RMIT University, Understanding the Business Environment, Assessment 3: Presentation
Summary
TLDRAndrew Hadra's presentation explores the economic impacts of taxes on consumer and producer welfare, focusing on consumption taxes and tariffs. He discusses how these taxes affect market equilibrium, leading to deadweight loss and reduced economic welfare. Andrew also touches on health taxes, suggesting that while they may initially decrease economic activity, they can boost long-term productivity and GDP by improving public health.
Takeaways
- 📈 Consumer Surplus is the difference between what consumers are willing to pay and what they actually pay, represented by the blue triangle.
- 🔶 Producer Surplus is the difference between the price a company receives and the price it is willing to sell at, represented by the orange triangle.
- 💔 Consumption taxes, like sales tax, increase the cost of goods and services, leading to a decrease in consumer and producer surplus, shown as a rectangle.
- 📉 The imposition of consumption taxes can cause a leftward shift in the supply curve (S), indicating a reduction in the supply of goods and services.
- 🛒 An increase in consumer spending due to taxes can lead to a lower overall demand, affecting the economy negatively.
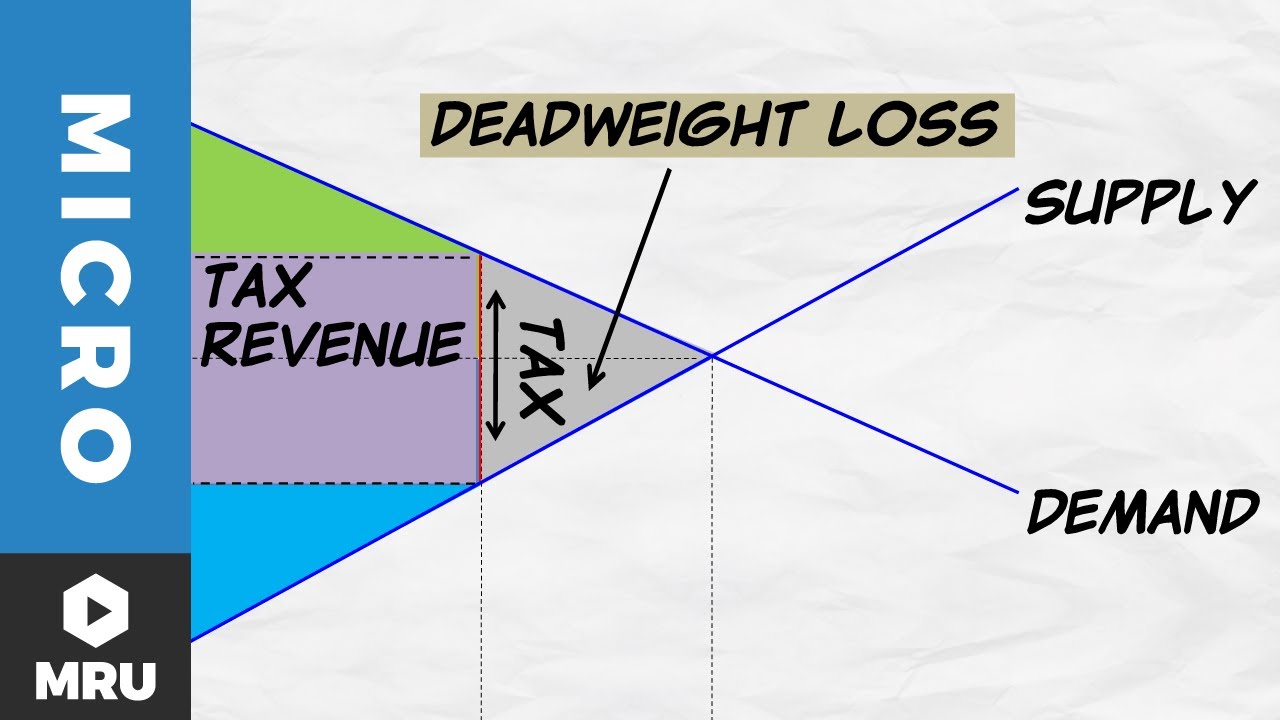
- 📉 The welfare impact of consumption taxes is shown by the reduction in consumer and producer surplus, creating a deadweight loss represented by the orange triangle.
- 🌐 Tariffs, as taxes on imports, protect domestic industries but can lead to inefficiencies and reduce welfare in the domestic economy.
- 📊 The introduction of tariffs causes a shift in the equilibrium price, leading to a decrease in the quantity of imports and a deadweight loss between domestic supply and demand curves.
- 💼 Macroeconomically, consumption taxes can lead to a decrease in aggregate demand, causing a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
- 🍏 Health taxes on harmful products can initially cause a leftward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve due to increased production costs.
- 🌿 In the long run, health taxes can improve public health, increasing workforce productivity and positively affecting the long-run aggregate supply curve.
- 📊 Econometric models can be used to analyze the correlation between health taxes and economic growth, with health as the dependent variable and taxes as the independent variable.
Q & A
What is consumer surplus and how is it represented in a demand and supply diagram?
-Consumer surplus is the difference between what consumers are willing to pay and what they actually pay. It is represented in a demand and supply diagram as the area of a triangle above the market price and below the demand curve, labeled in blue.
How does a consumption tax impact consumer surplus?
-A consumption tax increases the cost of goods and services, leading to a higher market price. This results in a decrease in consumer surplus as consumers pay more for the same quantity of goods, represented by a movement along the demand curve without a shift.
What is producer surplus and where is it located in the diagram?
