Geothermal 101
Summary
TLDRGeothermal energy harnesses heat from the Earth's interior, mainly generated by the decay of minerals and heat loss from the Earth's formation. Wells drilled into the Earth's crust extract this heat, often using water and steam. This heat can warm buildings directly or generate electricity by turning turbines. Geothermal energy is reliable for consistent power but poses risks such as CO2 emissions and lowered ground temperatures if not managed responsibly. Although it has high initial costs due to seismic testing and exploration, geothermal energy remains a promising, sustainable option for the future.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Geothermal energy is produced from the internal heat of the Earth.
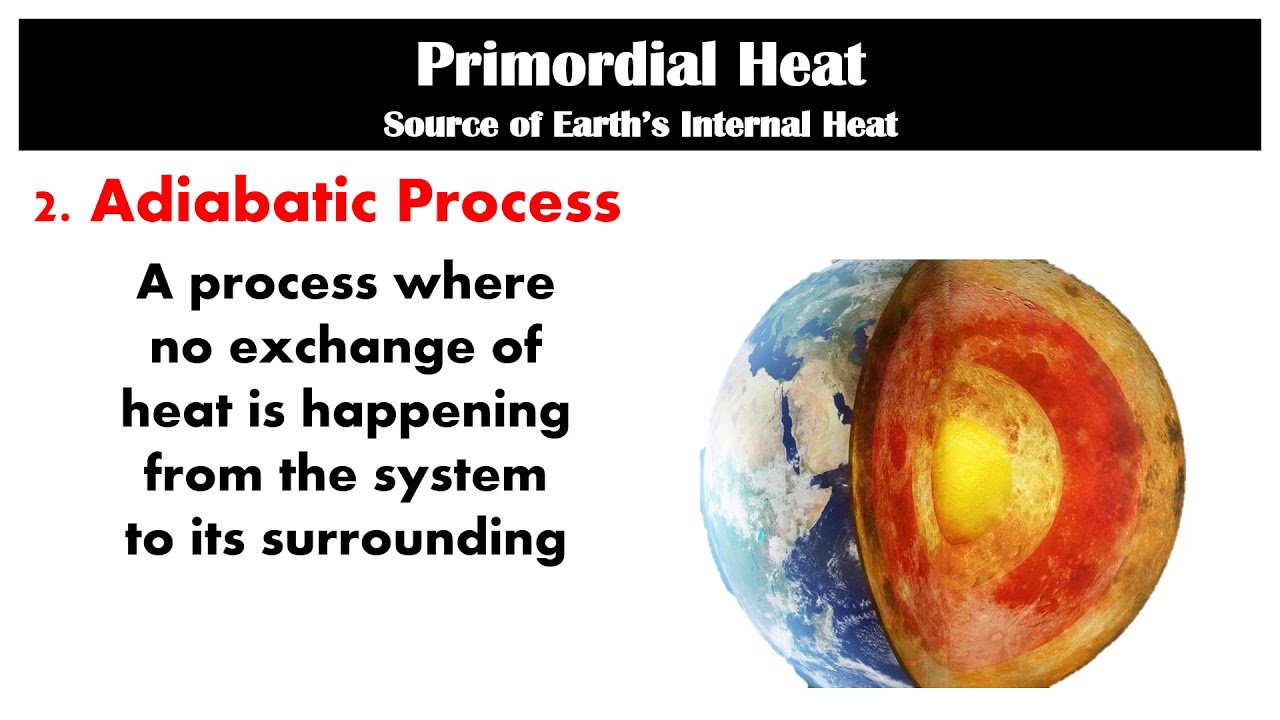
- 💥 The Earth's internal heat comes from radioactive decay of minerals and heat loss from its original formation.
- 🌡️ Geothermal wells are drilled 3 to 10 kilometers deep into the Earth's crust to access the heat.
- 🚿 Hot water and steam from geothermal sources can heat buildings or homes directly, either by circulation or through heat exchangers.
- ⚡ Geothermal energy can be used to produce electricity by generating steam that turns turbines on a generator.
- 🌋 The major regions for geothermal development are located in tectonically and volcanically active areas of the world.
- 🔋 Geothermal energy provides consistent power generation, making it a reliable source of baseload electricity.
- 💨 One environmental concern is the potential release of CO2 and hydrogen sulfide stored in groundwater during geothermal extraction.
- 🌡️ Drawing heat from the Earth's crust irresponsibly can lower ground temperatures below the surface.
- 💰 The upfront costs of geothermal energy production are high due to the need for seismic sensing, drilling, and testing to confirm production capabilities.
Q & A
What is geothermal energy?
-Geothermal energy refers to the production of energy using the internal heat of the Earth.
How is the Earth's internal heat generated?
-The Earth's internal heat is generated through the radioactive decay of minerals and the continual heat loss from the Earth's original formation.
