Sex Determination: More Complicated Than You Thought
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the fascinating diversity of sex determination systems across the animal kingdom. It begins with the human XY chromosome system, where the father's contribution determines the child's sex with a 50/50 chance. In contrast, birds and some reptiles have a ZW system where the mother's chromosomes dictate sex. Ants exhibit a unique haplodiploid system, leading to male ants having no fathers. The script also highlights environmental influences, such as temperature determining sex in alligators and turtles, and social hierarchies in clownfish where the largest male becomes female if the dominant female dies. It concludes with the example of whiptail lizards, an all-female species that reproduces through cloning, emphasizing the variety of mechanisms that determine sex in different species.
Takeaways
- 🤰 The common question 'Is it a boy or a girl?' assumes a 50/50 chance for human babies due to our XY chromosome system.
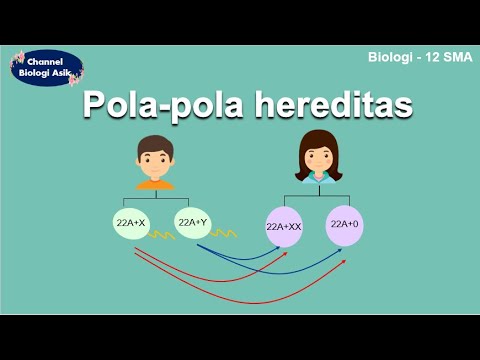
- 🧬 In mammals, sex is genetically determined by the XY chromosome system, where females contribute an X chromosome and males can contribute either an X or a Y.
- 🐦 Birds and some reptiles have a different genetic sex determination system where the ZW chromosome system is used, with females being ZW and males being ZZ.
- 🐜 Ants have a unique haplodiploid system where males develop from unfertilized eggs and thus have no fathers, living with only one copy of each gene.
- 🌡 For some reptiles like alligators and turtles, sex is determined by the temperature of the environment during a critical period of egg development.
- 🐠 In painted turtles, warmer temperatures result in female offspring, while cooler temperatures result in males, illustrating the impact of environmental temperature on sex determination.
- 🐟 Clownfish start as males and can change sex to become females, demonstrating that sex can change over the course of an individual's life.
- 🐚 The green spoonworm's sex is determined by where its larva lands on the sea floor, showing that environmental location can dictate sex in some species.
- 🦎 Whiptail lizards are an all-female species that reproduce asexually, laying eggs that hatch into female clones, bypassing the traditional need for sex determination.
- 👶 The speaker and his wife discovered they are expecting a baby boy, highlighting the personal relevance of sex determination in human life.
Q & A
What is the common assumption behind the question 'Is it a boy or is it a girl?'
-The common assumption is that there is a 50/50 chance of the baby being a boy or a girl, which is based on the human XY chromosome system of sex determination.
How does the XY chromosome system work in determining the sex of a human baby?
-In humans, females have two X chromosomes (XX) and males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). The sex of the baby is determined by the chromosome the father contributes: an X results in a girl, and a Y results in a boy.
What is the genetic sex determination system used by birds and some reptiles?
-Birds and some reptiles use a ZW sex-determination system, where ZZ results in a male and ZW results in a female. The sex is determined by the mother, as she can provide either a Z or a W chromosome.
How do ants determine sex in their colony, and why don't male ants have fathers?
-In ant colonies, sex is determined by whether an egg is fertilized or not. Fertilized eggs become females, while unfertilized eggs become males. Since male ants develop from unfertilized eggs, they do not have fathers and are haploid, like a walking sex cell.
What is the term for the sex determination system used by ants, bees, and wasps?
-The sex determination system used by ants, bees, and wasps is called the haplodiploid system, where males develop from unfertilized eggs and are haploid, while females develop from fertilized eggs and are diploid.
How do alligators and most turtles determine the sex of their offspring?
-In alligators and most turtles, the sex of the offspring is determined by the temperature of the environment during a critical period of egg development. Warmer temperatures typically produce females, while cooler temperatures produce males.
What is the process by which clownfish change their sex during their lifetime?
-Clownfish start their lives as males and, as they mature, they become female. If the dominant female in a group dies, the largest and most dominant male will quickly change sex to become female, taking her place.
How does the green spoonworm determine the sex of its offspring?
-For the green spoonworm, the sex of the offspring is determined by where a larva lands on the sea floor. Larvae that land on the open sea floor become female, while those that land on a female become male.
What is unique about the sex determination in whiptail lizards?
-Whiptail lizards are a nearly all-female species that reproduce by laying eggs that hatch into female clones of themselves. There is no genetic sex determination, as all offspring are female.
What does the narrator reveal about the sex of his and his wife's baby at the end of the script?
-The narrator reveals that he and his wife found out they are expecting a baby boy.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

The Reproductive System: How Gonads Go - CrashCourse Biology #34

Haplodiploid Sex Determination

Sexual & Asexual Reproduction: How Animals Do It: Crash Course Biology #47

Reprodução e evolução: invertebrados – Ciências – 8º ano – Ensino Fundamental

Animals: Tour of 9 Phyla
Pola-pola hereditas - Biologi kelas 12 SMA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
