Vietnam War in 13 Minutes - Manny Man Does History
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the history of Vietnam, focusing on its colonial past under French Indochina, the rise of the Viet Minh under Ho Chi Minh, and the subsequent conflicts that defined the 20th century. Key events include the First and Second Indochina Wars, the Vietnam War, and the eventual victory of communist forces. It delves into U.S. involvement, from initial military aid to full-scale intervention, and how the war left deep scars on both Vietnam and the United States. The video's narrative concludes with the unification of Vietnam and the long-lasting impacts of the war.
Takeaways
- 🇻🇳 Vietnam was part of French Indochina, a colony established in 1887, which remained under French control until World War II when Japan invaded.
- 👑 Emperor Bao Dai ruled Vietnam as a puppet under Japanese control during WWII.
- 🚩 Ho Chi Minh, leader of the Viet Minh, declared Vietnamese independence after Japan's defeat, starting the First Indochina War against France.
- ❄️ The Cold War tensions influenced the conflict, with China and the Soviet Union backing the Viet Minh and the USA and Britain supporting the French-backed South Vietnam.
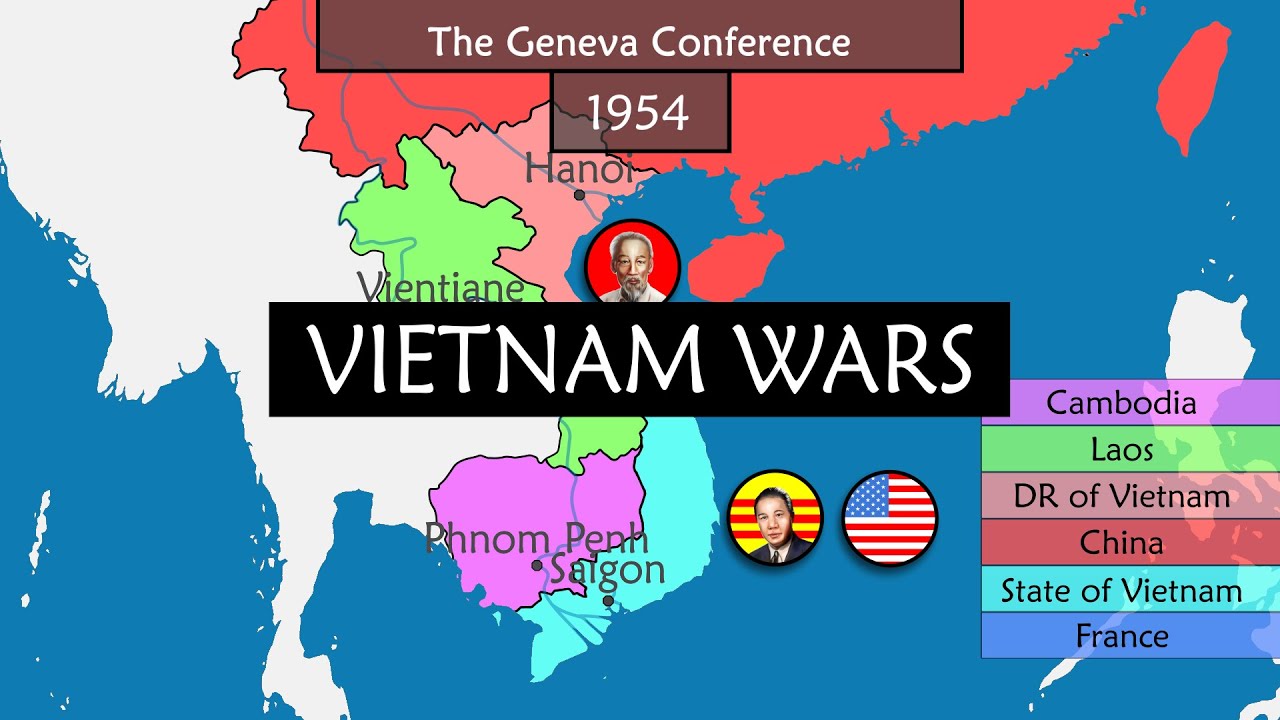
- ✌️ The Geneva Accords divided Vietnam into North and South, with Ngo Dinh Diem leading South Vietnam and Emperor Bao Dai in a ceremonial role.
- 🚶♂️ The USA gradually increased its involvement, providing military advisors but initially reluctant to deploy troops under President Eisenhower.
- 🔥 The Vietnam War escalated, with US President Johnson using the Gulf of Tonkin incident to push for direct involvement.
- 🔫 The war saw heavy US bombardments, including napalm attacks, and the conflict intensified despite high US troop deployments.
- 🎖️ The Tet Offensive in 1968 was a turning point in the war, leading to declining US public support for the conflict and damaging President Johnson’s credibility.
- 🏳️ The war ended in 1975 with the fall of Saigon, unifying North and South Vietnam under communist rule. Vietnam remains scarred by the war, both physically and psychologically.
Q & A
What was French Indochina, and why was it established?
-French Indochina was a French colony in Southeast Asia established in 1887, primarily to reinforce Catholic missionaries and expand French influence in the region.
What led to the end of French control in Vietnam during World War II?
-During World War II, France was invaded by Nazi Germany, and Japan took control of French Indochina. Japan ruled through the French protectorate Emperor Bao Dai, who acted as a puppet leader.
Who was Ho Chi Minh, and what was his role during and after World War II?
-Ho Chi Minh was the leader of the Viet Minh, a communist army that fought against the Japanese occupiers during World War II. After Japan's defeat, the Viet Minh declared Vietnamese independence and formed the Democratic Republic of Vietnam.
