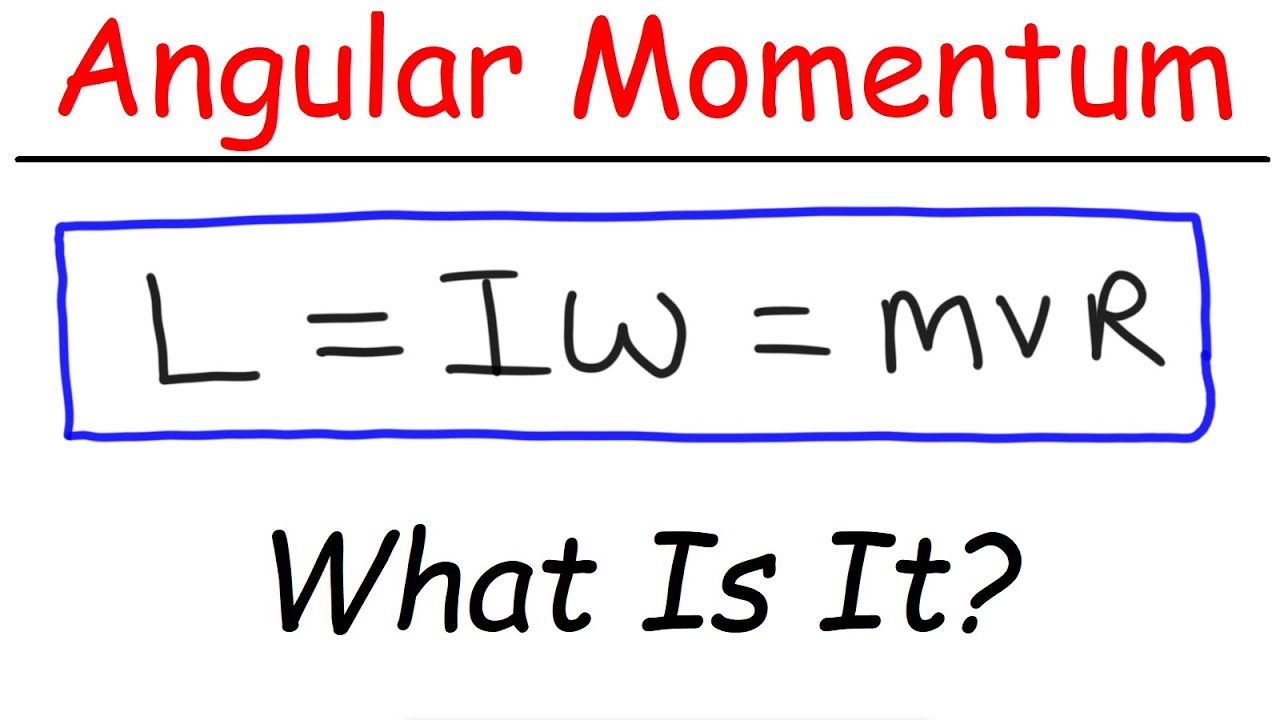
What Is Momentum?
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the concept of momentum as inertia in motion, defined as the product of mass and velocity. It emphasizes that both mass and speed affect an object's momentum, illustrated through examples like a massive truck compared to a mosquito, and a bullet versus an oil tanker. While a gentle throw makes a baseball easy to catch, a fast throw significantly increases its momentum. The video highlights that both a tiny bullet and a massive oil tanker have substantial momentum, making them difficult to stop, and concludes by reinforcing the idea of momentum as 'oomph' in motion.
Takeaways
- 😀 Momentum is defined as the product of mass and velocity, representing the amount of motion an object has.
- 🚚 A massive truck has significantly more momentum than a mosquito when moving at the same speed due to its greater mass.
- ⚾ A baseball thrown gently is easy to catch, while one thrown at high speed can cause injury due to its increased momentum.
- 🔫 A tiny bullet traveling at high speed has substantial momentum, illustrating that speed can greatly influence momentum.
- 🚢 An oil tanker moving slowly has a lot of momentum because of its enormous mass, making it hard to stop.
- 🏋️♂️ Inertia in motion is a key concept in understanding momentum, as objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by external forces.
- 🛳 Tugboats are often necessary to help maneuver large ships like oil tankers due to their significant momentum.
- 📏 Momentum can be affected by either increasing an object's mass or its velocity.
- ⚖️ The relationship between mass and velocity is crucial for understanding dynamics in physics and engineering.
- 🏀 Momentum principles are applicable in various fields, including automotive safety, sports, and engineering, influencing design and safety measures.
Q & A
What is momentum described as in the script?
-Momentum is described as inertia in motion and can be mathematically represented as the product of mass and velocity.
How can momentum be affected according to the transcript?
-Momentum can be affected by two factors: the mass of the object and its velocity.
Why does a massive truck have more momentum than a mosquito?
-A massive truck has more momentum than a mosquito because, at the same speed, its greater mass results in a higher momentum value.
What happens to the momentum of a baseball thrown at different speeds?
-A baseball thrown gently will be easy to catch, but if thrown at 100 miles per hour, it has significantly more momentum, making it difficult to catch and potentially dangerous.
How does the speed of a tiny bullet affect its momentum?
-A tiny bullet moving at high speed has a lot of momentum, which can cause substantial impact, demonstrating that even small objects can have significant momentum when moving quickly.
What example is given for a large object with high momentum at low speed?
-An oil tanker moving at only a few miles per hour is cited as an example of a large object with high momentum due to its great mass.
Why can't an oil tanker simply pull into the dock?
-An oil tanker can't just pull into the dock because its high momentum makes it difficult to stop, necessitating the assistance of powerful tugboats for maneuvering.
What is the relationship between mass, velocity, and momentum?
-The relationship is that momentum increases with either an increase in mass or an increase in velocity, which means that both factors contribute to the total momentum of an object.
What does the term 'oomph' refer to in the context of momentum?
-In this context, 'oomph' refers to the significant force or impact that an object with high momentum possesses, indicating its inertia in motion.
What two types of objects are compared to illustrate momentum?
-The script compares a fast-flying bullet and a creeping oil tanker to illustrate that both can have high momentum despite their differences in mass and speed.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)