Metamorphism
Summary
TLDRMetamorphic rocks are formed through metamorphism, a process involving physical and chemical changes caused by heat, pressure, and fluids. When rocks are buried deep beneath Earth's surface, they undergo transformation depending on the temperature, pressure, and water availability. Different geological settings, such as subduction zones, volcanic centers, and colliding continental plates, influence these changes. Key indicators of metamorphic conditions, such as index minerals like garnet and kyanite, provide clues to a rock’s formation environment. This summary highlights how metamorphic rocks differ from igneous and sedimentary rocks, with a focus on their unique formation processes.
Takeaways
- 🌋 Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing rocks undergo metamorphism due to high temperatures, pressures, or chemically active fluids.
- 🔥 If a rock is subjected to extreme heat and fully melts, it becomes magma and transforms into an igneous rock.
- 🔄 Metamorphic rocks sit between sedimentary and igneous rocks, formed under conditions of medium heat and pressure.
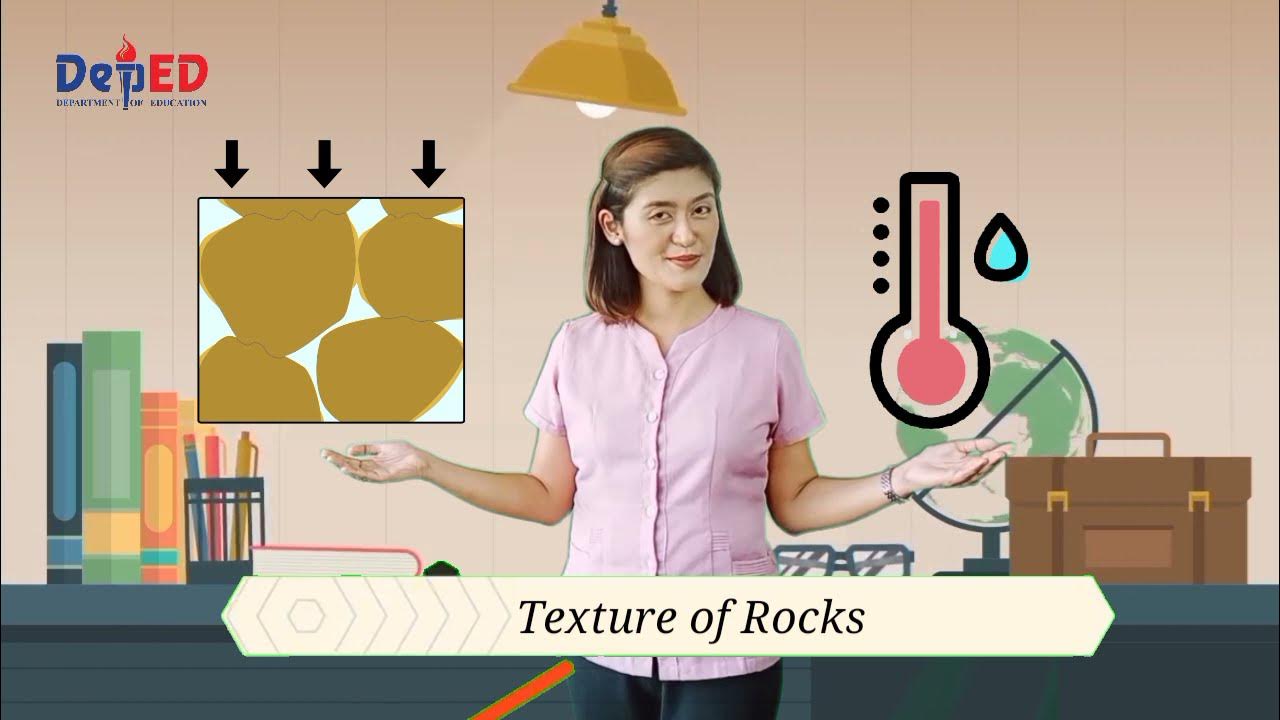
- 💧 The composition of metamorphic rocks depends on the parent rock's chemistry, temperature, pressure, and water availability.
- 🌍 Metamorphism occurs deep within Earth's crust, often due to burial or tectonic activities like subduction and continental collisions.
- 🗻 In subduction zones, high pressure but low temperatures lead to unique metamorphic environments due to the cold, sinking plate.
- ⛏️ Volcanic centers generate heat and water, resulting in chemical changes in rocks through processes like contact and hydrothermal metamorphism.
- 📏 Increased pressure leads to higher rock density and causes minerals with elongated shapes to align, forming foliation patterns.
- 🌡️ Heat can increase crystal size as atoms vibrate, migrate, and combine into larger structures without melting the rock.
- 🔍 Index minerals like garnet and kyanite help geologists identify the conditions under which metamorphic rocks were formed, providing clues about pressures and temperatures in specific geologic settings.
Q & A
What is metamorphism in rocks?
-Metamorphism is the process where rocks undergo physical and chemical changes due to exposure to elevated temperatures, pressures, or chemically active fluids beyond what is normally found near Earth's surface.
What happens to a rock if it melts completely during metamorphism?
-If a rock melts completely, it becomes magma and transitions into an igneous rock. This means that temperatures in metamorphism must be lower than the melting point.
How do temperature and pressure affect sedimentary and metamorphic rocks differently?
-Sedimentary rocks form under lower temperatures and pressures, compacting and cementing sediments. Metamorphic rocks form at higher temperatures and pressures, but not high enough for the rock to melt, sitting between sedimentary and igneous environments.
What factors determine the specific type of metamorphic rock that forms?
-The type of metamorphic rock depends on the parent rock's chemistry, the exact temperatures and pressures it was subjected to, and the amount of water available for chemical reactions.
Where is metamorphism likely to occur on Earth?
-Metamorphism occurs when surface rocks are buried beneath layers of sediment or lava, sinking deeper into the Earth's crust where pressures and temperatures increase. It also happens in geologic settings like subduction zones and converging continental plates.
What are the pressure and temperature conditions in subduction zones?
-In subduction zones, pressures increase significantly as the plate sinks deeper into the mantle, but temperatures rise more slowly because the subducting plate is cold and insulated.
How does water content influence metamorphic processes in subduction zones?
-Water content can be high in subduction zones due to water absorbed by sediments and rocks in contact with ocean water over millions of years. This water contributes to chemical reactions during metamorphism.
What is the difference between contact metamorphism and hydrothermal metamorphism?
-Contact metamorphism occurs near magma chambers where rocks undergo changes due to high temperatures, while hydrothermal metamorphism happens when hot chemically active fluids migrate through rocks, causing chemical alterations.
What physical changes occur in rocks during metamorphism?
-During metamorphism, rocks may experience increased density, and minerals with long or flat axes align to relieve pressure (foliation). Additionally, crystals can grow larger due to increased heat, as atoms migrate across solid structures.
What are index minerals and why are they important?
-Index minerals form under specific temperature and pressure conditions and serve as clues to the rock's metamorphic history. For example, garnet indicates higher pressures and temperatures, while kyanite suggests high pressure but relatively low temperature.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)