What were the Geneva Accords, and how did they affect Vietnam?
-The Geneva Accords, signed after the Viet Minh's victory over the French, divided Vietnam into two states: the State of Vietnam (South Vietnam) and the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North Vietnam). It also granted independence to Cambodia and Laos, effectively ending French Indochina.
What was the significance of the Ho Chi Minh Trail during the Vietnam War?
-The Ho Chi Minh Trail was a vital supply route used by North Vietnam to support the Viet Cong and NLF insurgents in South Vietnam. It ran through Laos and Cambodia, allowing the North to funnel troops and supplies to the South.
How did religious tensions contribute to instability in South Vietnam under Ngo Dinh Diem's leadership?
-Diem, a Roman Catholic, discriminated against the predominantly Buddhist population, banning Buddhist flags and raiding pagodas. This led to widespread protests and increased instability, culminating in a coup that resulted in Diem's assassination.
What was the Gulf of Tonkin incident, and how did it lead to increased U.S. involvement in Vietnam?
-The Gulf of Tonkin incident occurred in 1964 when the USS Maddox fired warning shots at North Vietnamese torpedo boats. Although a second reported attack turned out to be false, the event was used by President Johnson to gain Congressional approval for the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, allowing him to escalate U.S. military involvement without a formal declaration of war.
What was the Tet Offensive, and why was it significant in the Vietnam War?
-The Tet Offensive, launched by the NLF and North Vietnamese forces in 1968, was a surprise attack on over 100 cities in South Vietnam. While the U.S. and South Vietnam forces eventually countered the offensive, it was a psychological blow to U.S. morale, leading to increased anti-war sentiment in the U.S.
How did the U.S. public's perception of the Vietnam War change after the My Lai Massacre?
-The My Lai Massacre, where between 347 and 504 unarmed civilians were killed by U.S. troops, was exposed to the public in 1969. The revelation shocked the American public and further eroded support for the war.
What were the consequences of the Paris Peace Accords in 1973 for the Vietnam War?
-The Paris Peace Accords, signed in January 1973, officially ended U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War. All U.S. ground troops were withdrawn by March 1973, although fighting continued between North and South Vietnam.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

La Guerre du Vietnam et guerre d'Indochine

GCSE History Rapid Revision: Dien Bien Phu, 1954

August Revolution | Quick summary of Vietnamese history - EZ History

Vietnam War | The 20th century | World history | Khan Academy

The Vietnam War - Part 1 - Why Did The Vietnam War Start? - GCSE History
The Vietnam Wars - Summary on a Map
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