-Producer surplus is the difference between the price a company receives and the price it is willing to accept. It is shown as the area of a triangle below the market price and above the supply curve, labeled in orange.
How does a consumption tax affect producer surplus?
-A consumption tax can reduce producer surplus because it may lead to a decrease in the quantity of goods demanded, which in turn can lower the price received by producers due to the tax, causing a movement along the supply curve.
What is meant by deadweight loss in the context of consumption taxes?
-Deadweight loss refers to the inefficiency and underproduction caused by taxes, represented by the area between the equilibrium levels before and after the tax imposition, labeled in orange. It signifies the net loss of both consumer and producer welfare due to the tax.
How does a tariff on imports affect the domestic market?
-A tariff on imports raises the price for consumers and lowers the price received by producers, leading to a new equilibrium price that is higher than the free trade price. This causes domestic producers to supply more and consumers to demand less, reducing the quantity of imports.
What is the difference between the deadweight loss caused by a consumption tax and a tariff?
-The deadweight loss caused by a consumption tax is represented by the area between the initial and new equilibrium levels, while the loss due to a tariff is the area between the domestic supply and demand curves, showing the loss of overall economic welfare due to the tariff.
How does a consumption tax on the macroeconomic level affect aggregate demand?
-A consumption tax can lead to a decrease in consumer spending due to lower disposable income, which may cause a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve, representing a reduction in overall demand in the economy.
What are the potential long-term economic benefits of a health tax on harmful products?
-A health tax can improve public health by discouraging consumption of harmful products. This can increase workforce productivity and lifespans, positively affecting the long-run aggregate supply curve and potentially boosting real GDP and economic growth.
How can an econometric model help in understanding the impact of health taxes on economic growth?
-An econometric model can be used to find correlations between health taxes (independent variable) and health outcomes or economic growth (dependent variable). It can help identify potential core founders and guide the analysis to understand the true effects of imposing such taxes.
What is the short-term impact of a health tax on aggregate demand?
-In the short term, a health tax may lead to a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve as consumers reduce their spending on unhealthy goods. However, if the tax improves public health, it could lead to increased consumer spending and a rightward shift in the long run.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

LaiXinHong (s4042341) BUSM2562 Assessment 3 - Presentation and networking event
Tax Revenue and Deadweight Loss
Types of Taxes in the United States

National Income And Economic Welfare| Relation between National Income and Economic Welfare

PAJAK

Evaluating Government Intervention I A Level and IB Economics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