At what depth are geothermal wells drilled?
-Geothermal wells are typically drilled at a depth of 3 to 10 kilometers into the Earth's crust.
What methods are used to extract geothermal heat?
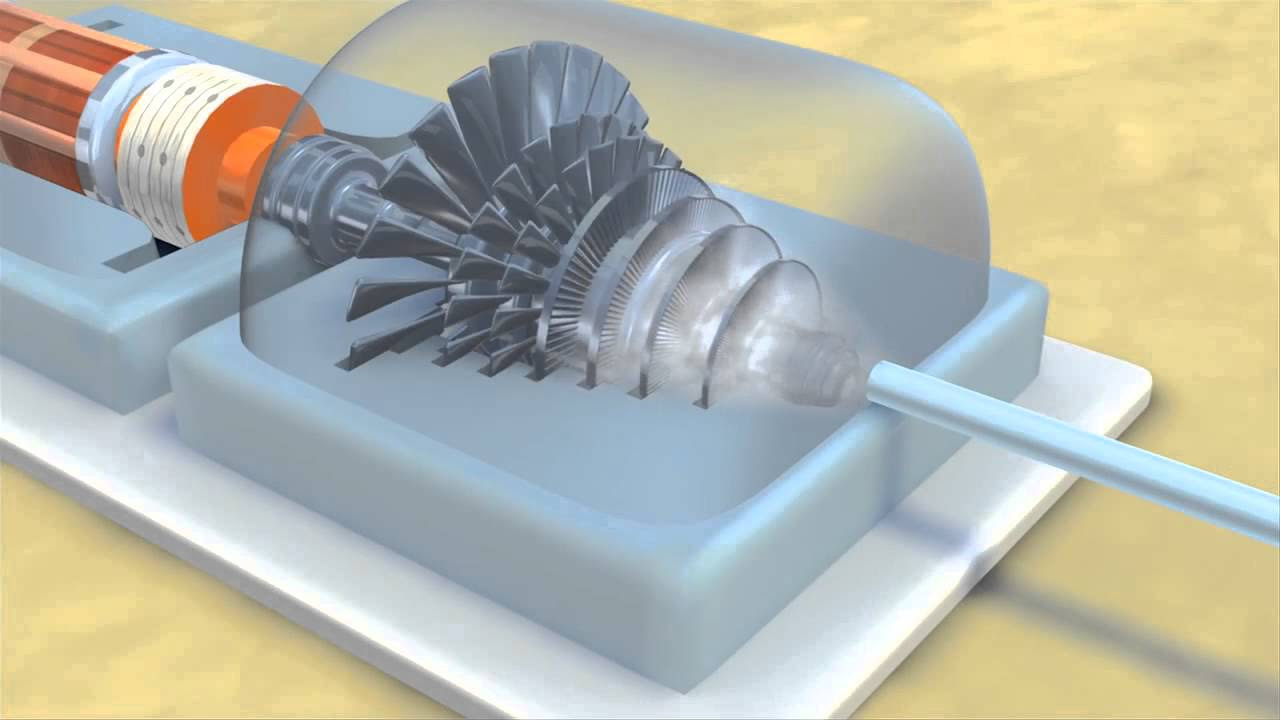
-Geothermal heat is extracted using various methods, but most commonly, water and steam are drawn from the Earth to capture the heat.
How is geothermal heat used to heat homes and buildings?
-Hot water from the Earth is either directly circulated through buildings or pumped through a heat exchanger to transfer heat to the building.
How does geothermal energy produce electricity?
-Geothermal energy produces electricity by using heat to generate steam, which turns turbines connected to a generator in a geothermal power plant.
Where are the major regions of geothermal development?
-The major regions of geothermal development are in volcanically and tectonically active areas of the world.
What is one key advantage of geothermal energy?
-One key advantage of geothermal energy is its reliability and consistent power generation, making it suitable for providing baseload electricity.
What environmental concerns are associated with geothermal energy?
-Concerns include the accidental release of CO2 and hydrogen sulfide emissions from the Earth's groundwater and the potential lowering of ground temperatures if heat is drawn irresponsibly.
Why are upfront costs for geothermal energy production high?
-Upfront costs are high due to the expenses of seismic sensing, drilling, confirmation testing, and other necessary preliminary investigations to ensure the geothermal plant will meet production goals.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

WHY IS THE EARTH'S INTERIOR HOT? | Sources of Internal Heat | Earth Science
Earth's Hot Interior | Lesson 2 | Second Quarter | Earth Science

EARTH'S INTERNAL HEAT / Primordial & Radioactive Heat / EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE / SCIENCE 11 - MELC 6

2 10 Earth's Internal Heat

How Geothermal Energy Works - Educational 3D Animated Video
Energy 101: Geothermal Energy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
