Map Skills - Calculating Bearings in a Geography Examination
Summary
TLDRThis educational video teaches viewers how to calculate bearings, a valuable skill for geography examinations like GCSE and A-Level. It explains that bearings offer precise directional guidance, contrasting with compass points. The process involves drawing a north line from the starting point, connecting the two points, and measuring the angle with a protractor. The video emphasizes the importance of starting from the north and measuring clockwise. It also addresses how to handle bearings over 180 degrees, either by adding to 180 or subtracting from 360. The presenter assures that mastering this skill can lead to easy points in exams.
Takeaways
- 🧭 Bearings are a map skill used to calculate precise directions, which is useful in geographical examinations like the GCSE, CIE, and A-level papers.
- 🗣 A bearing is more accurate than compass points, as it specifies the exact direction, not just a general one like 'north east'.
- 📏 When measuring bearings, always start from the north and measure clockwise to get an accurate direction.
- 🔢 Bearings are measured in degrees, with North being 0 degrees, East 90 degrees, South 180 degrees, and West 270 degrees.
- 🔄 Understanding the difference between bearings from point A to B and from B to A is crucial, as the direction and thus the bearing will differ.
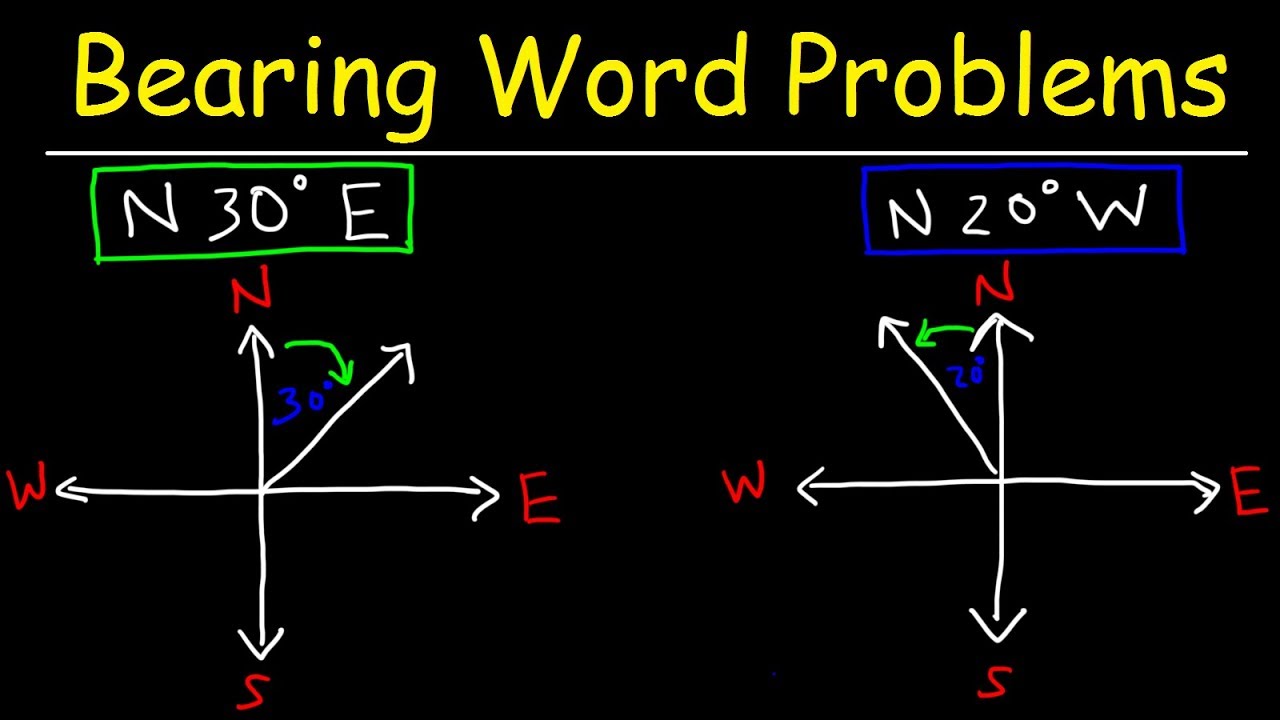
- 📐 To measure the bearing between two points, draw a north line from the starting point and then draw a line connecting the two points.
- 📏 Use a protractor to measure the angle between the north line and the line connecting the two points to find the bearing.
- ⚙️ If the angle exceeds 180 degrees, you can either add 180 degrees to the angle or subtract the angle from 360 degrees to find the bearing.
- 📝 It's important to be precise when calculating bearings, ensuring the protractor's center is on the intersection of the north line and the line connecting the points.
- 🎓 Mastering the skill of calculating bearings can lead to easy points in geography examinations and is a valuable practical skill.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of calculating bearings in geography?
-Calculating bearings is a map skill used to determine precise directions, which is extremely useful in practical examinations such as the GCSE, CIE paper, and some A-level papers.
How does a bearing differ from a compass point?
-A bearing provides a specific direction with exact degrees, whereas a compass point is less precise, indicating only general directions like north-east.
What is the starting point for measuring a bearing?
-When measuring a bearing, you always start from the north and measure around clockwise to get an accurate measurement.
What is the significance of the 0 degrees bearing?
-The 0 degrees bearing represents the exact north direction.
How do you determine the bearing between two points on a map?
-To determine the bearing between two points, you draw a north line from the starting point, connect the two points with a line, and measure the angle between the north line and the connecting line using a protractor.
Why is it important to identify the starting and destination points when calculating bearings?
-The bearing from point A to point B will be different from the bearing from B to A, so identifying the correct starting and destination points is crucial for accurate bearing calculations.
What should you do if the measured angle exceeds 180 degrees?
-If the angle exceeds 180 degrees, you can either measure the angle again going clockwise and add 180 degrees to it, or measure it counterclockwise and subtract it from 360 degrees to find the correct bearing.
What is the bearing from point A to point B if the measured angle is just shy of 135 degrees?
-The bearing from point A to point B would be approximately south-east or precisely 135 degrees.
How can you ensure accuracy when measuring bearings?
-Ensure accuracy by identifying the starting and destination points, drawing a north line, connecting the points, and using a protractor to measure the angle precisely.
What is the recommended approach to mastering the skill of calculating bearings?
-Mastering the skill of calculating bearings involves understanding the procedure, practicing with a protractor, and being precise in identifying starting points and measuring angles.
Why are bearings an important skill in geography examinations?
-Bearings are an important skill in geography examinations because they allow for precise navigation and direction measurement, which can lead to easy points in practical and theoretical exams.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)