What is DICOM | DICOM Explained
Summary
TLDRThis video script offers an insightful look into the DICOM standard, a critical protocol in healthcare for managing medical images. It follows Dr. Nugget, a radiologist, through his day as he interprets various images like X-rays and ultrasounds. The script explains how DICOM facilitates the standardization, storage, transmission, and viewing of these images, regardless of the equipment manufacturer. It also touches on the role of Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) and Electronic Medical Record Systems (EMRs) in the workflow, highlighting the universality of DICOM in healthcare IT.
Takeaways
- 📚 DICOM stands for Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine, which is a standard used in healthcare for medical imaging.
- 👨⚕️ Dr. Nugget, a radiologist, uses DICOM to interpret various medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs for his patients.
- 🏥 The Electronic Medical Record (EMR) system is used to track and record patient data, including orders for radiology procedures.
- 📈 Radiology Information System (RIS) updates with patient status, informing clinical staff when patients are ready for procedures.
- 🔬 X-rays use radioactive light to acquire two-dimensional, high-resolution, grayscale images.
- 📊 Ultrasounds use sound waves to create images that can be viewed in color, still image, or movie format.
- 💾 DICOM ensures that all medical images are stored in a universal format, regardless of the manufacturer.
- 🌐 DICOM allows for the transfer of images using the same standard, facilitating the use of Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS).
- 🖥️ Dr. Nugget can access and view images from PACS on his computer, using DICOM viewers, to interpret and create reports for patients.
- 🖨️ DICOM also supports the printing of images, enabling radiologists to discuss findings with patients using physical copies.
Q & A
What does DICOM stand for?
-DICOM stands for Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine.
What is the purpose of the DICOM standard?
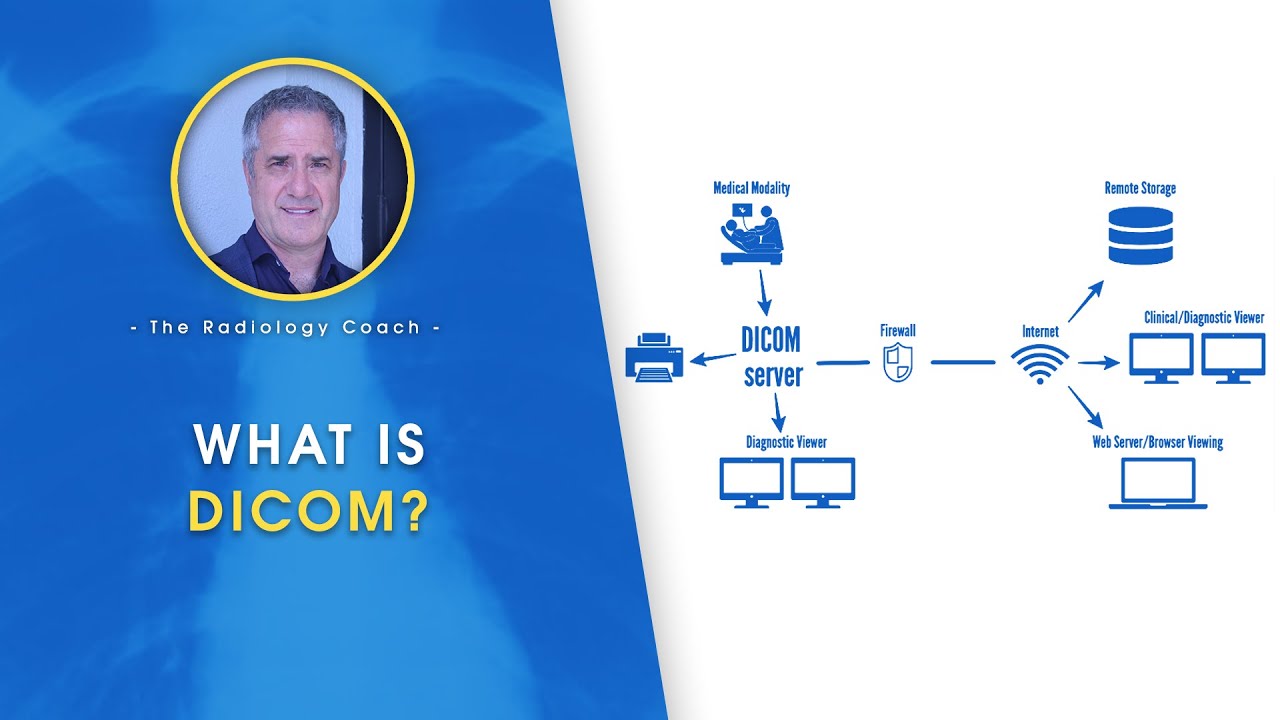
-The DICOM standard defines how to query, retrieve, display, store, transmit, and print images in a universal format.
What types of medical images does Dr. Nugget interpret in the script?
-Dr. Nugget interprets medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.
What is an EMR and how does it relate to DICOM?
-An EMR, or Electronic Medical Record, is a system for tracking and recording patient data. It is related to DICOM in that it can be used to order and schedule procedures that generate DICOM images.
How does the radiology information system (RIS) update when a patient checks in?
-When a patient checks in at the front desk, the RIS is updated with the new status of the patient, informing the clinical staff that the patient is ready to undergo procedures.
What is the difference between X-rays and ultrasounds as described in the script?
-X-rays use radioactive light to acquire monochromatic, two-dimensional images, while ultrasounds use sound waves to acquire images that can be viewed in color, still image, or movie format.
What is PACS and how does it interact with DICOM?
-PACS, or Picture Archiving and Communication System, is used to store, retrieve, distribute, and present images for clinical review. It interacts with DICOM by storing images in DICOM format, allowing for standardized transfer and viewing.
How does Dr. Nugget view the DICOM images?
-Dr. Nugget views the DICOM images using a PACS viewer or a DICOM viewer on his computer.
What is the clinical workflow described in the script?
-The clinical workflow described involves receiving orders, scheduling procedures, capturing and storing images in DICOM format, transferring images to PACS, viewing and interpreting images, creating reports, and discussing findings with patients.
What are some of the upcoming topics mentioned for future videos?
-Upcoming topics include imaging and healthcare IT as a whole, PACS radiology, HL7, deep dives into specific DICOM operations, and the clinical aspects of various imaging modalities.
How does the DICOM standard facilitate the workflow for Dr. Nugget?
-The DICOM standard facilitates Dr. Nugget's workflow by enabling the storage, transmission, viewing, and printing of images using a universal format, regardless of the modality or vendor.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)