Ex1: Find an Equation of a Degree 4 Polynomial Function From the Graph of the Function
Summary
TLDRThe video explains how to find the equation of a degree 4 polynomial in factored form using its x-intercepts and an additional point. The speaker identifies the polynomial's zeros at -3, -1, 2, and 5, and sets up the function with these factors. Then, by substituting the y-intercept (0, -15), the value of the constant 'A' is determined to be -1/2. The final polynomial function is presented, and the graph's behavior with a negative leading coefficient is discussed. This method demonstrates how to construct a polynomial from given roots and points.
Takeaways
- 🔢 The goal is to find an equation for a degree 4 polynomial function in factored form.
- 🔍 The function will have at most four real rational zeros, as indicated by its degree.
- 📉 The graph shows four rational zeros corresponding to the x-intercepts (-3, -1, +2, +5).
- 🧮 The polynomial can be written in factored form using the zeros (x + 3)(x + 1)(x - 2)(x - 5).
- 📐 A constant 'A' must be determined to complete the polynomial equation.
- 📝 To find 'A', the y-intercept (-15) is used, providing the point (0, -15) to substitute into the equation.
- ➗ By substituting x = 0 into the factored equation, the value of 'A' is found to be -1/2.
- ✅ The final polynomial equation is f(x) = -1/2(x + 3)(x + 1)(x - 2)(x - 5).
- ⬇️ The polynomial has a negative leading coefficient, which means the graph approaches negative infinity on both sides.
- 📊 The behavior of the graph matches what is expected for a degree 4 polynomial with a negative leading coefficient.
Q & A
What is the degree of the polynomial function discussed in the script?
-The degree of the polynomial function is 4.
How many real rational zeros or roots does the polynomial function have?
-The polynomial function has four real rational zeros or roots.
What are the x-intercepts of the polynomial function, according to the graph?
