HARMONIC SEQUENCE | GRADE 10 MATHEMATICS Q1
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial delves into the concept of harmonic sequences, exploring their connection to music and mathematics. It explains how harmonic sequences are derived from the reciprocals of arithmetic sequences, using examples of guitar strings to illustrate the point. The video teaches viewers how to find the nth term of a harmonic sequence by reversing the arithmetic sequence formula. Practical examples, including calculating specific terms of harmonic sequences, are provided to solidify understanding. The guide encourages engagement by prompting viewers to apply these concepts to solve related mathematical problems.
Takeaways
- 🎵 The term 'harmonic' is commonly associated with musical sounds and is used in both math and music.
- 📏 In music, harmonics are tones at frequencies that are multiples of the fundamental frequency, such as the second harmonic being twice the fundamental frequency.
- 🎸 On a guitar, the length of the string is proportional to the number of vibrations per second, which affects the sound's harmony.
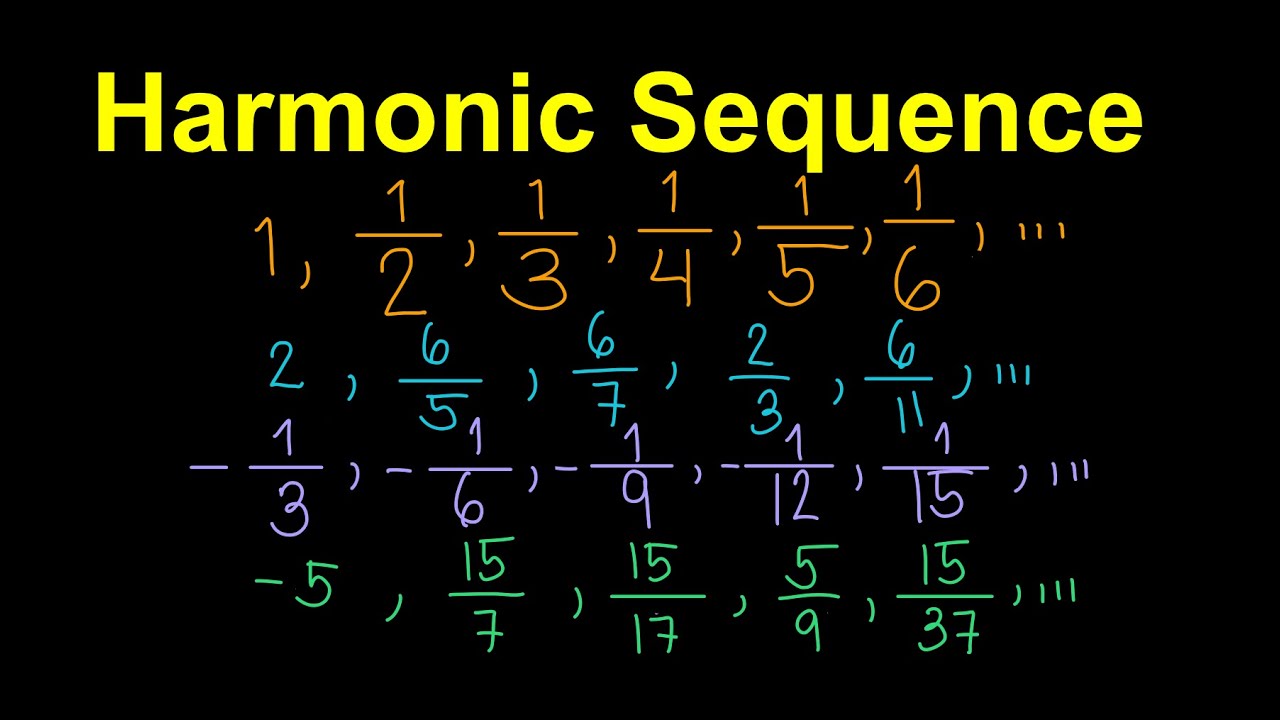
- 🔢 A harmonic sequence in math is a sequence where the string lengths are in the proportion of x, x/2, x/3, x/4, and so on, producing a harmonious sound when played.
- ♫ The reciprocal of a harmonic sequence forms an arithmetic sequence, where the difference between consecutive terms is constant.
- 🔄 The formula for the nth term of a harmonic sequence is the reciprocal of the formula for the nth term of an arithmetic sequence.
- 📐 To find the next terms of a harmonic sequence, first determine the common difference of the corresponding arithmetic sequence and then apply the harmonic formula.
- 🎼 Examples in the script demonstrate how to find the next terms and specific terms of harmonic sequences by using arithmetic sequences.
- 📉 The process involves identifying the first term and common difference of the arithmetic sequence, then using these to find terms in the harmonic sequence.
- 📚 The script provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the relationship between harmonic and arithmetic sequences and how to calculate terms within them.
Q & A
What is the relationship between harmonic and arithmetic sequences?
-A harmonic sequence is the reciprocal of an arithmetic sequence. If the reciprocals of a sequence form an arithmetic sequence, then the original sequence is called a harmonic sequence.
What is the formula for finding the nth term of a harmonic sequence?
-The nth term of a harmonic sequence is given by the formula \( \frac{1}{a_1 + (n - 1)d} \), where \( a_1 \) is the first term and \( d \) is the common difference of the corresponding arithmetic sequence.
How does the length of a string on a musical instrument like a guitar relate to harmonics?
-The length of a string on a guitar is proportional to the number of vibrations per second, which affects the harmonics produced. A set of strings with lengths proportional to each other produces a harmonious sound.
What is a second harmonic in the context of music?
-A second harmonic in music is a tone that has a frequency twice that of the fundamental frequency.
Can you provide an example of how to find the next term in an arithmetic sequence given the first few terms?
-To find the next term in an arithmetic sequence, first determine the common difference by subtracting the first term from the second term. Then, add this difference to the last term provided to find the next term.
How do you find the harmonic sequence given an arithmetic sequence?
-To find the harmonic sequence from an arithmetic sequence, take the reciprocal of each term in the arithmetic sequence.
What is the difference between an arithmetic and a harmonic sequence in terms of their formulas?
-The formula for the nth term of an arithmetic sequence is \( a_n = a_1 + (n - 1)d \), while for a harmonic sequence, it is the reciprocal of this, \( \frac{1}{a_1 + (n - 1)d} \).
How can you determine the common difference of a sequence from the given terms?
-To determine the common difference \( d \) of a sequence, subtract the preceding term from the current term, i.e., \( d = a_n - a_{n-1} \).
What is the significance of the reciprocal in the context of harmonic sequences?
-In the context of harmonic sequences, the reciprocal of each term forms an arithmetic sequence, which is used to identify and work with harmonic sequences.
Can you explain how to find the nth term of an arithmetic sequence using the formula?
-To find the nth term of an arithmetic sequence, use the formula \( a_n = a_1 + (n - 1)d \), where \( a_1 \) is the first term and \( d \) is the common difference.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)