Beginners Guide to MACROMOLECULES
Summary
TLDRThis video from MooMooMath and Science provides an overview of the four main macromolecules essential for life: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. It explains that macromolecules are large molecules formed by bonding elements like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Carbohydrates offer quick energy and structural support, while lipids store energy and form cell membranes. Proteins, made of amino acids, perform various cellular functions, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) store and transfer genetic information. These biomolecules are crucial for the proper functioning of living organisms.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Macromolecules, also known as biomolecules, are essential large molecules that help organisms function.
- 🍞 The four main macromolecules are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
- ⚛️ Macromolecules are formed when elements like hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphate bond together.
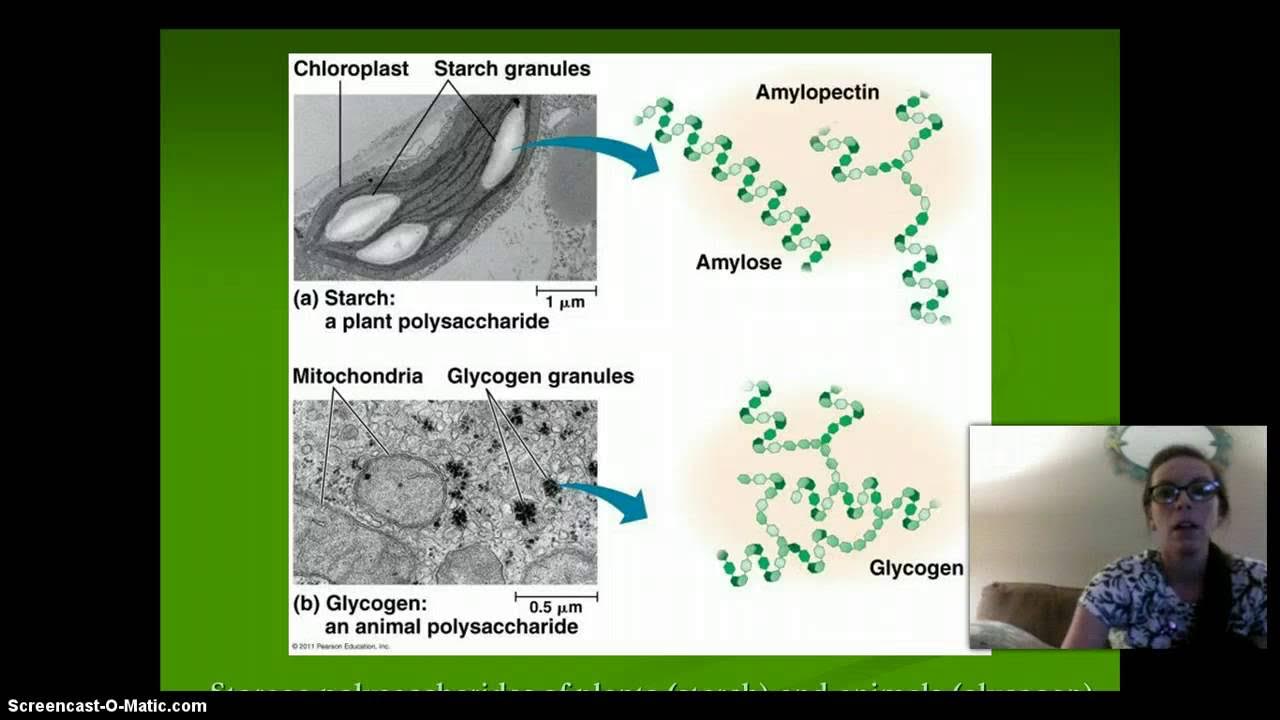
- 🥔 Carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio, providing quick energy and structural support.
- 🧈 Lipids, while technically not macromolecules, are grouped with them in biochemistry and include fats, waxes, and steroids.
- 💪 Proteins are large chains of amino acids that perform various functions in the body, such as communication and transportation.
- 🧬 Nucleic acids, composed of nucleotides, include DNA and RNA and are crucial for storing and transferring genetic information.
- ⚡ Carbohydrates provide quick energy and examples include sugars and starches.
- 🧪 Lipids are great for energy storage and are a key part of cell membranes.
- 📜 Nucleic acids hold and transmit hereditary and genetic information, vital for life processes.
Q & A
What are macromolecules, and why are they important?
-Macromolecules are large molecules formed when elements and smaller molecules bond together. They are essential for the survival and proper functioning of cells in living organisms.
What are the four main types of macromolecules mentioned in the script?
-The four main types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Which elements are commonly found in macromolecules?
-Macromolecules are made up of elements such as hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphate.
What is the main function of carbohydrates in living organisms?
-Carbohydrates primarily store energy and provide structural support. They also offer quick energy for humans.
What is the general composition of carbohydrates?
-Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. For example, glucose follows this composition.
Are lipids considered macromolecules, and what are their functions?
-Technically, lipids are not considered macromolecules, but in biochemistry, they are grouped with them. Lipids store energy, make up cell membranes, and include fats, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids.
What are proteins made of, and what role do they play in the body?
-Proteins are large chains of amino acids. They perform various functions such as communication, transportation, and structural support. For example, the protein amylase helps break down food, and collagen binds skin together.
How many amino acids are used by the human body, and how are they organized?
-The human body uses 20 amino acids, and their organization is directed by RNA, which carries instructions to the ribosome.
What are nucleic acids, and why are they important?
-Nucleic acids are long chains of nucleotides composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphate. They are crucial because they store and transfer genetic and hereditary information.
Can you give examples of nucleic acids and their roles?
-Examples of nucleic acids include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA stores genetic information, while RNA helps transfer and translate that information for cellular functions.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)