-The x-intercepts of the polynomial function are -3, -1, +2, and +5.
How do you write the polynomial function in factored form using the zeros?
-The polynomial function in factored form is written as F(x) = A(x + 3)(x + 1)(x - 2)(x - 5), where A is a constant.
What additional information is needed to determine the value of the constant 'A'?
-To determine the value of 'A', we need an additional point on the graph, such as the y-intercept.
What is the y-intercept of the function, and how is it used to find 'A'?
-The y-intercept is -15, and the point (0, -15) is used to substitute into the equation to solve for 'A'.
How is the value of 'A' calculated from the point (0, -15)?
-Substituting 0 for x into the equation gives 30A = -15. Solving for A gives A = -1/2.
What is the final equation of the polynomial function in factored form?
-The final equation of the polynomial function in factored form is F(x) = -1/2(x + 3)(x + 1)(x - 2)(x - 5).
What does the leading coefficient tell us about the end behavior of the polynomial function?
-Since the leading coefficient is negative and the degree is even, the function approaches negative infinity in both directions.
Why do the signs of the constants in the factors have the opposite sign of the zeros from the graph?
-The constants in the factors have the opposite sign of the zeros because when we solve for the roots, setting each factor to zero gives the corresponding zero.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Grade 10 - Illustrating and graphing polynomial functions | SirABC
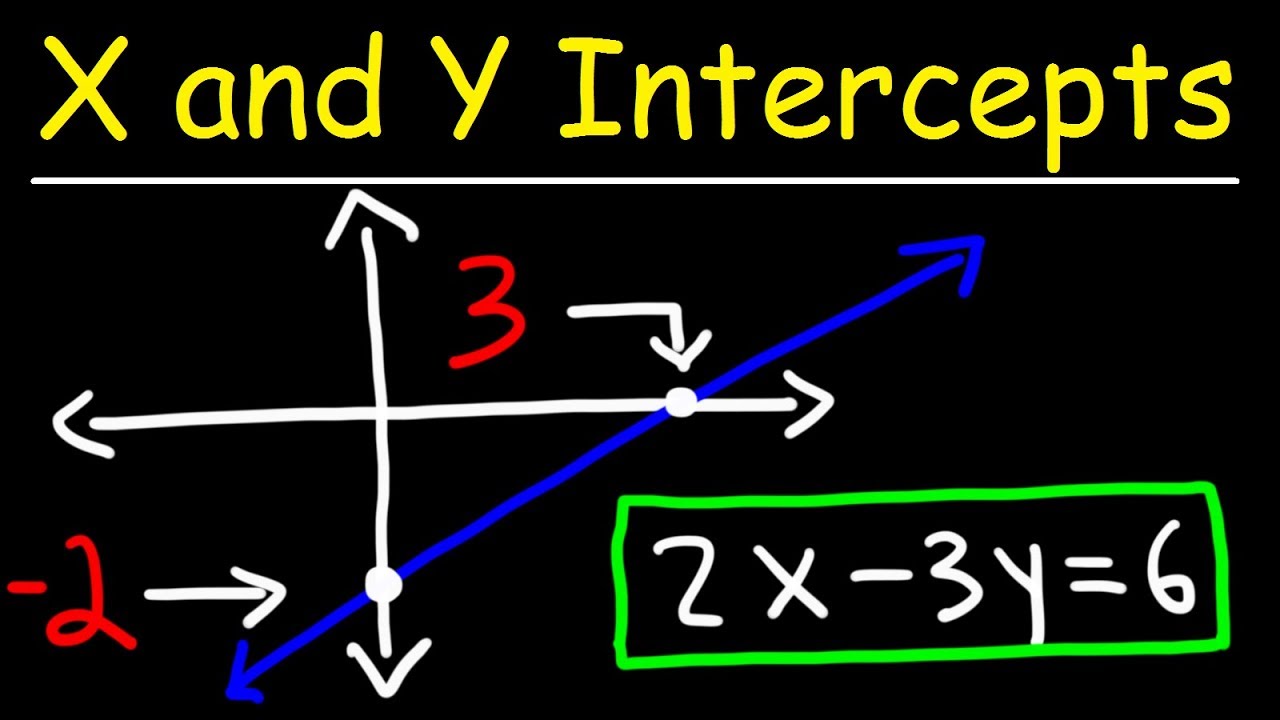
How To Find The X and Y Intercepts of a Line
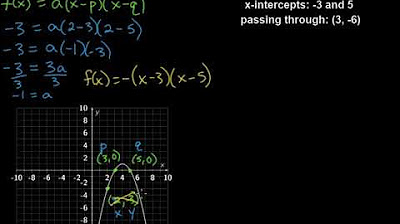
Writing Quadratic Functions in Intercept Form
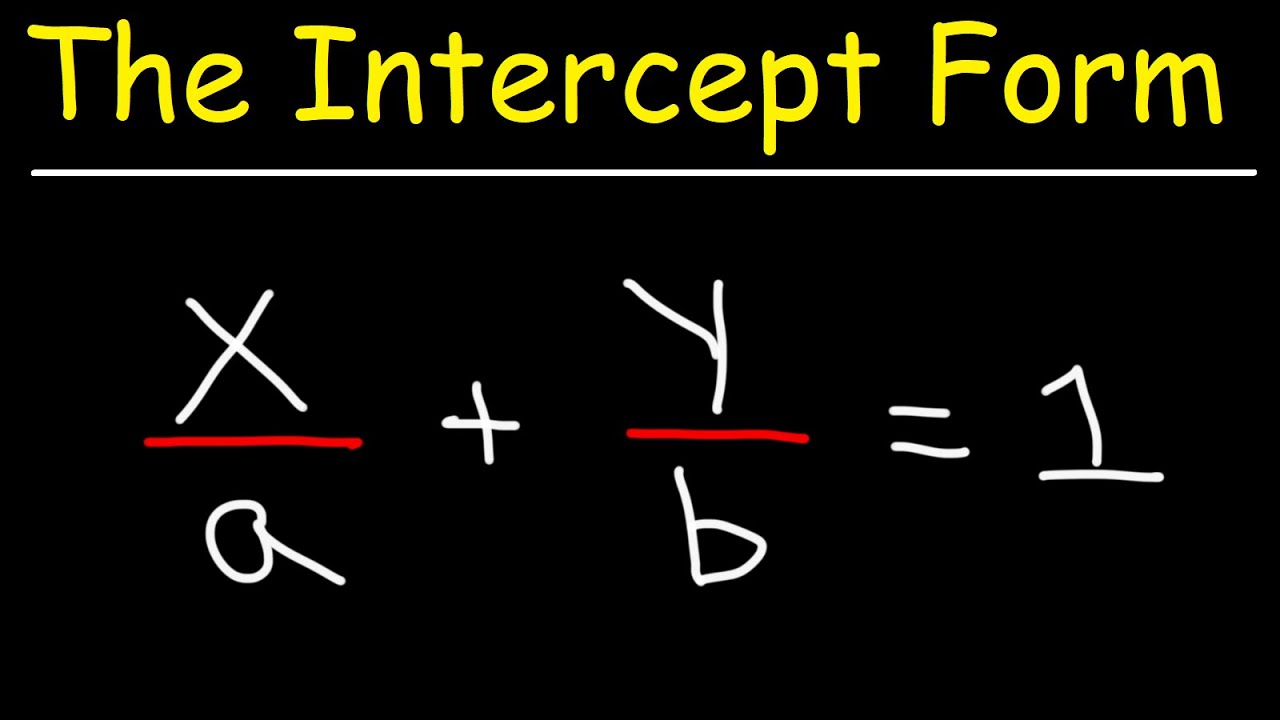
Linear Equations - The Intercept Form - Algebra
Lec 37 - Zeroes of Polynomial Functions
How To Find The Vertex of a Parabola - Standard Form, Factored & Vertex Form
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
