Recombinant DNA
Summary
TLDRThis lesson covers the process of creating recombinant DNA, where DNA molecules are formed by combining genetic material from different sources. The video explains key terms such as plasmids, enzymes, and sticky ends. It illustrates the steps of isolating a target gene, cutting DNA with enzymes, and combining it with a bacterial plasmid to form recombinant DNA. The bacterial cells replicate this recombinant DNA, which has been used in fields like medicine to produce synthetic drugs such as insulin. Viewers are encouraged to explore more benefits of recombinant DNA in scientific research.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Recombinant DNA is created by combining genetic material from different sources to form sequences that wouldn't naturally occur in organisms.
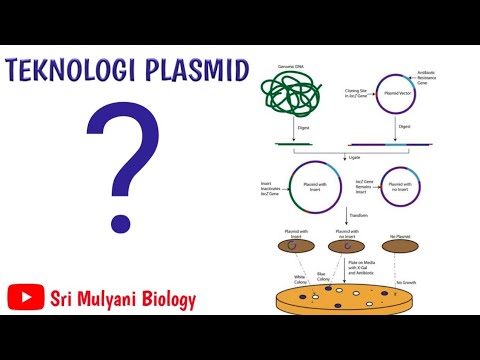
- 🧬 A plasmid is a circular, self-replicating DNA found in bacteria and is used in recombinant DNA processes.
- ✂️ Enzymes act as molecular scissors that cut DNA at specific sequences, facilitating the recombination process.
- 🔗 The process of cutting DNA with enzymes is called digestion, which creates 'sticky ends' that allow DNA pieces to be joined.
- 🔄 In recombinant DNA processes, human genes (e.g., for growth hormones) are combined with bacterial plasmids, creating a new DNA structure.
- 🦠 Recombinant DNA plasmids are inserted into bacterial cells, which replicate the plasmid and produce many copies of the recombinant DNA.
- 💉 A key medical application of recombinant DNA is the production of synthetic drugs, such as insulin.
- 📅 Before 1977, insulin was obtained from animals, which was expensive and risky; recombinant DNA technology has made synthetic insulin production safer and more efficient.
- 🧪 Recombinant DNA technology allows for large-scale production of biologically important substances in lab conditions.
- 📚 Recombinant DNA has broad applications in medical and scientific research, such as creating synthetic drugs and exploring genetic therapies.
Q & A
What is recombinant DNA?
-Recombinant DNA is DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination, such as molecular cloning, which bring together genetic material from multiple sources to create new sequences that would not otherwise be found in biological organisms.
What is the basic process of creating recombinant DNA?
-The process involves taking a piece of DNA and combining it with another strand of DNA, using enzymes to cut and join these segments, and then inserting the combined DNA into a host cell for replication.
What is a plasmid, and how is it relevant in recombinant DNA technology?
-A plasmid is a circular, self-replicating piece of DNA found in bacteria, separate from the chromosomal DNA. It is used in recombinant DNA technology as a vector to carry and replicate foreign genes.
What role do enzymes play in the creation of recombinant DNA?
-Enzymes act as molecular scissors, cutting the DNA at specific sequences. This cutting process is called digestion, and the enzymes help create 'sticky ends' on the DNA fragments, which facilitate the joining of different DNA segments.
What are 'sticky ends' in the context of recombinant DNA?
-'Sticky ends' are overhangs created on the DNA when it is cut by specific enzymes. These ends have a sequence that allows them to pair with complementary sticky ends on another DNA fragment, facilitating the recombination process.
What is the significance of using the same enzyme to cut both the plasmid and the target gene?
-Using the same enzyme ensures that the sticky ends of the plasmid and the target gene are compatible and can easily pair together, enabling the formation of recombinant DNA.
How is recombinant DNA introduced into bacterial cells?
-The recombinant DNA plasmid is inserted into a bacterial cell, where the cell then replicates, creating many copies of the recombinant DNA for further use.
What medical application of recombinant DNA is highlighted in the script?
-The script mentions the production of human insulin using recombinant DNA technology. Before this technique, insulin was sourced from animals, which was expensive and carried risks of allergic reactions. Using recombinant DNA to produce insulin is more efficient and safer.
Who were the researchers responsible for producing human insulin using recombinant DNA?
-Dr. Riggs, Dr. Iur, and Dr. Boer were the researchers who first produced human insulin using recombinant DNA in 1977.
What are the broader benefits of recombinant DNA technology in science and medicine?
-Recombinant DNA technology enables the production of synthetic drugs like insulin, development of genetically modified organisms, and advancement in genetic research, offering new tools for treating diseases and understanding genetic functions.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)