Electrophoresis of amino acids
Summary
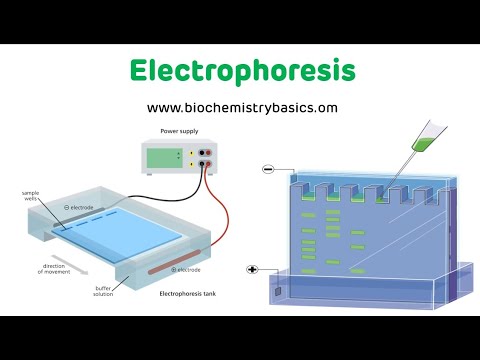
TLDRThe video explains the process of electrophoresis, an analytical tool used to separate amino acids and proteins. In a typical experiment, a mixture of amino acids is placed on special paper, soaked with a buffer, and subjected to an electric field. Positively charged ions move towards the negative electrode, while negatively charged ions migrate in the opposite direction. Neutral molecules remain at the origin. Once the separation is complete, the compounds are made visible by spraying with ninhydrin, which reacts with amino acids to form purple spots.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Electrophoresis is an important analytical tool for studying amino acids and proteins.
- 🧪 A mixture of amino acids is placed in the center of a long strip of special paper for analysis.
- 💧 Both ends of the paper are soaked in a buffer solution during the experiment.
- ⚡ A voltage is applied to electrodes in the buffer solution, creating an electric field.
- ➕ Positively charged ions move toward the negative electrode, while negatively charged ions move in the opposite direction.
- 🌀 Neutral species, like zwitterions, stay at the origin due to their lack of net charge.
- 🔍 After the electrophoresis is complete, separated compounds are visualized using ninhydrin.
- 🟣 Ninhydrin reacts with most alpha-amino acids, forming purple spots to indicate their presence.
- 🧬 The process helps separate and analyze different amino acids in the mixture.
- ⚙️ Electrophoresis is a key technique for identifying the properties and behaviors of amino acids and proteins.
Q & A
What is electrophoresis used for in the experiment described?
-Electrophoresis is used as an analytical tool to separate amino acids and proteins based on their charge.
Where is the mixture of amino acids placed during electrophoresis?
-The mixture of amino acids is placed in the center of a long strip of special paper.
What is the purpose of the buffer solution in electrophoresis?
-The buffer solution helps maintain a stable pH, allowing charged species to migrate toward the respective electrodes during the process.
What happens when a voltage is applied in the electrophoresis experiment?
-When a voltage is applied, positively charged ions move towards the negative electrode, and negatively charged ions move towards the positive electrode.
What happens to species with no net electrical charge, like zwitterions, during electrophoresis?
-Species with no net electrical charge, such as zwitterions, remain at the origin and do not migrate towards any electrode.
How are the separated compounds made visible after the electrophoresis experiment?
-The separated compounds are made visible by spraying the paper with ninhydrin, which reacts with most alpha-amino acids to form purple products.
What is the role of ninhydrin in the electrophoresis experiment?
-Ninhydrin is used to form a purple-colored reaction with most alpha-amino acids, allowing the separated amino acids to be visually detected.
Why do different amino acids migrate at different rates in electrophoresis?
-Different amino acids migrate at different rates due to variations in their net charge, which affects how strongly they are attracted to the respective electrodes.
What factors influence the direction of movement of amino acids in electrophoresis?
-The direction of movement is influenced by the net charge of the amino acids, with positively charged ones moving towards the negative electrode and negatively charged ones moving towards the positive electrode.
What type of ions move towards the negative electrode during electrophoresis?
-Positively charged ions, such as cations, move towards the negative electrode.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)