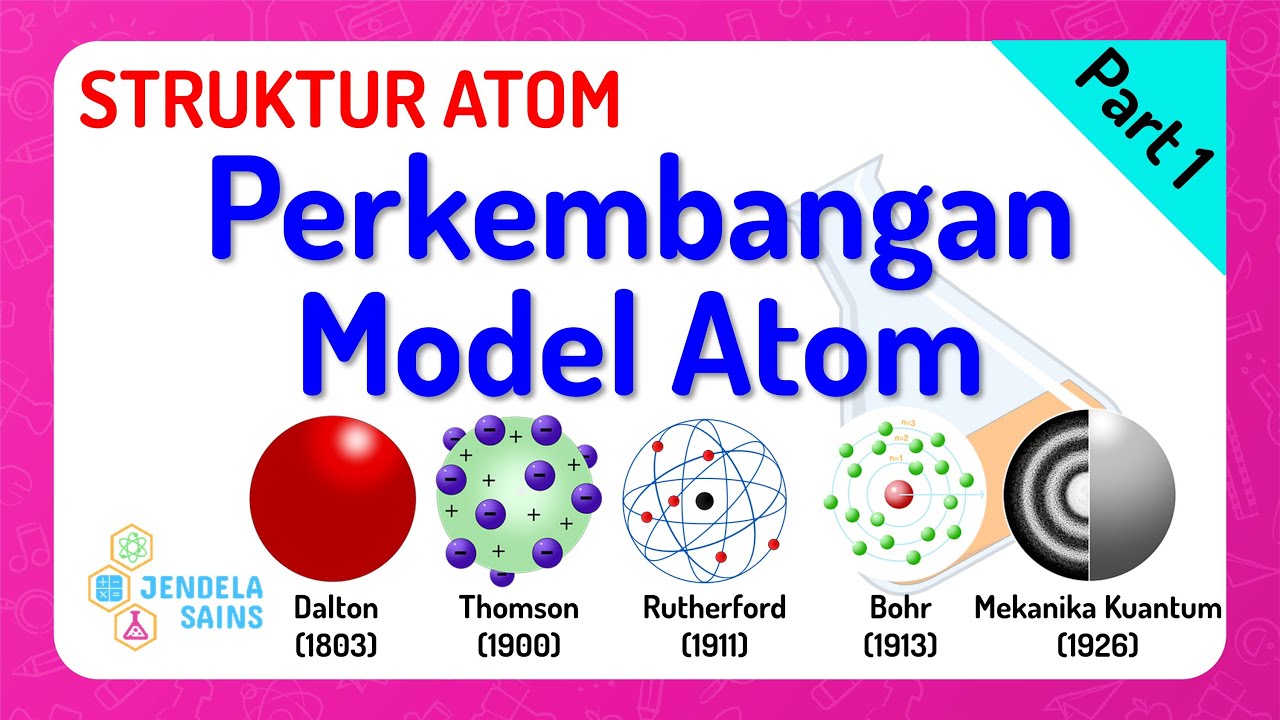
TLDRThe script discusses the evolution of atomic models, starting with Bohr's model based on classical mechanics, which treated electrons as discrete particles. This model faced challenges with the advent of quantum mechanics, introduced by Louis de Broglie, who proposed the wave-particle duality of matter. De Broglie's hypothesis suggested that small mass particles like electrons are better explained by their wave nature. Subsequent developments by Schrödinger and Heisenberg further refined atomic theory, introducing the concept of electron probability distributions, represented as 'clouds' around the nucleus, known as orbitals, which describe the regions of highest likelihood for finding electrons.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The Bohr model of the atom was initially based on classical mechanics, treating electrons as discrete particles.
- ⚛️ The emergence of wave mechanics, known as quantum theory, challenged the Bohr model.
- 📏 Louis de Broglie's hypothesis introduced the duality of matter, suggesting that particles like electrons exhibit both particle and wave characteristics.
- 🌊 De Broglie's theory posited that the behavior of small mass particles, such as electrons, is better explained through wave properties.
- 🌀 Electron trajectories within atoms should be understood as waves rather than fixed paths.
- 📜 In 1926, Erwin Schrödinger formulated a wave equation to explain the wave nature of electrons.
- ❓ Werner Heisenberg introduced the uncertainty principle, stating it's nearly impossible to measure two properties of a particle simultaneously, such as position and momentum.
- 🔗 Schrödinger's wave equation and Heisenberg's uncertainty principle together redefined atomic structure and electron behavior.
- 🌌 The quantum atomic theory suggests that electron positions in an atom are better explained through wave functions and probability distributions.
- 🌩️ Electrons are depicted as forming a negative charge cloud around the nucleus, known as an orbital, which represents areas with the highest likelihood of finding an electron.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the script regarding atomic models?
-The script discusses the transition from Bohr's atomic model, which was based on classical mechanics, to the quantum mechanical model that incorporates wave mechanics.
Who proposed the idea of wave-particle duality?
-Louis de Broglie proposed the concept of wave-particle duality, suggesting that matter, like electrons, can exhibit both particle and wave characteristics.
What does de Broglie's hypothesis state about small mass particles?
-De Broglie's hypothesis states that particles with small mass, such as electrons, are better described by their wave properties rather than their particle properties.
How did the understanding of electron trajectories change over time?
-Initially thought to be discrete paths, electron trajectories were later understood to be wave-like, leading to the concept of electron clouds around the nucleus.
What significant equation did Erwin Schrödinger formulate?
-Erwin Schrödinger formulated the wave equation in 1926, which explains the wave properties of electrons.
What is the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle?
-The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that it is impossible to measure both the position and momentum of a particle simultaneously with precision.
How did Max Born contribute to the interpretation of quantum mechanics?
-Max Born interpreted the probability of an electron's position in an atom, leading to the understanding that electrons are described as probability clouds rather than fixed orbits.
What is meant by the term 'orbital' in quantum mechanics?
-An orbital refers to a region in space around the nucleus where there is a high probability of finding an electron, depicted as a negatively charged cloud.
How does the modern quantum atomic theory differ from Bohr's model?
-The modern quantum atomic theory views electrons as existing in probabilistic clouds (orbitals) rather than in fixed paths, reflecting a more complex and accurate understanding of atomic structure.
What was the significance of the developments in quantum mechanics in the 1920s?
-The developments in quantum mechanics during the 1920s, including the contributions of de Broglie, Schrödinger, and Heisenberg, fundamentally changed the understanding of atomic structure and the behavior of subatomic particles.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)